The European Respiratory Journal targets tuberculosis EDITORIAL C. Lange*, W.W. Yew
... infectious diseases, have in vitro and in vivo activity against M. tuberculosis, novel drugs without cross-resistance against existing antituberculosis drugs are urgently needed. Few candidate drugs (including moxifloxacin) have entered phase II clinical trials [13, 14]; however, it is likely that n ...
... infectious diseases, have in vitro and in vivo activity against M. tuberculosis, novel drugs without cross-resistance against existing antituberculosis drugs are urgently needed. Few candidate drugs (including moxifloxacin) have entered phase II clinical trials [13, 14]; however, it is likely that n ...
Flaitz, Oral Pathology 22-2 - American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry
... Management of these lesions should be conservative in children because spontaneous resolution may occur in a few months to several years. Surgical excision may be indicated for lesions that are frequently traumatized and/or for esthetic purposes. Other treatment modalities with variable effectivenes ...
... Management of these lesions should be conservative in children because spontaneous resolution may occur in a few months to several years. Surgical excision may be indicated for lesions that are frequently traumatized and/or for esthetic purposes. Other treatment modalities with variable effectivenes ...
The Epidemiology of Hepatitis A, B, and C
... Post-vaccination testing: 1-2 months after last shot, if establishing response is critical (HCW). ...
... Post-vaccination testing: 1-2 months after last shot, if establishing response is critical (HCW). ...
The mosquitoes Aedes
... joint pains, often in the hands and feet • Joint pains persist in 50% for > 1 year ...
... joint pains, often in the hands and feet • Joint pains persist in 50% for > 1 year ...
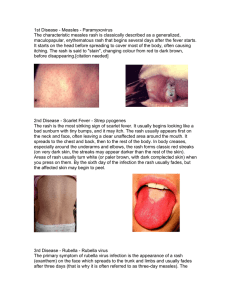
1st Disease - Measles
... with the upper arms and legs being the most common locations. The rash typically lasts a couple of days and may itch; some cases have been known to last for several weeks. Patients are usually no longer infectious once the rash has appeared. ...
... with the upper arms and legs being the most common locations. The rash typically lasts a couple of days and may itch; some cases have been known to last for several weeks. Patients are usually no longer infectious once the rash has appeared. ...
Hospital for Tropical Diseases powerpoint template
... 1 hospital admission with pneumonia aged 10 months UTI 6 months ago (normal ultrasound scan) 4 year old sister Fully vaccinated ...
... 1 hospital admission with pneumonia aged 10 months UTI 6 months ago (normal ultrasound scan) 4 year old sister Fully vaccinated ...
Overview - BioMed Central
... Boar population dynamics emerge from individual behaviour, defined by agedependent seasonal reproduction and mortality probabilities and age- and densitydependent dispersal behaviour, all including stochasticity. The epidemic course emerges from within and between group virus transmission, boar disp ...
... Boar population dynamics emerge from individual behaviour, defined by agedependent seasonal reproduction and mortality probabilities and age- and densitydependent dispersal behaviour, all including stochasticity. The epidemic course emerges from within and between group virus transmission, boar disp ...
Immunisation and Infection Control Policy
... onset, or if jaundice (yellow eyes or skin) occurs, for 7 days after the onset of jaundice. Exclusion is not necessary. If the Human immunodeficiency person is severely immune virus (HIV) suppressed he or she will be infection vulnerable to other people’s infections. Influenza and Exclude until well ...
... onset, or if jaundice (yellow eyes or skin) occurs, for 7 days after the onset of jaundice. Exclusion is not necessary. If the Human immunodeficiency person is severely immune virus (HIV) suppressed he or she will be infection vulnerable to other people’s infections. Influenza and Exclude until well ...
Bangladesh - UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine
... Bangladesh provides a unique opportunity for human, domestic animal, and wildlife interaction due to the high density of people co-occurring with rich biodiversity in a country that depends on both human and animal labor to drive agriculture and intensive livestock production. The high density of pe ...
... Bangladesh provides a unique opportunity for human, domestic animal, and wildlife interaction due to the high density of people co-occurring with rich biodiversity in a country that depends on both human and animal labor to drive agriculture and intensive livestock production. The high density of pe ...
Raw Milk Pathogens - BC Centre for Disease Control
... Infections and - 10% of those initially infected will develop active infection Complications: - HIV+ more at risk - drug resistance problematic Fatality Rate: - significant, 65% of those infected will die within 5 years (if untreated) ...
... Infections and - 10% of those initially infected will develop active infection Complications: - HIV+ more at risk - drug resistance problematic Fatality Rate: - significant, 65% of those infected will die within 5 years (if untreated) ...
Sources and spread of infection
... C/C ratio is low in typhoid or dysentery where cases hugely outnumber carriers. C/C ratio is high say, for Staphyloccus where carriers greatly outnumber cases ...
... C/C ratio is low in typhoid or dysentery where cases hugely outnumber carriers. C/C ratio is high say, for Staphyloccus where carriers greatly outnumber cases ...
Goat Parasites
... al, 2003. The effect of birdsfoot trefoil (Lotus corniculatus) and chicory (Cichorium intybus) on parasite intensities and performance of lambs naturally infected with helminth parasites. Vet. Parasitol. 112, 147-155. ...
... al, 2003. The effect of birdsfoot trefoil (Lotus corniculatus) and chicory (Cichorium intybus) on parasite intensities and performance of lambs naturally infected with helminth parasites. Vet. Parasitol. 112, 147-155. ...
