The Where, Why, How and Who of Geography
... – Geography is the science of place and space. Geographers ask where things are located on the surface of the earth, why they are located where they are, how places differ from one another, and how people interact with the environment—AAG – Geography is all about trying to make sense of the ...
... – Geography is the science of place and space. Geographers ask where things are located on the surface of the earth, why they are located where they are, how places differ from one another, and how people interact with the environment—AAG – Geography is all about trying to make sense of the ...
Basics of Geography
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
PHYSICAL FRAMEWORK
... National Geography Standards--1. How to use maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective; 3. How to analyze the spatial organization of people, places, and environments on Earth’s surface; 5. That people cre ...
... National Geography Standards--1. How to use maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective; 3. How to analyze the spatial organization of people, places, and environments on Earth’s surface; 5. That people cre ...
1. 2. Which ocean borders South Carolina? Which two states border
... What is the name of an area of land inside of a state that has its own government to take care of the needs of the people in that area? How many counties are there in South Carolina? ...
... What is the name of an area of land inside of a state that has its own government to take care of the needs of the people in that area? How many counties are there in South Carolina? ...
thinking like a geographer test review
... • 25. What imaginary line divides the earth into eastern and western halves? (Hint: The line of longitude that runs through Greenwich, England at 0 degrees) Prime Meridian • 26. A person, who creates map projections, calculates latitude and longitude, calculates exact locations, and is known as a m ...
... • 25. What imaginary line divides the earth into eastern and western halves? (Hint: The line of longitude that runs through Greenwich, England at 0 degrees) Prime Meridian • 26. A person, who creates map projections, calculates latitude and longitude, calculates exact locations, and is known as a m ...
The Geographer`s Tools
... • Geographers use geospatial technologies to study the use of the earth’s surface. ...
... • Geographers use geospatial technologies to study the use of the earth’s surface. ...
Year 5 Geography Age Related Expectations
... Make appropriate observations about human and physical features Explain why human and physical features in South Africa are the way they are. Investigate how the UK compares to South Africa. Offer observations about river features Identify how people affect the environment and recognise ways in whic ...
... Make appropriate observations about human and physical features Explain why human and physical features in South Africa are the way they are. Investigate how the UK compares to South Africa. Offer observations about river features Identify how people affect the environment and recognise ways in whic ...
Geography Enquiry and Skill
... Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping 'What do I think about it?'] (Google Earth) to locate countries and describe features studied Collect and record evidence [i.e. carrying out a survey of shop Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, functions and sho ...
... Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping 'What do I think about it?'] (Google Earth) to locate countries and describe features studied Collect and record evidence [i.e. carrying out a survey of shop Use the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, functions and sho ...
AP Human Geography Exam
... Acculturation: Process of adopting only certain customs that will be to their advantage Transculturation: A near equal exchange of culture traits or customs Assimilation: Process of less dominant cultures losing their culture to a more dominant culture Environmental determinism: A 19th- and early 20 ...
... Acculturation: Process of adopting only certain customs that will be to their advantage Transculturation: A near equal exchange of culture traits or customs Assimilation: Process of less dominant cultures losing their culture to a more dominant culture Environmental determinism: A 19th- and early 20 ...
APReviewSheet1
... -Functional Region- (nodal) Area organized around a node or focal point. The characteristic chosen to define a functional region dominates at a central focus or node and diminishes in importance outward. This region is tied to the central point by transportation or communication systems or by econom ...
... -Functional Region- (nodal) Area organized around a node or focal point. The characteristic chosen to define a functional region dominates at a central focus or node and diminishes in importance outward. This region is tied to the central point by transportation or communication systems or by econom ...
Chapter 2 Post-Assessment: Answer Key 1. Which of the following
... A map legend or key. It explains the meaning of each symbol used on the map. ...
... A map legend or key. It explains the meaning of each symbol used on the map. ...
Science 4th Unit 2 4-ESS2-2
... volcanoes occur in bands that are often along the boundaries between continents and oceans. Major mountain chains form inside continents or near their edges. Maps can help locate the different land and water ...
... volcanoes occur in bands that are often along the boundaries between continents and oceans. Major mountain chains form inside continents or near their edges. Maps can help locate the different land and water ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Revere Local Schools
... 3. New Ideas- Ex. Recycling and conservation. 4. Diffusion- movement of customs and beliefs from one place to another. They move with people. Ex. The wheel to rock, music. Diffusion can be forced when groups take over others. 5. Traditions change over time- sometimes aided by tech. Need to find ways ...
