NAME: DATE: PERIOD: ______ VIRUS SPREAD SIMULATOR I. 1
... 1) Ebola virus particles occupy an infected person’s ____________ and other bodily fluids, which can enter another person through the __________, mucous membranes, scratches on the __________or from a hypodermic needle — not from from the __________ or from insects. The bodies of people who have die ...
... 1) Ebola virus particles occupy an infected person’s ____________ and other bodily fluids, which can enter another person through the __________, mucous membranes, scratches on the __________or from a hypodermic needle — not from from the __________ or from insects. The bodies of people who have die ...
HepatitisB
... Possible forms: sexual contact, blood transfusion, and reuse of contaminated needles and syringes Mothers can pass it to their children during childbirth ...
... Possible forms: sexual contact, blood transfusion, and reuse of contaminated needles and syringes Mothers can pass it to their children during childbirth ...
EDITORIAL Ebola virus disease in West Africa: outbreak or epidemic?
... By definition, a disease “outbreak” is “the occurrence of cases of disease in a community or region where it would not normally be expected, or at a much greater level than expected”, while an “epidemic” is “the occurrence of disease at a level greater than would normally be expected”.1 In other wor ...
... By definition, a disease “outbreak” is “the occurrence of cases of disease in a community or region where it would not normally be expected, or at a much greater level than expected”, while an “epidemic” is “the occurrence of disease at a level greater than would normally be expected”.1 In other wor ...
S004
... Chagas disease, the debilitating infection caused by the intracellular parasite, Trypanosoma cruzi, affects approximately 16 to 18 million individuals in Latin America and leads to about 50, 000 deaths per annum. Host microvesicles (MVs) help pathogens, such as the intracellular parasite, T. cruzi, ...
... Chagas disease, the debilitating infection caused by the intracellular parasite, Trypanosoma cruzi, affects approximately 16 to 18 million individuals in Latin America and leads to about 50, 000 deaths per annum. Host microvesicles (MVs) help pathogens, such as the intracellular parasite, T. cruzi, ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
... • Without treatment these ulcers take between 2 and 6 weeks to heal • If the infection does not get treated at all it will move onto the Secondary stage of Syphilis ...
... • Without treatment these ulcers take between 2 and 6 weeks to heal • If the infection does not get treated at all it will move onto the Secondary stage of Syphilis ...
Blood and Tissue Protozoa of Dogs and Cats
... The hemolytic anemia caused by M. haemofelis is called feline infectious anemia (FIA) and is usually regenerative in nature (unless underlying disease suppresses the regenerative response, e.g. Feline Leukemia Virus infection). Therefore, a non-regenerative anemia in a cat with H. felis should not b ...
... The hemolytic anemia caused by M. haemofelis is called feline infectious anemia (FIA) and is usually regenerative in nature (unless underlying disease suppresses the regenerative response, e.g. Feline Leukemia Virus infection). Therefore, a non-regenerative anemia in a cat with H. felis should not b ...
Ambulatory Care Lecture: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
... – allergic reaction – lymphoma – infections ...
... – allergic reaction – lymphoma – infections ...
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKAEMIA CLL
... routine physical exam.or by routine CBC. Clinical manifestation develop as the leukemic cell acumalate on lymph nodes ,liver ,spleen & bone marrow . Presenting problems may be anaemia, infections,painless lymphadenopathy, and systemic symptoms such as night sweats or weight loss. However, these more ...
... routine physical exam.or by routine CBC. Clinical manifestation develop as the leukemic cell acumalate on lymph nodes ,liver ,spleen & bone marrow . Presenting problems may be anaemia, infections,painless lymphadenopathy, and systemic symptoms such as night sweats or weight loss. However, these more ...
Microorganisms
... muscles. NF can occur from minor trama but is usually related to surgery. • The NF Bacteria is commonly called strep type A. ...
... muscles. NF can occur from minor trama but is usually related to surgery. • The NF Bacteria is commonly called strep type A. ...
Hand, foot and mouth disease
... area. It is generally only a mild disease that lasts seven to ten days. HFMD is more common during warmer weather and tends to spread easily between children. There is no connection between this disease and the foot and mouth disease that affects cattle and some other animals. HFMD occurs mainly in ...
... area. It is generally only a mild disease that lasts seven to ten days. HFMD is more common during warmer weather and tends to spread easily between children. There is no connection between this disease and the foot and mouth disease that affects cattle and some other animals. HFMD occurs mainly in ...
Burkholderia Mallei
... antibiotic treatment of the organism in humans. Sulfadiazine has been found to be effective in experimental animals and in humans. Burkholderia mallei is usually sensitive to tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin, streptomycin, novobiocin, gentamicin, imipenem, ceftrazidime, and the sulfonamides. Resistance ...
... antibiotic treatment of the organism in humans. Sulfadiazine has been found to be effective in experimental animals and in humans. Burkholderia mallei is usually sensitive to tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin, streptomycin, novobiocin, gentamicin, imipenem, ceftrazidime, and the sulfonamides. Resistance ...
