Lymphadenopathy - Cook Children`s
... information are the history and physical examination, followed by select laboratory and imaging studies. History The majority of enlarged nodes in children will be secondary to infectious causes. A complete history should survey for characteristics of infectious diseases, including: • Environmental: ...
... information are the history and physical examination, followed by select laboratory and imaging studies. History The majority of enlarged nodes in children will be secondary to infectious causes. A complete history should survey for characteristics of infectious diseases, including: • Environmental: ...
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Minnesota (PDF: 141KB/12 pages)
... the early 1980s, approximately 20 years after the introduction of methicillin. The term “community-acquired MRSA” has been used to describe MRSA infection diagnosed outside of the hospital or within 48 to 72 hours of admission. In some early studies, persons with recent hospitalization or long-term ...
... the early 1980s, approximately 20 years after the introduction of methicillin. The term “community-acquired MRSA” has been used to describe MRSA infection diagnosed outside of the hospital or within 48 to 72 hours of admission. In some early studies, persons with recent hospitalization or long-term ...
Rickettsial Diseases - Journal of the Association of Physicians of India
... pneumonia, interstitial myocarditis, perivascular glial nodules of central nervous system, and similar vascular lesions in skin, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, liver, skeletal muscles and kidneys. Platelets are consumed locally.7 ...
... pneumonia, interstitial myocarditis, perivascular glial nodules of central nervous system, and similar vascular lesions in skin, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, liver, skeletal muscles and kidneys. Platelets are consumed locally.7 ...
... intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7, 14, and 28). II the risk of rabies is high, postexposure prophylaxis should be initiated immediately. If the risk is low, treatment can be delayed for up to 4 8 hours pending laboratory examination. Examination of the animal's brain tissue is the only reliable method ...
Infectious Diseases
... state-of-the-art information in the prevention, diagnosis, and management of important infectious diseases. This highly rated course focuses on major clinical syndromes as well as management controversies in infectious disease. Topics with major impact on clinical practice are emphasized, including: ...
... state-of-the-art information in the prevention, diagnosis, and management of important infectious diseases. This highly rated course focuses on major clinical syndromes as well as management controversies in infectious disease. Topics with major impact on clinical practice are emphasized, including: ...
Imaging of Bacterial Infections with 99mTc-Labeled Human
... expressed as the number of CFUs per gram of infected tissue. All cultures with negative findings were assigned the value 100 CFU/mL, the lower limit of detection. Peritoneum Model. A peritoneal K. pneumoniae infection model was used to quantify the binding of tracers to both bacteria and leukocytes ...
... expressed as the number of CFUs per gram of infected tissue. All cultures with negative findings were assigned the value 100 CFU/mL, the lower limit of detection. Peritoneum Model. A peritoneal K. pneumoniae infection model was used to quantify the binding of tracers to both bacteria and leukocytes ...
Handwashing - Advocate Health Care
... a necessary part of controlling worker exposure to bloodborne pathogens. • Cleaning schedules and decontamination methods depend on: – type of surface to be cleaned – type of soil that is present – particular tasks or procedures that are being performed ...
... a necessary part of controlling worker exposure to bloodborne pathogens. • Cleaning schedules and decontamination methods depend on: – type of surface to be cleaned – type of soil that is present – particular tasks or procedures that are being performed ...
Disease of Aquatic Organisms 112:9
... the muscosa. Inset in (B) shows higher magnification of outlined area. (C) Rare areas of necrosis (arrows) were observed within the liver. (D) Vascular (arrows) and perivascular necrosis were best discerned in tissues that were less affected, such as in the muscle wall of this section of intestine ...
... the muscosa. Inset in (B) shows higher magnification of outlined area. (C) Rare areas of necrosis (arrows) were observed within the liver. (D) Vascular (arrows) and perivascular necrosis were best discerned in tissues that were less affected, such as in the muscle wall of this section of intestine ...
Vaccinations - e-Bug
... system to work properly so preventing infection. Another means of assisting our immune system is through vaccinations. Vaccines are used to prevent, NOT treat infection. A vaccine is usually made from weak or inactive versions of the same microbes that make us ill. In some cases, the vaccines are ma ...
... system to work properly so preventing infection. Another means of assisting our immune system is through vaccinations. Vaccines are used to prevent, NOT treat infection. A vaccine is usually made from weak or inactive versions of the same microbes that make us ill. In some cases, the vaccines are ma ...
Suk et al., 2014. The interconnected and cross
... unemployment and the prospect of public health budget cuts can increase the risk of infectious disease transmission (24, 26), with the most prominent example being an outbreak of HIV among people who inject drugs in Greece (see section 3.2) (27, 28). In a similar fashion, it has been speculated that ...