Molecular characterization of urdbean (Vigna mungo) germplasm
... markers was not significant (Sivaprakash et al., 2004). Past studies showed that DNAbased markers used in the study of genetic variation of various Vigna species were not up to their potential use (Amadou et al., 2001). A large number of molecular marker techniques have been employed to quantify the ...
... markers was not significant (Sivaprakash et al., 2004). Past studies showed that DNAbased markers used in the study of genetic variation of various Vigna species were not up to their potential use (Amadou et al., 2001). A large number of molecular marker techniques have been employed to quantify the ...
Monitoring for Diseases in Wildlife Populations
... Mass mortality events involving wildlife may often occur unpredictably, and opportunities to investigate such events may be short-lived. Examples of this include recovery of dead marine mammals, fish or seabirds from beaches or coastal waterways, discovery of dead birds or mammals in forests, agricu ...
... Mass mortality events involving wildlife may often occur unpredictably, and opportunities to investigate such events may be short-lived. Examples of this include recovery of dead marine mammals, fish or seabirds from beaches or coastal waterways, discovery of dead birds or mammals in forests, agricu ...
STAPHYLOCOCCI - TOP Recommended Websites
... - Exfoliative toxin disrupt vascular smooth muscle - Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 - Enterotoxins (Ato E) ...
... - Exfoliative toxin disrupt vascular smooth muscle - Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 - Enterotoxins (Ato E) ...
Workshop Instructions
... Pre and post workshop surveys have indicated the workshop is considered useful. We believe the format of this workshop is easy to reproduce and can serve as a foundation for a curriculum in emerging infections and communicable disease management, and can easily be applied to other educational topi ...
... Pre and post workshop surveys have indicated the workshop is considered useful. We believe the format of this workshop is easy to reproduce and can serve as a foundation for a curriculum in emerging infections and communicable disease management, and can easily be applied to other educational topi ...
Heart disease: the greatest `risk`
... disease such as heart disease must be multifactorial, degenerative and non-infectious. Yet it was the very inability of ‘established’ risk factors such as hypercholesterolemia, hypertension and smoking to completely explain the incidence and trends in cardiovascular disease that resulted in historic ...
... disease such as heart disease must be multifactorial, degenerative and non-infectious. Yet it was the very inability of ‘established’ risk factors such as hypercholesterolemia, hypertension and smoking to completely explain the incidence and trends in cardiovascular disease that resulted in historic ...
Conjunctivitis ("Pink Eye") Fact Sheet
... People can get conjunctivitis by coming into contact with the tears or discharges from the eyes of an infected person and then touching their own eyes. Also conjunctivitis, when associated with an upper respiratory infection (common cold), can be spread by droplets (e.g., coughing, sneezing). ...
... People can get conjunctivitis by coming into contact with the tears or discharges from the eyes of an infected person and then touching their own eyes. Also conjunctivitis, when associated with an upper respiratory infection (common cold), can be spread by droplets (e.g., coughing, sneezing). ...
Arboviral diseases - Ministry of Health
... Advise those exposed to the same risk factors as the index case to protect against mosquitoes for at least 2 weeks after leaving the risk area. Advise also regarding the incubation period and common symptoms of arboviral infections and encourage contacts to seek early medical attention if symptoms d ...
... Advise those exposed to the same risk factors as the index case to protect against mosquitoes for at least 2 weeks after leaving the risk area. Advise also regarding the incubation period and common symptoms of arboviral infections and encourage contacts to seek early medical attention if symptoms d ...
The Value of Well-Designed Experiments in Studying Diseases with
... temperatures of 37°C cured infected animals. No amount of investigation at the molecular level or under standard laboratory conditions would have uncovered this fact, and because they performed a properly designed experiment, no molecular analysis was needed to confirm their result. More complex exp ...
... temperatures of 37°C cured infected animals. No amount of investigation at the molecular level or under standard laboratory conditions would have uncovered this fact, and because they performed a properly designed experiment, no molecular analysis was needed to confirm their result. More complex exp ...
2012-Week3_Bio - Teaching Terrorism
... 2) Ingestion or injection: vomiting and diarrhea, severe dehydration, and low blood pressure, all within less than 6 hours of exposure; possible liver, spleen and kidney failure; potentially fatal within 48 hours 3) Skin and eye exposure has limited effects; unlikely to be fully absorbed through nor ...
... 2) Ingestion or injection: vomiting and diarrhea, severe dehydration, and low blood pressure, all within less than 6 hours of exposure; possible liver, spleen and kidney failure; potentially fatal within 48 hours 3) Skin and eye exposure has limited effects; unlikely to be fully absorbed through nor ...
African trypanosomiasis

African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness is a parasitic disease of humans and other animals. It is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei. There are two types that infect humans, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (T.b.g) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (T.b.r.). T.b.g causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis is via finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first and second stage disease.Prevention of severe disease involves screening the population at risk with blood tests for T.b.g. Treatment is easier when the disease is detected early and before neurological symptoms occur. Treatment of the first stage is with the medications pentamidine or suramin. Treatment of the second stage involves: eflornithine or a combination of nifurtimox and eflornithine for T.b.g. While melarsoprol works for both it is typically only used for T.b.r. due to serious side effects.The disease occurs regularly in some regions of sub-Saharan Africa with the population at risk being about 70 million in 36 countries. As of 2010 it caused around 9,000 deaths per year, down from 34,000 in 1990. An estimated 30,000 people are currently infected with 7000 new infections in 2012. More than 80% of these cases are in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Three major outbreaks have occurred in recent history: one from 1896 to 1906 primarily in Uganda and the Congo Basin and two in 1920 and 1970 in several African countries. Other animals, such as cows, may carry the disease and become infected.