Scanning Electron Microscope - i-Explore International Research
... The combined effect of the elastic and inelastic interactions is to distribute the beam electrons over a three-dimensional “interaction volume” [6]. The concept of interaction volume of the primary beam electrons and the sampling volume of the emitted secondary radiation are important both in interp ...
... The combined effect of the elastic and inelastic interactions is to distribute the beam electrons over a three-dimensional “interaction volume” [6]. The concept of interaction volume of the primary beam electrons and the sampling volume of the emitted secondary radiation are important both in interp ...
Lecture 1 TEM
... only in some low index direction, so that atoms are exactly on top of each other. For 3 dimensional analysis, several views can be combined from different angles into a 3D map, this technique is called Electron Crystallography. One of the limitations with HRTEM is that image formation relies on phas ...
... only in some low index direction, so that atoms are exactly on top of each other. For 3 dimensional analysis, several views can be combined from different angles into a 3D map, this technique is called Electron Crystallography. One of the limitations with HRTEM is that image formation relies on phas ...
Imaging Laboratory Exercise Scanning Electron Microscope
... lens, etc.) are used for their optics. In almost all of these, the role of these magnets is the same as the optical elements in a standard optical microscope. For the transmission electron microscopes (TEM) the principle of image formation is very similar to that of an optical microscope. In the TEM ...
... lens, etc.) are used for their optics. In almost all of these, the role of these magnets is the same as the optical elements in a standard optical microscope. For the transmission electron microscopes (TEM) the principle of image formation is very similar to that of an optical microscope. In the TEM ...
Total view of the AFM
... What are the SEM associated techniques that can give elemental composition? ...
... What are the SEM associated techniques that can give elemental composition? ...
Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
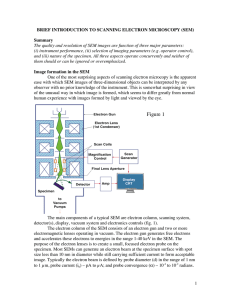
... In order to produce images the electron beam is focused into a fine probe, which is scanned across the surface of the specimen with the help of scanning coils (fig. 1). Each point on the specimen that is struck by the accelerated electrons emits signal in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Sele ...
... In order to produce images the electron beam is focused into a fine probe, which is scanned across the surface of the specimen with the help of scanning coils (fig. 1). Each point on the specimen that is struck by the accelerated electrons emits signal in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Sele ...
No Slide Title
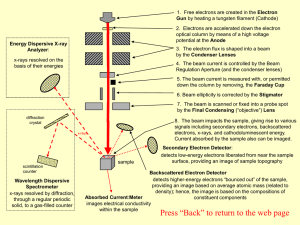
... 4. The beam current is controlled by the Beam Regulation Aperture (and the condenser lenses) 5. The beam current is measured with, or permitted down the column by removing, the Faraday Cup 6. Beam ellipticity is corrected by the Stigmator 7. The beam is scanned or fixed into a probe spot by the Fina ...
... 4. The beam current is controlled by the Beam Regulation Aperture (and the condenser lenses) 5. The beam current is measured with, or permitted down the column by removing, the Faraday Cup 6. Beam ellipticity is corrected by the Stigmator 7. The beam is scanned or fixed into a probe spot by the Fina ...
Scanning electron microscope

A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that can be detected and that contain information about the sample's surface topography and composition. The electron beam is generally scanned in a raster scan pattern, and the beam's position is combined with the detected signal to produce an image. SEM can achieve resolution better than 1 nanometer. Specimens can be observed in high vacuum, in low vacuum, in wet conditions (in environmental SEM), and at a wide range of cryogenic or elevated temperatures.The most common SEM mode is detection of secondary electrons emitted by atoms excited by the electron beam. The number of secondary electrons depends on the angle at which beam meets surface of specimen, i.e. on specimen topography. By scanning the sample and collecting the secondary electrons with a special detector, an image displaying the topography of the surface is created.