Document
... • Factors affecting nosocomial infection acquisition: ─ Presence of microorganisms in hospital ─ Compromised health/immune status of the host ...
... • Factors affecting nosocomial infection acquisition: ─ Presence of microorganisms in hospital ─ Compromised health/immune status of the host ...
7-3.4 Notes
... A disease that results in the glucose (sugar) level of the blood being higher than the normal range. It is caused by a person’s inability to either produce or use properly a natural chemical produced in the body called insulin. The higher level of blood sugar results in many disorders of the b ...
... A disease that results in the glucose (sugar) level of the blood being higher than the normal range. It is caused by a person’s inability to either produce or use properly a natural chemical produced in the body called insulin. The higher level of blood sugar results in many disorders of the b ...
SL 1991-225 - North Carolina General Assembly
... "(e) The local health director shall ensure that control measures prescribed by the Commission have been given to prevent the spread of all reportable communicable diseases or communicable conditions and any other communicable disease or communicable condition that represents a significant threat to ...
... "(e) The local health director shall ensure that control measures prescribed by the Commission have been given to prevent the spread of all reportable communicable diseases or communicable conditions and any other communicable disease or communicable condition that represents a significant threat to ...
Two Revolutions - Stanford Computer Science
... discovered a frozen corpse. A number of bodies of dead climbers having been found in the mountains earlier that year, the find at first seemed tragic but unremarkable. Scientists who later examined the body, however, dated it as approximately 5,300 years old, among the oldest, if not the oldest, pre ...
... discovered a frozen corpse. A number of bodies of dead climbers having been found in the mountains earlier that year, the find at first seemed tragic but unremarkable. Scientists who later examined the body, however, dated it as approximately 5,300 years old, among the oldest, if not the oldest, pre ...
Lowy-Concepts_of_ID
... infections • Different mechanisms involved in the development of pathology in the host ...
... infections • Different mechanisms involved in the development of pathology in the host ...
Oral Health for Older Adults by Ira B. Lamster, DDS
... Drs. Lamster and Papapanou unfortunately are not able to share their PowerPoint presentations because much of the content from their discussions is the property of Columbia University and also may contain research information that has yet to be published. Dr. Lamster writes: Let me suggest the follo ...
... Drs. Lamster and Papapanou unfortunately are not able to share their PowerPoint presentations because much of the content from their discussions is the property of Columbia University and also may contain research information that has yet to be published. Dr. Lamster writes: Let me suggest the follo ...
coccidia - Spirit MinPins
... asymptomatic; however, young or immuno-compromised animals may suffer severe symptoms, including death. While coccidian organisms can infect a wide variety of animals, including humans andlivestock, they are usually species-specific. One well-known exception is toxoplasmosis, caused by Toxoplasma go ...
... asymptomatic; however, young or immuno-compromised animals may suffer severe symptoms, including death. While coccidian organisms can infect a wide variety of animals, including humans andlivestock, they are usually species-specific. One well-known exception is toxoplasmosis, caused by Toxoplasma go ...
Lesson 1: Understanding Communicable Diseases
... What is the difference between a cold and the flu? The flu and the common cold are both respiratory illnesses but they are caused by different viruses. Because these two types of illnesses have similar flu-like symptoms, it can be difficult to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone ...
... What is the difference between a cold and the flu? The flu and the common cold are both respiratory illnesses but they are caused by different viruses. Because these two types of illnesses have similar flu-like symptoms, it can be difficult to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone ...
Ascaridia galli
... chickens, and the chickens kept in cages Is less common. The nematode infects fowl of all ages, but the chickens at three months of age is most susceptible and the disease is more serious . ...
... chickens, and the chickens kept in cages Is less common. The nematode infects fowl of all ages, but the chickens at three months of age is most susceptible and the disease is more serious . ...
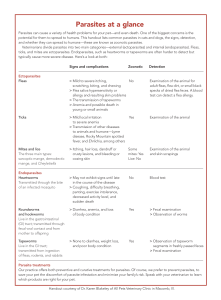
African trypanosomiasis

African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness is a parasitic disease of humans and other animals. It is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei. There are two types that infect humans, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (T.b.g) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (T.b.r.). T.b.g causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis is via finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first and second stage disease.Prevention of severe disease involves screening the population at risk with blood tests for T.b.g. Treatment is easier when the disease is detected early and before neurological symptoms occur. Treatment of the first stage is with the medications pentamidine or suramin. Treatment of the second stage involves: eflornithine or a combination of nifurtimox and eflornithine for T.b.g. While melarsoprol works for both it is typically only used for T.b.r. due to serious side effects.The disease occurs regularly in some regions of sub-Saharan Africa with the population at risk being about 70 million in 36 countries. As of 2010 it caused around 9,000 deaths per year, down from 34,000 in 1990. An estimated 30,000 people are currently infected with 7000 new infections in 2012. More than 80% of these cases are in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Three major outbreaks have occurred in recent history: one from 1896 to 1906 primarily in Uganda and the Congo Basin and two in 1920 and 1970 in several African countries. Other animals, such as cows, may carry the disease and become infected.