Declarative Programming
... - A static-scoped functional language with syntax that is closer to Pascal than to LISP - Uses type declarations, but also does type inferencing to determine the types of undeclared variables (See Chapter 4) - It is strongly typed (whereas Scheme is essentially typeless) and has no type coercions - ...
... - A static-scoped functional language with syntax that is closer to Pascal than to LISP - Uses type declarations, but also does type inferencing to determine the types of undeclared variables (See Chapter 4) - It is strongly typed (whereas Scheme is essentially typeless) and has no type coercions - ...
Functional Paradigm
... – The notions of variable, assignment and (non recursive) looping are NOT part of the ‘pure’ functional programming model • Functional paradigm seen by some as a more reliable paradigm for software design than the imperative paradigm ...
... – The notions of variable, assignment and (non recursive) looping are NOT part of the ‘pure’ functional programming model • Functional paradigm seen by some as a more reliable paradigm for software design than the imperative paradigm ...
Functional programming
... Pro: promotes building more complex functions from other functions that serve as building blocks (component reuse) Pro: behavior of functions defined by the values of input arguments ...
... Pro: promotes building more complex functions from other functions that serve as building blocks (component reuse) Pro: behavior of functions defined by the values of input arguments ...
CS 170 * Intro to Programming for Scientists and Engineers
... • A mid-1970s dialect of LISP, designed to be a cleaner, ...
... • A mid-1970s dialect of LISP, designed to be a cleaner, ...
Functional Programming: Introduction Introduction (Cont.)
... Pure Functional Languages • When all functions are pure, referential transparency and the manifest interface principle are upheld, and thus: – No side-effects, rograms are much easier to formally analyze a) Once we know the local behaviors of functions, we can reason about the system in terms of ind ...
... Pure Functional Languages • When all functions are pure, referential transparency and the manifest interface principle are upheld, and thus: – No side-effects, rograms are much easier to formally analyze a) Once we know the local behaviors of functions, we can reason about the system in terms of ind ...
LISP
... are bound variables, and all the other variables that appear in the body of the function are free variables. When a function is called any bindings that a bound variable may have in the global environment are saved and the variable is rebound to the calling parameter. After the function has complete ...
... are bound variables, and all the other variables that appear in the body of the function are free variables. When a function is called any bindings that a bound variable may have in the global environment are saved and the variable is rebound to the calling parameter. After the function has complete ...
scheme1 - Computer Science and Electrical Engineering
... • S-expression as the universal data type – either at atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representation of Data & Cod ...
... • S-expression as the universal data type – either at atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representation of Data & Cod ...
Chapter 11 slides
... well-defined, so applicative order can be used • A non-strict language does not require all arguments to be well-defined; it requires normal-order evaluation ...
... well-defined, so applicative order can be used • A non-strict language does not require all arguments to be well-defined; it requires normal-order evaluation ...
Functions, recursion and lists
... Computer programs can write or manipulate other programs (or themselves) as their data If can modify themselves --- reflective programming Lisp program can be represented using Lisp atoms and lists ...
... Computer programs can write or manipulate other programs (or themselves) as their data If can modify themselves --- reflective programming Lisp program can be represented using Lisp atoms and lists ...
15. Functional Programming
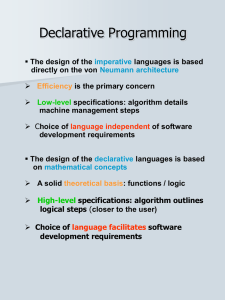
... relatively unconcerned with the architecture of the machines on which programs will run ...
... relatively unconcerned with the architecture of the machines on which programs will run ...
Introduction to Emacs and Emacs lisp
... List can have number in it e.g. (+ 2 2) In Lisp, both data and programs are represented the same way which are both lists of words, numbers, or other lists, separated by whitespace and surrounded by parentheses. E.g.'(this list has (a list inside of it)) ...
... List can have number in it e.g. (+ 2 2) In Lisp, both data and programs are represented the same way which are both lists of words, numbers, or other lists, separated by whitespace and surrounded by parentheses. E.g.'(this list has (a list inside of it)) ...
This article discusses the programming language LISP. The
... many dialects that did not inter-operate came into existence. The two major dialects were MACLISP and INTERLISP. Consequently, in 1984 Guy Steele with help from a large number of Lispers created the book Common Lisp. The Language. A second edition came out in 1990 [7]. In 1994 Common Lisp was standa ...
