Maimonides` The Guide for the Perplexed is quite possibly his most
... understand how he translates the heavy material of the Guide to less philosophically attuned individuals. So now we turn to Maimonides’ famed Epistle to Yemen. Written as a response, or possibly series of responsa, to Rabbi Jacob ben Nethan’el al-Fayyumi, the Epistle addresses a legendary Jewish com ...
... understand how he translates the heavy material of the Guide to less philosophically attuned individuals. So now we turn to Maimonides’ famed Epistle to Yemen. Written as a response, or possibly series of responsa, to Rabbi Jacob ben Nethan’el al-Fayyumi, the Epistle addresses a legendary Jewish com ...
File - TLCC Studies of Religion 2015
... much Jewish teaching. The extent of the effect of his contributions is evident in that he is held in high acclaim by all strands of Judaism. Moses Maimonides was born in Cordoba in Spain 1135. At his time, Spain was dominated by Islamic culture and religion and Jews were considered to be second clas ...
... much Jewish teaching. The extent of the effect of his contributions is evident in that he is held in high acclaim by all strands of Judaism. Moses Maimonides was born in Cordoba in Spain 1135. At his time, Spain was dominated by Islamic culture and religion and Jews were considered to be second clas ...
Moses Maimonides - Year 11-12 Studies of Religion 2Unit 2013-4
... - He said it would guide people in every single situation ! - He said that just by looking at the Torah and his book, people would be able to understand and they wouldn’t have to spend time going through the Talmud! - Rabbi’s did not take this well.! - Reaction was so bad that some people burnt his ...
... - He said it would guide people in every single situation ! - He said that just by looking at the Torah and his book, people would be able to understand and they wouldn’t have to spend time going through the Talmud! - Rabbi’s did not take this well.! - Reaction was so bad that some people burnt his ...
book review
... Prior to Maimonides, Judaism had little by way of dogma. Jews were expected to believe in one God and to follow the Torah's commandments, but no list of beliefs defined Judaism. But Maimonides' quest to delineate Jewish belief, as Mr. Halbertal explains, wasn't some philosophical exercise but a hist ...
... Prior to Maimonides, Judaism had little by way of dogma. Jews were expected to believe in one God and to follow the Torah's commandments, but no list of beliefs defined Judaism. But Maimonides' quest to delineate Jewish belief, as Mr. Halbertal explains, wasn't some philosophical exercise but a hist ...
Summary Points
... Within this Commentary Maimonides formulated the thirteen principles of faith which is recognised as a creed for Judaism. Commentary on the Mishnah was written in Arabic - easily accessible to Jews living in Muslim areas. Mishneh Torah - code of Jewish law - fourteen books written in Hebrew - in a s ...
... Within this Commentary Maimonides formulated the thirteen principles of faith which is recognised as a creed for Judaism. Commentary on the Mishnah was written in Arabic - easily accessible to Jews living in Muslim areas. Mishneh Torah - code of Jewish law - fourteen books written in Hebrew - in a s ...
Explain rambam contribution
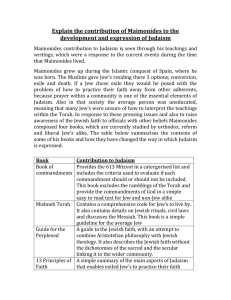
... development and expression of Judaism Maimonides contribution to Judaism is seen through his teachings and writings, which were a response to the current events during the time that Maimonides lived. Maimonides grew up during the Islamic conquest of Spain, where he was born. The Muslims gave Jew’s r ...
... development and expression of Judaism Maimonides contribution to Judaism is seen through his teachings and writings, which were a response to the current events during the time that Maimonides lived. Maimonides grew up during the Islamic conquest of Spain, where he was born. The Muslims gave Jew’s r ...
The Philosophy of Maimonides
... God in Scripture should be understood literally. According to Maimonides, this would be an error. In his view, such depictions are meant to be understood figuratively. Otherwise, one would incorrectly conclude that God is a corporeal being. Was Maimonides correct? Does Scripture teach that God is in ...
... God in Scripture should be understood literally. According to Maimonides, this would be an error. In his view, such depictions are meant to be understood figuratively. Otherwise, one would incorrectly conclude that God is a corporeal being. Was Maimonides correct? Does Scripture teach that God is in ...
Maimonides

Moshe ben Maimon (Hebrew: משה בן-מימון), or Mūsā ibn Maymūn (Arabic: موسى بن ميمون), acronymed Rambam (/ˈrɑːmbɑːm/; Hebrew: רמב""ם – for ""Rabbeinu Moshe Ben Maimon"", ""Our Rabbi/Teacher Moses Son of Maimon""), and Latinized Moses Maimonides (/maɪˈmɒnɪdiːz/ my-MON-i-deez), a preeminent medieval Sephardic Jewish philosopher and astronomer, became one of the most prolific and influential Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages. Born in Córdoba (present-day Spain), Almoravid Empire on Passover Eve, 1135 or 1138, he died in Egypt on December 12, 1204, whence his body was taken to the lower Galilee and buried in Tiberias. He worked as a rabbi, physician, and philosopher in Morocco and Egypt.Although most Jews greeted his writings on Jewish law and ethics with acclaim and gratitude, even as far off as Iraq and Yemen, and although he rose to become the revered head of the Jewish community in Egypt, there were also vociferous critics of some of his writings, particularly in Spain. Nonetheless, he was posthumously acknowledged as among the foremost rabbinical arbiters and philosophers in Jewish history, and his copious work comprises a cornerstone of Jewish scholarship. His fourteen-volume Mishneh Torah still carries significant canonical authority as a codification of Talmudic law. In the Yeshiva world, he is called sometimes ""haNesher haGadol"" (the great eagle) in recognition of his outstanding status as a bona fide exponent of the Oral Torah.Aside from being revered by Jewish historians, Maimonides also figures very prominently in the history of Islamic and Arab sciences and is mentioned extensively in studies. Influenced by Avicenna (c. 980 – 1037), Averroes (1126–1198) and Al-Farabi (ca. 872–950/951), he in his turn influenced other prominent Arab and Muslim philosophers and scientists. He became a prominent philosopher and polymath in both the Jewish and Islamic worlds.