The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC)
... Only 1 region reported sporadic activity (BC) in week 34. No new outbreaks of influenza/ILI were reported No influenza-associated hospitalizations were reported over the two-week period The ILI consultation rate in weeks 33 and 34 were within the expected levels for this time of year Basical ...
... Only 1 region reported sporadic activity (BC) in week 34. No new outbreaks of influenza/ILI were reported No influenza-associated hospitalizations were reported over the two-week period The ILI consultation rate in weeks 33 and 34 were within the expected levels for this time of year Basical ...
HEPATITIS A
... With adults, an antibodies detection is advised 1-3 months after the complete vaccination scheme; in persons with a normal immunity, the presence of (at least 10 IE/ml) antibodies means a lifelong protection against asymptomatic forms of the disease and chronic support; this is obtained in more than ...
... With adults, an antibodies detection is advised 1-3 months after the complete vaccination scheme; in persons with a normal immunity, the presence of (at least 10 IE/ml) antibodies means a lifelong protection against asymptomatic forms of the disease and chronic support; this is obtained in more than ...
impacts of Yersinia pestis - Invasive Species Specialist Group
... population of Europe. While Y. pestis no longer causes problems of such magnitude, it is still a public health concern in Africa, Asia and South America (Titball and Williamson 2001). There are at least 2000 cases of plague reported annually. In the United States it is a rare disease of humans, with ...
... population of Europe. While Y. pestis no longer causes problems of such magnitude, it is still a public health concern in Africa, Asia and South America (Titball and Williamson 2001). There are at least 2000 cases of plague reported annually. In the United States it is a rare disease of humans, with ...
Handwashing - Canadian Association of University Teachers
... to ease in the spread of infection due to the numbers of people and the close proximity in which they interact. You can also spread microbes by being in contact with or sharing items like food ustensils, straws, etc. Once your hands have these microbes on them, you may touch your face (mouth, eyes, ...
... to ease in the spread of infection due to the numbers of people and the close proximity in which they interact. You can also spread microbes by being in contact with or sharing items like food ustensils, straws, etc. Once your hands have these microbes on them, you may touch your face (mouth, eyes, ...
MRSA brochure - Cook County Department of Public Health
... commonly found on the skin or in noses of healthy people without causing infection, MRSA is a type of staph that is resistant to antibiotics; making it more difficult to treat. ...
... commonly found on the skin or in noses of healthy people without causing infection, MRSA is a type of staph that is resistant to antibiotics; making it more difficult to treat. ...
Effective use of Vaccinations on Cow Calf operations to reduce the
... be tailored to the operation. If you have a high incidence of BRD in calves less than 6 months of age, it may be necessary to vaccinate younger calves or vaccinate cows prior to calving to increase BRD spe‐ cific immunity in their colostrum. If a killed virus vaccine is being used, then a 2nd ( ...
... be tailored to the operation. If you have a high incidence of BRD in calves less than 6 months of age, it may be necessary to vaccinate younger calves or vaccinate cows prior to calving to increase BRD spe‐ cific immunity in their colostrum. If a killed virus vaccine is being used, then a 2nd ( ...
Bridging the Gap: Linking animal and human medicine through
... of our physical and even mental health – just as we, and our behaviour, are so important to them. At the centre of all this is veterinary research. Coordinating with colleagues across many sectors, veterinary researchers work to bridge the gap between animal and human medicine. Veterinary schools ar ...
... of our physical and even mental health – just as we, and our behaviour, are so important to them. At the centre of all this is veterinary research. Coordinating with colleagues across many sectors, veterinary researchers work to bridge the gap between animal and human medicine. Veterinary schools ar ...
View Full Text-PDF
... latency. Viremia continues can first be detected, typically at least 6 months in adults and several years in young children. Although an initial persistent infection is often observed, clearance of acute infection is the norm in all immunocompetent individuals and it is correlated with a slow rise i ...
... latency. Viremia continues can first be detected, typically at least 6 months in adults and several years in young children. Although an initial persistent infection is often observed, clearance of acute infection is the norm in all immunocompetent individuals and it is correlated with a slow rise i ...
