Acute childhood exanthems
... dermatomes and can be painful. In adults, treatment with aciclovir is recommended within 72 h of onset to prevent the complication of post-herpetic neuralgia, a very uncommon sequela in children. In immunocompromised individuals, intravenous aciclovir should be started to prevent dissemination of va ...
... dermatomes and can be painful. In adults, treatment with aciclovir is recommended within 72 h of onset to prevent the complication of post-herpetic neuralgia, a very uncommon sequela in children. In immunocompromised individuals, intravenous aciclovir should be started to prevent dissemination of va ...
information sheet – comparison of the effects of diseases
... There are an estimated 3000 deaths in people older than 50 years of age each year in Australia. Causes increased hospitalisation in the very young (under 5 years of age) and the elderly. Other high-risk groups include pregnant women, people who are obese, diabetics and others with certain chronic me ...
... There are an estimated 3000 deaths in people older than 50 years of age each year in Australia. Causes increased hospitalisation in the very young (under 5 years of age) and the elderly. Other high-risk groups include pregnant women, people who are obese, diabetics and others with certain chronic me ...
Neonatal calf diarrhea Neonatal calf diarrhea (NCD), also known as
... digestive and absorptive capability of the intestine as well as inflamemation. Other infectiou gents produce toxins that cause the cell lining of the intestine to produce fluid rather than absorb it. Diarrhea,dehydration and electrolyte loss occur in both instances and have especiallysevere effects ...
... digestive and absorptive capability of the intestine as well as inflamemation. Other infectiou gents produce toxins that cause the cell lining of the intestine to produce fluid rather than absorb it. Diarrhea,dehydration and electrolyte loss occur in both instances and have especiallysevere effects ...
Information Sheet Yellow Fever Vaccination
... What is yellow fever and why should I have a vaccination? Yellow fever is an acute life-threatening infectious disease which can be fatal. The yellow fever virus is transmitted by mosquitos. It occurs in certain tropical regions of South America and Africa designated by the World Health Organization ...
... What is yellow fever and why should I have a vaccination? Yellow fever is an acute life-threatening infectious disease which can be fatal. The yellow fever virus is transmitted by mosquitos. It occurs in certain tropical regions of South America and Africa designated by the World Health Organization ...
Is My Child Ill - Prior Lake Savage Area Schools
... cough develops that can occur in explosive bursts (paroxysmal or whooping cough), sometimes followed by vomiting. Coughing occurs more frequently at night. Symptoms are less severe in older children and adults, so they may unknowingly infect infants and preschoolers who are at risk for serious illne ...
... cough develops that can occur in explosive bursts (paroxysmal or whooping cough), sometimes followed by vomiting. Coughing occurs more frequently at night. Symptoms are less severe in older children and adults, so they may unknowingly infect infants and preschoolers who are at risk for serious illne ...
Communicable Disease Prevention
... Our report is intended to share information which will help you protect yourself from contracting a communicable disease--a major source of illness. Everybody is aflutter about the dreaded bird flu. It has us making emergency plans for a disease which we are unsure if it will come, when it will come ...
... Our report is intended to share information which will help you protect yourself from contracting a communicable disease--a major source of illness. Everybody is aflutter about the dreaded bird flu. It has us making emergency plans for a disease which we are unsure if it will come, when it will come ...
Measles is a serious disease * Vaccination is the only effective
... The MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine is a combination vaccine that protects against the three diseases with only one shot. Some people fear that combination vaccines or giving several vaccines at the same time overloads a child’s immune system or increases the risk of harmful side effects. B ...
... The MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine is a combination vaccine that protects against the three diseases with only one shot. Some people fear that combination vaccines or giving several vaccines at the same time overloads a child’s immune system or increases the risk of harmful side effects. B ...
Modeling of Fish Disease Dynamics - Turkish Journal of Fisheries
... usefulness and weaknesses. They reported four important and “justified” aspects of mathematical models in disease epidemics. First of all, mathematical models are useful in providing insight into the relative importance of factors influencing spread, and also improving our understanding of the relat ...
... usefulness and weaknesses. They reported four important and “justified” aspects of mathematical models in disease epidemics. First of all, mathematical models are useful in providing insight into the relative importance of factors influencing spread, and also improving our understanding of the relat ...
