The ABC`s of Lyme Disease
... blood cells which causes a malarial like illness. Children may complain of intermittent fevers, chills, day and night sweats, as well as having an increased severity and duration of Lyme disease symptoms. Diagnosis is made by antibody titers (IFA), blood smear, DNA (PCR) and RNA analysis (FISH assay ...
... blood cells which causes a malarial like illness. Children may complain of intermittent fevers, chills, day and night sweats, as well as having an increased severity and duration of Lyme disease symptoms. Diagnosis is made by antibody titers (IFA), blood smear, DNA (PCR) and RNA analysis (FISH assay ...
Epidemiology, disease and control of infections in ruminants by
... Infection by alphaherpesviruses mostly occurs through the respiratory tract via virus aerosol18, while infection of genital tract surfaces usually occurs after viraemia resulting from the respiratory tract infection. At both these sites virus replicates in epithelial cells. The released progeny viru ...
... Infection by alphaherpesviruses mostly occurs through the respiratory tract via virus aerosol18, while infection of genital tract surfaces usually occurs after viraemia resulting from the respiratory tract infection. At both these sites virus replicates in epithelial cells. The released progeny viru ...
Isolation, Characterization and Standardization of New Infectious
... rapidly spread all over the world including Europe, Africa, the Middle East, South America and Asia (7, 8). The strains have been characterized by severe clinical signs and high mortality ranging from 60-100%. The disease in younger chickens is usually sub-clinical and results in immunosuppression w ...
... rapidly spread all over the world including Europe, Africa, the Middle East, South America and Asia (7, 8). The strains have been characterized by severe clinical signs and high mortality ranging from 60-100%. The disease in younger chickens is usually sub-clinical and results in immunosuppression w ...
Surveillance of Fish Diseases in the Nordic Countries
... Authorities that is responsible for the implementation of measures that will be used in order to control a given notifiable disease. The implementation involves both central and regional veterinary officers. In all the Nordic countries except non-approved zones in Denmark, stamping out procedures fo ...
... Authorities that is responsible for the implementation of measures that will be used in order to control a given notifiable disease. The implementation involves both central and regional veterinary officers. In all the Nordic countries except non-approved zones in Denmark, stamping out procedures fo ...
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
... pulmonary edema and resolution of fever and shock (4). 4) Convalescence Phase: In survivors, recovery from acute infection is rapid, but full recovery may require weeks to months (7). Asymptomatic and mild forms of disease are rare but have been documented (5, 8). Limited information suggests that c ...
... pulmonary edema and resolution of fever and shock (4). 4) Convalescence Phase: In survivors, recovery from acute infection is rapid, but full recovery may require weeks to months (7). Asymptomatic and mild forms of disease are rare but have been documented (5, 8). Limited information suggests that c ...
Infectious Diseases in New Mexico
... Salmonellosis represents a major burden of infectious disease in New Mexico and across the United States. Infection with the rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacilli Salmonella can cause diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal cramps, typically lasting several days. In severe cases, the bacteria may invad ...
... Salmonellosis represents a major burden of infectious disease in New Mexico and across the United States. Infection with the rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacilli Salmonella can cause diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal cramps, typically lasting several days. In severe cases, the bacteria may invad ...
Updated advice for family and friends of HAW
... Follow-up of people who are well when they return to the UK The follow-up required for each category of returning worker is dependent on the type of work that they have undertaken while in Ebola affected areas. The local health protection team will be sent their details before they return to the UK ...
... Follow-up of people who are well when they return to the UK The follow-up required for each category of returning worker is dependent on the type of work that they have undertaken while in Ebola affected areas. The local health protection team will be sent their details before they return to the UK ...
Seasonal population movements and the surveillance and control of
... incidence will be over-estimated in places with high numbers of migrants and underestimated in areas where many residents are absent. An important consideration for the impact of these shifting population densities is the demographic structure of the mobile populations [20]; in East Africa for examp ...
... incidence will be over-estimated in places with high numbers of migrants and underestimated in areas where many residents are absent. An important consideration for the impact of these shifting population densities is the demographic structure of the mobile populations [20]; in East Africa for examp ...
QFT use in HIV patients
... May be used for surveillance/screening, or to find those who will benefit from treatment May be used in place of TST to test contacts; confirm negative via retest 8–10 weeks post exposure Use same test for repeat testing to reduce misclassification errors Generally should not be used to test chi ...
... May be used for surveillance/screening, or to find those who will benefit from treatment May be used in place of TST to test contacts; confirm negative via retest 8–10 weeks post exposure Use same test for repeat testing to reduce misclassification errors Generally should not be used to test chi ...
Update on bovine spongiform encephalopathy
... trained more than 250 state and federal veterinarians located throughout the United States in the recognition of BSE. Any person or veterinarian suspecting an animal of BSE should report the animal immediately to the nearest diagnostic laboratory and the state veterinarian. ...
... trained more than 250 state and federal veterinarians located throughout the United States in the recognition of BSE. Any person or veterinarian suspecting an animal of BSE should report the animal immediately to the nearest diagnostic laboratory and the state veterinarian. ...