Infection Control Guidelines
... source of infection. They can become contaminated with micro-organisms from unwashed hands, body fluids or by people putting their mouth to them. Although many micro-organisms will not grow in the absence of water, some can survive on the surface of a toy in sufficient numbers to present a risk of i ...
... source of infection. They can become contaminated with micro-organisms from unwashed hands, body fluids or by people putting their mouth to them. Although many micro-organisms will not grow in the absence of water, some can survive on the surface of a toy in sufficient numbers to present a risk of i ...
Infectious Disease Boogies
... • Infection - the virus enters the body – initial symptoms are a cold, flu like syndrome, body aches, etc…which pass within a few days. The ELISA test is negative at this time. • Incubation – 3 months to one year, where the virus enters other cells, but no symptoms are present. This is when sero-con ...
... • Infection - the virus enters the body – initial symptoms are a cold, flu like syndrome, body aches, etc…which pass within a few days. The ELISA test is negative at this time. • Incubation – 3 months to one year, where the virus enters other cells, but no symptoms are present. This is when sero-con ...
Campylobacter and Helicobacter
... Sporadic infections in humans far outnumber those affected in point-source outbreaks Sporadic cases peak in the summer in temperate climates with a secondary peak in the late fall seen in the U.S. Globally, C. jejuni subsp. jejuni accounts for more than 80% of all Campylobacter enteriti C. c ...
... Sporadic infections in humans far outnumber those affected in point-source outbreaks Sporadic cases peak in the summer in temperate climates with a secondary peak in the late fall seen in the U.S. Globally, C. jejuni subsp. jejuni accounts for more than 80% of all Campylobacter enteriti C. c ...
Roche drug Esbriet (pirfenidone) approved in Switzerland for the
... The approval of Esbriet is based on data from a large, placebo-controlled phase III study (ASCEND) and is supported by two other large phase III trials (known as CAPACITY 1 and 2). In the ASCEND study, significantly more patients who received Esbriet showed delayed progression of the disease – corre ...
... The approval of Esbriet is based on data from a large, placebo-controlled phase III study (ASCEND) and is supported by two other large phase III trials (known as CAPACITY 1 and 2). In the ASCEND study, significantly more patients who received Esbriet showed delayed progression of the disease – corre ...
clostridium difficile disease
... Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a spore-forming bacterium that can cause serious intestinal disease that is potentially life-threatening. The risk of contracting a C. difficile infection (CDI) increases with age, antibiotic treatment and time spent in hospitals or nursing homes, where outbre ...
... Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a spore-forming bacterium that can cause serious intestinal disease that is potentially life-threatening. The risk of contracting a C. difficile infection (CDI) increases with age, antibiotic treatment and time spent in hospitals or nursing homes, where outbre ...
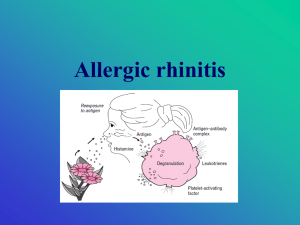
Allergic Rhinitis
... 1. First step: avoidance of the offending allergens 2. Pharmacotherapy is used if the avoidance measures are not feasible or do not adequately relieve the symptoms • Treatment of allergic rhinitis should be targeted at the patient’s specific symptoms • Drugs: antihistamines, decongestants, mast cell ...
... 1. First step: avoidance of the offending allergens 2. Pharmacotherapy is used if the avoidance measures are not feasible or do not adequately relieve the symptoms • Treatment of allergic rhinitis should be targeted at the patient’s specific symptoms • Drugs: antihistamines, decongestants, mast cell ...
Diseases of the Respiratory System PowerPoint
... v) the bacteria can survive in the tubercle for many years c) Most individuals recover completely from this infection ...
... v) the bacteria can survive in the tubercle for many years c) Most individuals recover completely from this infection ...
Shingles Fact Sheet
... also through the air. Persons with disseminated shingles should consult with their physician to determine how long they should be off from school/work. Is it contagious? The virus that causes shingles can be passed on to others up to one week after onset of rash. A person is not infectious before bl ...
... also through the air. Persons with disseminated shingles should consult with their physician to determine how long they should be off from school/work. Is it contagious? The virus that causes shingles can be passed on to others up to one week after onset of rash. A person is not infectious before bl ...