... 3. New Ideas- Ex. Recycling and conservation. 4. Diffusion- movement of customs and beliefs from one place to another. They move with people. Ex. The wheel to rock, music. Diffusion can be forced when groups take over others. 5. Traditions change over time- sometimes aided by tech. Need to find ways ...
Year 4 Background knowledge Fieldwork
... A global positioning system (GPS) is a network of satellites that transmit signals to receiving devices, which allow the exact position of something on Earth to be calculated. GPS has become a part of daily life, for example in satellite navigation systems in cars. A global information system (GIS) ...
... A global positioning system (GPS) is a network of satellites that transmit signals to receiving devices, which allow the exact position of something on Earth to be calculated. GPS has become a part of daily life, for example in satellite navigation systems in cars. A global information system (GIS) ...
Chapter 1 Homework Assignments 2015
... Instructions: Hand-write the answers on the blank space, the back, or on a separate sheet of paper and staple to the question sheet. For multiple choice questions circle the correct response. ASSIGNMENT 1 Multiple-Choice: 1. The science of making maps is a. demography. b. cartography. c. topography. ...
... Instructions: Hand-write the answers on the blank space, the back, or on a separate sheet of paper and staple to the question sheet. For multiple choice questions circle the correct response. ASSIGNMENT 1 Multiple-Choice: 1. The science of making maps is a. demography. b. cartography. c. topography. ...
ap human geography - Henry County Schools
... the physical environment causes and/or limits social development. the physical environment set limits on human actions. people can adjust to the physical environment. people can choose a course of action from many alternatives offered by the physical environment. E. geographers should examine the wo ...
... the physical environment causes and/or limits social development. the physical environment set limits on human actions. people can adjust to the physical environment. people can choose a course of action from many alternatives offered by the physical environment. E. geographers should examine the wo ...
GEOG 1303 Unit 1 Review
... question that the earliest humans asked, "What's over there?" Exploration and the discovery of new places, new culture, and new ideas have always been basic components of geography geography is often called the "mother of all sciences" as studying other people and other places led to other scientifi ...
... question that the earliest humans asked, "What's over there?" Exploration and the discovery of new places, new culture, and new ideas have always been basic components of geography geography is often called the "mother of all sciences" as studying other people and other places led to other scientifi ...
KS2 Geography Curriculum
... physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; ...
... physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; ...
06a -Test Geography Study Guide
... curved surface of the earth cannot be shown accurately on a flat map. 39. The four cardinal directions are — north, south, east, and west. Usually found at top of map. 40. Every map contains a map legend — a key that explains what the symbols stand for. 41. The Mercator projection, once the most com ...
... curved surface of the earth cannot be shown accurately on a flat map. 39. The four cardinal directions are — north, south, east, and west. Usually found at top of map. 40. Every map contains a map legend — a key that explains what the symbols stand for. 41. The Mercator projection, once the most com ...
Sample_reading_tasks
... maps whose primary purpose is to 3……. of main characteristics conveyed by the map. Communication in colour is more effective if the 4…….. . Colours choices, as mistakes or misunderstandings, are often highlighted: too many colours, 5…... , too meaningful colours, etc. involving disturbances when rea ...
... maps whose primary purpose is to 3……. of main characteristics conveyed by the map. Communication in colour is more effective if the 4…….. . Colours choices, as mistakes or misunderstandings, are often highlighted: too many colours, 5…... , too meaningful colours, etc. involving disturbances when rea ...
Human geography
... area that is connected to the node by some defined function. For example, a cell tower provides the central node for a surrounding area in which cell phone users can obtain phone reception. • Perceptual region uses a looser standard for characterization, defined more by commonly accepted tradition o ...
... area that is connected to the node by some defined function. For example, a cell tower provides the central node for a surrounding area in which cell phone users can obtain phone reception. • Perceptual region uses a looser standard for characterization, defined more by commonly accepted tradition o ...
About Texas
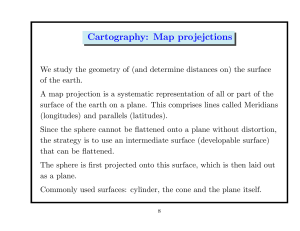
... surface of the Earth on the flat surface of a map Three major categories of map projections: 1. ______________ (or azimuthal): projects an image of the Earth onto a geometric plane a. often used for maps of the Poles 2. __________________: how a globe would look if projected onto a cylinder and unro ...
... surface of the Earth on the flat surface of a map Three major categories of map projections: 1. ______________ (or azimuthal): projects an image of the Earth onto a geometric plane a. often used for maps of the Poles 2. __________________: how a globe would look if projected onto a cylinder and unro ...