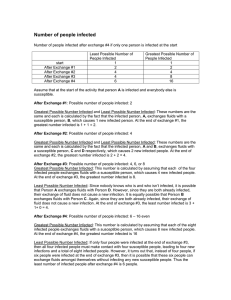
Number of people infected
... same and each is calculated by the fact that the infected person, A, exchanges fluids with a susceptible person, B, which causes 1 new infected person. At the end of exchange #1, the greatest number infected is 1 + 1 = 2. After Exchange #2: Possible number of people infected: 4 Greatest Possible Num ...
... same and each is calculated by the fact that the infected person, A, exchanges fluids with a susceptible person, B, which causes 1 new infected person. At the end of exchange #1, the greatest number infected is 1 + 1 = 2. After Exchange #2: Possible number of people infected: 4 Greatest Possible Num ...
Feline Enteropathies:
... – Both trophozoite form and encysted form are passed in the feces Transmission: fecal-oral route – Cysts are environmentally resistant and highly infectious Clinical signs – Not all infected cats show clinical signs – Most common clinical signs are diarrhea and weight loss – Diarrhea may be small- o ...
... – Both trophozoite form and encysted form are passed in the feces Transmission: fecal-oral route – Cysts are environmentally resistant and highly infectious Clinical signs – Not all infected cats show clinical signs – Most common clinical signs are diarrhea and weight loss – Diarrhea may be small- o ...
Document
... Severity or Duration of a Disease Acute disease: Symptoms develop rapidly. Chronic disease: Disease develops slowly. Latent disease: Disease with a period of no symptoms when the patient is inactive. ...
... Severity or Duration of a Disease Acute disease: Symptoms develop rapidly. Chronic disease: Disease develops slowly. Latent disease: Disease with a period of no symptoms when the patient is inactive. ...
SQHN Infection Control 2016 Drmutiu
... process in detail including sequencing of events and actual and potential risks, failure or points of vulnerability; and that, through a logical process, prioritizes areas for ...
... process in detail including sequencing of events and actual and potential risks, failure or points of vulnerability; and that, through a logical process, prioritizes areas for ...
elephantiasis elephantiasis - Men in White
... small organ behind the breastbone that is thought to play an important role in the immune system until puberty, as well as the bone marrow, which is the spongy tissue inside the cavities of bones that manufactures blood cells. Lymphatic tissue may also be located in other regions of the body, such a ...
... small organ behind the breastbone that is thought to play an important role in the immune system until puberty, as well as the bone marrow, which is the spongy tissue inside the cavities of bones that manufactures blood cells. Lymphatic tissue may also be located in other regions of the body, such a ...
1 MAIN epid cntrl prev of comm dis - Copy
... • Inflammation of the pharynx caused by a viruses& bacteria (group A streptococcus). • Discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow. ...
... • Inflammation of the pharynx caused by a viruses& bacteria (group A streptococcus). • Discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow. ...
Project Directorate on Animal Disease Monitoring and Surveillance
... by the detection of group-specific antibodies against the virus. Exotic sheep are more susceptible than indigenous and cross-bred sheep. A serological survey has indicated the presence of bluetongue virus (BTV) antibodies in cattle and buffalo in several states in India. However, clinical BT has not ...
... by the detection of group-specific antibodies against the virus. Exotic sheep are more susceptible than indigenous and cross-bred sheep. A serological survey has indicated the presence of bluetongue virus (BTV) antibodies in cattle and buffalo in several states in India. However, clinical BT has not ...
C difficile
... most common bacterial agent in a general population (1980) • Lyerly and colleagues purify two toxins, A and B, from C. difficile and also produce an important anti-toxin against these organisms (1982) ...
... most common bacterial agent in a general population (1980) • Lyerly and colleagues purify two toxins, A and B, from C. difficile and also produce an important anti-toxin against these organisms (1982) ...
Schistosomiasis

Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, snail fever, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic worms of the Schistosoma type. It may infect the urinary tract or the intestines. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. In those who have been infected for a long time, liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer may occur. In children it may cause poor growth and learning difficulty.The disease is spread by contact with water contaminated with the parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in developing countries as they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Other high risk groups include farmers, fishermen, and people using unclean water for their daily chores. It belongs to the group of helminth infections. Diagnosis is by finding the eggs of the parasite in a person's urine or stool. It can also be confirmed by finding antibodies against the disease in the blood.Methods to prevent the disease include improving access to clean water and reducing the number of snails. In areas where the disease is common entire groups may be treated all at once and yearly with the medication praziquantel. This is done to decrease the number of people infected and therefore decrease the spread of the disease. Praziquantel is also the treatment recommended by the World Health Organization for those who are known to be infected.Schistosomiasis affects almost 210 million people worldwide, and an estimated 12,000 to 200,000 people die from it a year. The disease is most commonly found in Africa, as well as Asia and South America. Around 700 million people, in more than 70 countries, live in areas where the disease is common. Schistosomiasis is second only to malaria, as a parasitic disease with the greatest economic impact. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.