Parvovirus B19 (Fifth Disease)
... Parvovirus B19 (Fifth Disease) What is "fifth disease?" Fifth disease is a mild rash illness that occurs most commonly in children. The ill child typically has a "slapped-cheek" rash on the face and a lacy red rash on the trunk and limbs. Occasionally, the rash may itch. An ill child may have a low- ...
... Parvovirus B19 (Fifth Disease) What is "fifth disease?" Fifth disease is a mild rash illness that occurs most commonly in children. The ill child typically has a "slapped-cheek" rash on the face and a lacy red rash on the trunk and limbs. Occasionally, the rash may itch. An ill child may have a low- ...
Hepatitis B Vaccination (at a glance) Schedule
... Alcoholics are also reported as having lower seroconversion rates, particularly those with advanced liver disease. Patients who are immunosuppressed or on renal dialysis may also respond less well and require larger or more doses of vaccine. Failure to gain antibody after 2 complete courses should n ...
... Alcoholics are also reported as having lower seroconversion rates, particularly those with advanced liver disease. Patients who are immunosuppressed or on renal dialysis may also respond less well and require larger or more doses of vaccine. Failure to gain antibody after 2 complete courses should n ...
Vaccine Preventable Disease and Chapter 9 Foodborne Illness
... forms of invasive meningoccocal disease include meningitis (49%), blood infections (33%), and meningococcal pneumonia (9%). The disease can have abrupt onset and progress rapidly. It occurs most often in the first year of life and during late adolescence. Annually, 1,400 to 2,800 cases of invasive m ...
... forms of invasive meningoccocal disease include meningitis (49%), blood infections (33%), and meningococcal pneumonia (9%). The disease can have abrupt onset and progress rapidly. It occurs most often in the first year of life and during late adolescence. Annually, 1,400 to 2,800 cases of invasive m ...
Eosinophilic Meningitis.
... manipulation, although some symptoms including headache may persist for > 4 weeks. Most of the patients affected with eosinophilic meningitis can be adequately managed with supportive therapy with analgesics plus rehydration. NSAIDs should be avoided since they are occasionally the direct cause of C ...
... manipulation, although some symptoms including headache may persist for > 4 weeks. Most of the patients affected with eosinophilic meningitis can be adequately managed with supportive therapy with analgesics plus rehydration. NSAIDs should be avoided since they are occasionally the direct cause of C ...
National Immunization Awareness Month Fact Sheet
... approximately 700,000 to 2.2 million people in the United States are chronically infected ...
... approximately 700,000 to 2.2 million people in the United States are chronically infected ...
Update From the ACIP
... Adolescent Immunization Schedule Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 7 through 18 years – United States, 2012 For those who fall behind or start late, see the catch-up schedule ...
... Adolescent Immunization Schedule Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 7 through 18 years – United States, 2012 For those who fall behind or start late, see the catch-up schedule ...
Bridging Taxonomic and Disciplinary Divides in Infectious Disease
... microbes. The vast majority of microbes are not pathogenic, and thus pathogen infection in many cases is akin to the invasion of a novel microbe into an existing community within a host. Current work in both plant and animal hosts is revealing that colonies of microbes can produce antimicrobial comp ...
... microbes. The vast majority of microbes are not pathogenic, and thus pathogen infection in many cases is akin to the invasion of a novel microbe into an existing community within a host. Current work in both plant and animal hosts is revealing that colonies of microbes can produce antimicrobial comp ...
12_Course_and_forms_of_infection_-_I - IS MU
... Focal infection – I Focal infection theory: chronic infection limited to a certain focus can result in a systemic illness with symptoms in quite a different site Concept of focal infection used to be very fashionable formerly in diverse medical branches In the name of so-called sanation of focuses ...
... Focal infection – I Focal infection theory: chronic infection limited to a certain focus can result in a systemic illness with symptoms in quite a different site Concept of focal infection used to be very fashionable formerly in diverse medical branches In the name of so-called sanation of focuses ...
Newer Vaccines
... • Protection for at least 15 years and probably for life. Boosters are not recommended. • Because of the prolonged incubation period of hepatitis B, some protection will be afforded to most travellers following the second dose given before travel. The final dose should always be given upon return. • ...