Name and Address of Childcare Facility Date: RE: Slapped Cheek
... appears. By the time a child has the characteristic “slapped cheek” rash he/she is probably no longer contagious and may return to school crèche/preschool. How does someone get infected with parvovirus B19? Parvovirus B19 has been found in the respiratory secretions (e.g., saliva, sputum, or nasal m ...
... appears. By the time a child has the characteristic “slapped cheek” rash he/she is probably no longer contagious and may return to school crèche/preschool. How does someone get infected with parvovirus B19? Parvovirus B19 has been found in the respiratory secretions (e.g., saliva, sputum, or nasal m ...
DATURA ORGANISM METEL
... control fever and as a drug for criminal purposes [7][8]. Bacterial Cold Water Disease It was first described by Borg in 1948 and the causative organism was identified has Flavobacterium psychrophilum which produces acute septicemic infection in salmonids and few other species [9][10]. Flavobacteriu ...
... control fever and as a drug for criminal purposes [7][8]. Bacterial Cold Water Disease It was first described by Borg in 1948 and the causative organism was identified has Flavobacterium psychrophilum which produces acute septicemic infection in salmonids and few other species [9][10]. Flavobacteriu ...
Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection
... Interventions for Tuberculosis Control and Elimination, IUATLD 2002 Interventions for Tuberculosis Control and Elimination, IUATLD 2002 ...
... Interventions for Tuberculosis Control and Elimination, IUATLD 2002 Interventions for Tuberculosis Control and Elimination, IUATLD 2002 ...
GIARDIASIS HISTORY Giardiasis is known by its commonly called
... survive outside the body. They cysts however, can. The cysts have been found to live for long periods of time outside the body. They can live for months in lower temperatures and only a few days in warmer temperatures. Cysts often contaminate river, pond or lake water because they have been known to ...
... survive outside the body. They cysts however, can. The cysts have been found to live for long periods of time outside the body. They can live for months in lower temperatures and only a few days in warmer temperatures. Cysts often contaminate river, pond or lake water because they have been known to ...
Acute_Pharyngitis
... Occurs 1-2 weeks after untreated GAS throat or 2-4 weeks after a skin infection (impetigo) Most common in ages 6-10 Symptoms: decreased urine output rust-colored urine (or gross hematuria) generalized edema Rx: antibiotics, BP meds, diuretics as indicated Referral to nephrology Resolves over weeks t ...
... Occurs 1-2 weeks after untreated GAS throat or 2-4 weeks after a skin infection (impetigo) Most common in ages 6-10 Symptoms: decreased urine output rust-colored urine (or gross hematuria) generalized edema Rx: antibiotics, BP meds, diuretics as indicated Referral to nephrology Resolves over weeks t ...
B-Specific tests for syphilis
... They can immobilize T. pallidum when patient's serum is put on living spirochetes suspension. The test is positive when 70% or more of living T. pallidum are immobilized. ...
... They can immobilize T. pallidum when patient's serum is put on living spirochetes suspension. The test is positive when 70% or more of living T. pallidum are immobilized. ...
REVIEWS
... uman hunter/gatherer populations currently suffer, and presumably have suffered for millions of years, from infectious diseases similar or identical to diseases of other wild primate populations. However, the most important infectious diseases of modern food-producing human populations also include ...
... uman hunter/gatherer populations currently suffer, and presumably have suffered for millions of years, from infectious diseases similar or identical to diseases of other wild primate populations. However, the most important infectious diseases of modern food-producing human populations also include ...
Bird flu - European Lung Foundation
... What can be done to prevent or treat H5N1 bird flu? Unfortunately, the current flu vaccine that many people take each year does not protect against bird flu and there is no vaccine currently available for bird flu. Anti-viral drugs can be used for bird flu, for example oseltamivir (known as Tamiflu® ...
... What can be done to prevent or treat H5N1 bird flu? Unfortunately, the current flu vaccine that many people take each year does not protect against bird flu and there is no vaccine currently available for bird flu. Anti-viral drugs can be used for bird flu, for example oseltamivir (known as Tamiflu® ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.