... many dialects that did not inter-operate came into existence. The two major dialects were MACLISP and INTERLISP. Consequently, in 1984 Guy Steele with help from a large number of Lispers created the book Common Lisp. The Language. A second edition came out in 1990 [7]. In 1994 Common Lisp was standa ...
COS_470-Practice
... then the function returns a list constructed by num and the list nums which constructor will you use? ...
... then the function returns a list constructed by num and the list nums which constructor will you use? ...
PLD VII Haddad
... i l semantics i – Simple syntax – Inefficient execution – Programs can automatically be made concurrent ...
... i l semantics i – Simple syntax – Inefficient execution – Programs can automatically be made concurrent ...
15. Functional Programming
... In an FPL, variables are not necessary, as is the case in mathematics ...
... In an FPL, variables are not necessary, as is the case in mathematics ...
scheme1
... LISP Features • S-expression as the universal data type – either as atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representatio ...
... LISP Features • S-expression as the universal data type – either as atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representatio ...
Fall 2000 Final Exam answers
... 8. Lisp passes integers by ___value__, but passes lists by __reference___. 9. J.A. Robinson invented __resolution__, which is the basis for Prolog. 10. Prolog's unique control structure called __backtracking_ allows it to find all answers for a _goal____. 11. Prolog variables must start with a __cap ...
... 8. Lisp passes integers by ___value__, but passes lists by __reference___. 9. J.A. Robinson invented __resolution__, which is the basis for Prolog. 10. Prolog's unique control structure called __backtracking_ allows it to find all answers for a _goal____. 11. Prolog variables must start with a __cap ...
LISP:Power and Elegance in ONE
... Russell, figured out a way to translate the eval function into machine language. “Steve Russell said, look, why don’t I program this eval… and I said to him, ho, ho, you’re confusing theory with practice, this eval is intended for reading, not for computing, But he went ahead and did it. That is, he ...
... Russell, figured out a way to translate the eval function into machine language. “Steve Russell said, look, why don’t I program this eval… and I said to him, ho, ho, you’re confusing theory with practice, this eval is intended for reading, not for computing, But he went ahead and did it. That is, he ...
scheme1 - Department of Computer Science and Electrical
... • S-expression as the universal data type – either at atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representation of Data & Cod ...
... • S-expression as the universal data type – either at atom (e.g., number, symbol) or a list of atoms or sublists • Functional Programming Style – computation done by applying functions to arguments, functions are first class objects, minimal use of side-effects • Uniform Representation of Data & Cod ...
1 Introduction 2 An Interpreter
... the major data structures of the language. Lisp source code itself is made up of lists. As a result, Lisp programs can manipulate source code as a data structure, giving rise to the macro systems that allow programmers to create new syntax or even new domain-specific programming languages embedded i ...
... the major data structures of the language. Lisp source code itself is made up of lists. As a result, Lisp programs can manipulate source code as a data structure, giving rise to the macro systems that allow programmers to create new syntax or even new domain-specific programming languages embedded i ...
4.6 Lisp - University of Hawaii
... – Designed to be a cleaner and simpler version of LISP – Uses only static scoping – Functions are first-class entities • Can be the values of expressions and elements of lists • Can be assigned to variables and passed as parameters ...
... – Designed to be a cleaner and simpler version of LISP – Uses only static scoping – Functions are first-class entities • Can be the values of expressions and elements of lists • Can be assigned to variables and passed as parameters ...
Document
... LISP definitions of the primitives. Use only the built-in LISP functions listed above. 2. Load your primitives file and test each function thoroughly 3. Create a second file using a text editor that contains the LISP definitions of the functionals. Note: You do not have define composition or conditi ...
... LISP definitions of the primitives. Use only the built-in LISP functions listed above. 2. Load your primitives file and test each function thoroughly 3. Create a second file using a text editor that contains the LISP definitions of the functionals. Note: You do not have define composition or conditi ...
TEKCOMMON LISP PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE - Wirfs
... language an appropriate candidate for expert systems, natural language interfaces, and all types of symbolic programming. Tek Common Lisp goes beyond the specifications of the language to provide; ■ On-line documentation ■ User-definable error handler ...
... language an appropriate candidate for expert systems, natural language interfaces, and all types of symbolic programming. Tek Common Lisp goes beyond the specifications of the language to provide; ■ On-line documentation ■ User-definable error handler ...