... unemployment and the prospect of public health budget cuts can increase the risk of infectious disease transmission (24, 26), with the most prominent example being an outbreak of HIV among people who inject drugs in Greece (see section 3.2) (27, 28). In a similar fashion, it has been speculated that ...
Mycoplasma genitalium E D I T O R I A L C...
... As long as M. genitalium testing is available only to a limited number of sexually transmitted disease research clinics, optimal empirical NGU treatment should cover both M. genitalium and non–M. genitalium, nonchlamydial NGU. The group with the latter is commonly larger than both the chlamydial and ...
... As long as M. genitalium testing is available only to a limited number of sexually transmitted disease research clinics, optimal empirical NGU treatment should cover both M. genitalium and non–M. genitalium, nonchlamydial NGU. The group with the latter is commonly larger than both the chlamydial and ...
Infection Control and Extracorporeal Life Support
... It is the recommendation of the task force that ECMO teams take this data into consideration in choosing empiric antibiotics for patients on ECMO with suspected or presumed infections. In addition, bec ...
... It is the recommendation of the task force that ECMO teams take this data into consideration in choosing empiric antibiotics for patients on ECMO with suspected or presumed infections. In addition, bec ...
Vaccinations - e-Bug
... system to work properly so preventing infection. Another means of assisting our immune system is through vaccinations. Vaccines are used to prevent, NOT treat infection. A vaccine is usually made from weak or inactive versions of the same microbes that make us ill. In some cases, the vaccines are ma ...
... system to work properly so preventing infection. Another means of assisting our immune system is through vaccinations. Vaccines are used to prevent, NOT treat infection. A vaccine is usually made from weak or inactive versions of the same microbes that make us ill. In some cases, the vaccines are ma ...
complexities and challenges for the elimination of infectious diseases
... the population may increase during the ‘honeymoon period’ of low incidence (and consequently low transmission) following mass vaccination campaigns [35], or following local extinction. Both phenomena may result in huge outbreaks after susceptible numbers reach a threshold level, or the infection is ...
... the population may increase during the ‘honeymoon period’ of low incidence (and consequently low transmission) following mass vaccination campaigns [35], or following local extinction. Both phenomena may result in huge outbreaks after susceptible numbers reach a threshold level, or the infection is ...
Ruling Out Novel H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection with Direct
... At our hospital, where we perform DFA testing as our rapid test of choice for influenza diagnosis, we knew that our test had sufficient sensitivity (⭓95% sensitivity compared with viral culture) to allow us to effectively rule out seasonal influenza, but we were uncertain how the test would perform ...
... At our hospital, where we perform DFA testing as our rapid test of choice for influenza diagnosis, we knew that our test had sufficient sensitivity (⭓95% sensitivity compared with viral culture) to allow us to effectively rule out seasonal influenza, but we were uncertain how the test would perform ...
presence of amphibian chytrid fungus batrachochytrium
... histological sections. No pathogenic bacteria were isolated in cultures of the internal organs. The bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila was isolated from the intestines of 10 of 21 tadpoles; this bacterium was isolated from at least one tadpole from each of the 4 fish hatcheries. No significant protozoan ...
... histological sections. No pathogenic bacteria were isolated in cultures of the internal organs. The bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila was isolated from the intestines of 10 of 21 tadpoles; this bacterium was isolated from at least one tadpole from each of the 4 fish hatcheries. No significant protozoan ...
Communicable Disease Control Manual For Schools and Childcare
... Administrative Assistant to Health Protection Nurse Specialists ...
... Administrative Assistant to Health Protection Nurse Specialists ...
Hepatitis A Virus
... intermediate rates of disease Staff and residents of closed communities Refugees residing in temporary camps after catastrophes Close personal contacts of a case Staff and parents of children in day-care centers Common-source exposure to infected food or water ...
... intermediate rates of disease Staff and residents of closed communities Refugees residing in temporary camps after catastrophes Close personal contacts of a case Staff and parents of children in day-care centers Common-source exposure to infected food or water ...
Filament formation associated with spirochetal infection: a comparative approach to Morgellons disease
... In 2006, pressure from the Morgellons Research Foundation prompted the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to announce that it had launched an investigation. In May 2007, Dan Rutz, a CDC communication specialist, was quoted as saying in a television interview, “There is nothing to im ...
... In 2006, pressure from the Morgellons Research Foundation prompted the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to announce that it had launched an investigation. In May 2007, Dan Rutz, a CDC communication specialist, was quoted as saying in a television interview, “There is nothing to im ...
Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings Core
... So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in health care settings ...
... So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in health care settings ...
Sequelae of Traveler`s Diarrhea: Focus on Postinfectious Irritable
... for diagnosing IBS, alternative causes of persistent bowel symptoms were often not assessed or were not reported to have been assessed. This is especially true for patients thought to have PIIBS during the first 3 months after travel, when other causes, such as C. difficile, protozoan pathogens, and ...
... for diagnosing IBS, alternative causes of persistent bowel symptoms were often not assessed or were not reported to have been assessed. This is especially true for patients thought to have PIIBS during the first 3 months after travel, when other causes, such as C. difficile, protozoan pathogens, and ...
States (sum up to the whole population)
... People moving out of Q1 can go to either Q2 or to R. We use 1/μ2 to capture the delay between states (will not know that an individual has actually recovered until they make it through an incubation period without getting sick). The ratios with s(t)+e(t) in the denominator use used to differentiate ...
... People moving out of Q1 can go to either Q2 or to R. We use 1/μ2 to capture the delay between states (will not know that an individual has actually recovered until they make it through an incubation period without getting sick). The ratios with s(t)+e(t) in the denominator use used to differentiate ...
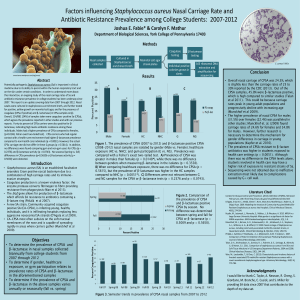
Staphylococcus aureus - York College of Pennsylvania
... 2007. This report is an update covering data from 2007 through 2012. Nasal swabs were cultured in staphylococcus enrichment broth, and further tested for positive, yellow growth on mannitol-salt agar, and for the presence of coagulase (CPSa if positive) and β- lactamase( in CPSa samples only). Overa ...
... 2007. This report is an update covering data from 2007 through 2012. Nasal swabs were cultured in staphylococcus enrichment broth, and further tested for positive, yellow growth on mannitol-salt agar, and for the presence of coagulase (CPSa if positive) and β- lactamase( in CPSa samples only). Overa ...
Immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis using recombinant
... as a fusion protein containing the proregion, supplied with six histidyl residues at the N-terminal end (rproCL1). In this study we tested its potential as antigen for the serologic diagnosis of F. hepatica infections by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The analyzed human sera included 16 ...
... as a fusion protein containing the proregion, supplied with six histidyl residues at the N-terminal end (rproCL1). In this study we tested its potential as antigen for the serologic diagnosis of F. hepatica infections by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The analyzed human sera included 16 ...
APPENDIX 1: INTRODUCTION, DETAILED METHODS AND DEFINITIONS Introduction
... provide useful clinical recommendations. By providing clinicians with information on the best available evidence with respect to risk factors for and the occurrence, diagnosis, prognosis and management of community-acquired LRTI (CA-LRTI), we aim to maximise the potential benefits for patients with ...
... provide useful clinical recommendations. By providing clinicians with information on the best available evidence with respect to risk factors for and the occurrence, diagnosis, prognosis and management of community-acquired LRTI (CA-LRTI), we aim to maximise the potential benefits for patients with ...
Oesophagostomum
.jpg?width=300)
Oesophagostomum is a genus of free-living nematodes of the family Strongyloidae. These worms occur in Africa, Brazil, China, Indonesia and the Philippines. The majority of human infection with Oesophagostomum is localized to northern Togo and Ghana. Because the eggs may be indistinguishable from those of the hookworms (which are widely distributed and can also rarely cause helminthomas), the species causing human helminthomas are rarely identified with accuracy. Oesophagostomum, especially O. bifurcum, are common parasites of livestock and animals like goats, pigs and non-human primates, although it seems that humans are increasingly becoming favorable hosts as well. The disease they cause, oesophagostomiasis, is known for the nodule formation it causes in the intestines of its infected hosts, which can lead to more serious problems such as dysentery. Although the routes of human infection have yet to be elucidated sufficiently, it is believed that transmission occurs through oral-fecal means, with infected humans unknowingly ingesting soil containing the infectious filariform larvae.Oesophagostomum infection is largely localized to northern Togo and Ghana in western Africa where it is a serious public health problem. Because it is so localized, research on intervention measures and the implementation of effective public health interventions have been lacking. In recent years, however, there have been advances in the diagnosis of Oesophagostomum infection with PCR assays and ultrasound and recent interventions involving mass treatment with albendazole shows promise for controlling and possibly eliminating Oesophagostomum infection in northern Togo and Ghana.