... • Protection for at least 15 years and probably for life. Boosters are not recommended. • Because of the prolonged incubation period of hepatitis B, some protection will be afforded to most travellers following the second dose given before travel. The final dose should always be given upon return. • ...
Open Letter Supporting Adult Immunizations
... infect individuals, for up to two hours. 18,19 Complications from measles are more common among adults than children. Approximately 20 percent of those with measles experience one or more complications including pneumonia, encephalitis, seizures, and death. 20 After controlling the disease for over ...
... infect individuals, for up to two hours. 18,19 Complications from measles are more common among adults than children. Approximately 20 percent of those with measles experience one or more complications including pneumonia, encephalitis, seizures, and death. 20 After controlling the disease for over ...
Re-emerging Infectious Diseases: Is ASEAN Prepared?
... reports of cases of infection due to close human-to-human contact, the risk of virus spread warrants increased surveillance. While the WHO has yet to issue travel advisories, the virulence of the new viruses has already prompted warnings of a possible pandemic from the US Centers for Disease Control ...
... reports of cases of infection due to close human-to-human contact, the risk of virus spread warrants increased surveillance. While the WHO has yet to issue travel advisories, the virulence of the new viruses has already prompted warnings of a possible pandemic from the US Centers for Disease Control ...
Legionnaires’ Disease for Flint Residents Frequently Asked Questions about
... increases the chances that you'll develop Legionnaires' disease if you're exposed to Legionella bacteria. There are no vaccines that can help protect you from Legionnaires’ disease. However, there are vaccines available that can prevent other types of pneumonia. Two types of vaccines that are especi ...
... increases the chances that you'll develop Legionnaires' disease if you're exposed to Legionella bacteria. There are no vaccines that can help protect you from Legionnaires’ disease. However, there are vaccines available that can prevent other types of pneumonia. Two types of vaccines that are especi ...
Unit 4 - The Spread of Disease
... EXAMPLE OF HIERARCHAL DIFFUSION • The H1N1 Virus and other diseases. • H1N1 started in Mexico City, but first saw prevalence in other large cities (LA, NYC, Chicago) before seeing a presence in smaller ...
... EXAMPLE OF HIERARCHAL DIFFUSION • The H1N1 Virus and other diseases. • H1N1 started in Mexico City, but first saw prevalence in other large cities (LA, NYC, Chicago) before seeing a presence in smaller ...
The Spread of Disease
... • There are some cases of malaria in the US every year for example, and most of those are close to airports. Mosquitoes survive in the plane just long enough to bite someone when they leave. ...
... • There are some cases of malaria in the US every year for example, and most of those are close to airports. Mosquitoes survive in the plane just long enough to bite someone when they leave. ...
Pertussis Epidemic
... Tetanus, Dipthera, Pertussis All persons > 10 years old considered susceptible to pertussis due to waning immunity unless given single dose of TDaP *Single dose of TDaP should now replace Td booster ...
... Tetanus, Dipthera, Pertussis All persons > 10 years old considered susceptible to pertussis due to waning immunity unless given single dose of TDaP *Single dose of TDaP should now replace Td booster ...
Internal Medicine Board Review: Infectious Diseases
... PLUS levofloxacin 750 mg IV qd or gentamicin 7 mg/kg IV daily PLUS linezolid or vancomycin (if MRSA suspected) ...
... PLUS levofloxacin 750 mg IV qd or gentamicin 7 mg/kg IV daily PLUS linezolid or vancomycin (if MRSA suspected) ...
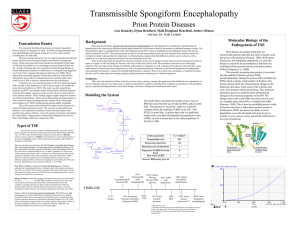
Meningococcal disease

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated but is a vaccine-preventable disease. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection can result in sepsis, which is a more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.The disease's pathogenesis is not fully understood. The pathogen colonises a large number of the general population harmlessly, but in some very small percentage of individuals it can invade the blood stream, and the entire body but notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.While meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold (which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.