An Unshunted Comparator as a Device for Quantum Measurements
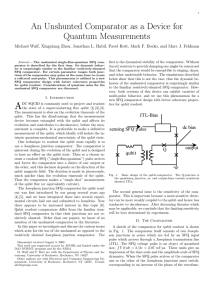
... Of course, any noise blurs this decision. As the comparator bias is changed, the transition from zero to full probability of output is not sharp. Assuming linear dynamics this transition is given by the error function (erf+1)/2 (the erf is simply the integrated Gaussian) and even though the comparat ...
... Of course, any noise blurs this decision. As the comparator bias is changed, the transition from zero to full probability of output is not sharp. Assuming linear dynamics this transition is given by the error function (erf+1)/2 (the erf is simply the integrated Gaussian) and even though the comparat ...
Spin Foam Models of Quantum Spacetime
... Relativity in terms of the Ashtekar variables [12]. In recent years many different approaches on the non-perturbative and background-independent side have been converging to the formalism of the so-called spin foams [13, 14, 15], and this class of models in the subject of this thesis. Why do we want ...
... Relativity in terms of the Ashtekar variables [12]. In recent years many different approaches on the non-perturbative and background-independent side have been converging to the formalism of the so-called spin foams [13, 14, 15], and this class of models in the subject of this thesis. Why do we want ...
The density-matrix renormalization group in the age of matrix
... In fact, both questions are intimately related: as was realized quite soon, DMRG is only moderately successful when applied to two-dimensional lattices: while relatively small systems can be studied with high accuracy[21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28], the amount of numerical resources needed essentia ...
... In fact, both questions are intimately related: as was realized quite soon, DMRG is only moderately successful when applied to two-dimensional lattices: while relatively small systems can be studied with high accuracy[21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28], the amount of numerical resources needed essentia ...
Full text in PDF form
... not attempt to define an information content of a physical system as a whole, but rather we wish to set appropriate measures of uncertainty and information for concrete pure states of a quantum system. A particular quantum state should not be misinterpreted to provide a complete description of the c ...
... not attempt to define an information content of a physical system as a whole, but rather we wish to set appropriate measures of uncertainty and information for concrete pure states of a quantum system. A particular quantum state should not be misinterpreted to provide a complete description of the c ...
University of Florida - University of Missouri
... ・The CCSD model is one of the most reliable quantum chemical methods. However, it is often necessary to incorporate higher order cluster operators than connected doubles to achieve the chemical accuracy. ・ CCSDT, CCSDTQ, and CCSDTQP are implemented and they produce highly accurate computational resu ...
... ・The CCSD model is one of the most reliable quantum chemical methods. However, it is often necessary to incorporate higher order cluster operators than connected doubles to achieve the chemical accuracy. ・ CCSDT, CCSDTQ, and CCSDTQP are implemented and they produce highly accurate computational resu ...
IBS for CLIC damping ring/Lattice design for IBS - Indico
... – Quantum lower scattering angle limit must be included in IBS process – However, CLIC and VEPP-4M Touschek calculations show that considering the quantum limit of minimal scattering angle instead of the classical one does not change notably the results » This seems to be true for all existing and d ...
... – Quantum lower scattering angle limit must be included in IBS process – However, CLIC and VEPP-4M Touschek calculations show that considering the quantum limit of minimal scattering angle instead of the classical one does not change notably the results » This seems to be true for all existing and d ...
∗ ∗
... if one is interested in statistical predictions for measurement outcomes only, and does not worry as to what these outcomes or probabilities refer to, then quantum mechanics is a rewarding subject of study. Nonetheless, I do think that quantum mechanics is not just problematic for a realist, and in ...
... if one is interested in statistical predictions for measurement outcomes only, and does not worry as to what these outcomes or probabilities refer to, then quantum mechanics is a rewarding subject of study. Nonetheless, I do think that quantum mechanics is not just problematic for a realist, and in ...
Quantum groups: A survey of de nitions, motivations, and results
... been to write this in a relatively small space (long works are usually too daunting) and with this in mind I have chosen not to include any proofs. In many cases, providing a full proof would require introducing and developing some fairly sophisticated tools. My main focus in these notes is to give ...
... been to write this in a relatively small space (long works are usually too daunting) and with this in mind I have chosen not to include any proofs. In many cases, providing a full proof would require introducing and developing some fairly sophisticated tools. My main focus in these notes is to give ...
A Few Good Examples why to Refute Classical Logic in Quantum
... Lovre Grisogono Mateo Paulišić University of Zagreb Faculty of Science Department of Physics ...
... Lovre Grisogono Mateo Paulišić University of Zagreb Faculty of Science Department of Physics ...
Nonlinear Dynamics - CAMTP
... The character of our Schools/Conferences is strongly international, we have invited lecturers and participants from all over the world, from almost all continents, and the national component of the Slovenian participants in total (invitees and others) is about 10%. They are strongly interdisciplinar ...
... The character of our Schools/Conferences is strongly international, we have invited lecturers and participants from all over the world, from almost all continents, and the national component of the Slovenian participants in total (invitees and others) is about 10%. They are strongly interdisciplinar ...
M15/07
... weak* topology on the set of regular Borel probability measures. Instead, Dobrushin [24] introduced a notion of “metrically tights” sets of probability measures, on which the restriction of the Monge-Kantorovich metric does induces the weak* topology. Generalizing these ideas is not a straightforwar ...
... weak* topology on the set of regular Borel probability measures. Instead, Dobrushin [24] introduced a notion of “metrically tights” sets of probability measures, on which the restriction of the Monge-Kantorovich metric does induces the weak* topology. Generalizing these ideas is not a straightforwar ...
Graphene plasmonics: A platform for strong light
... are well defined. At larger energies above the plasmon cutoff, one recovers the same rate as in undoped graphene, characterized by a 1/z 6 dependence at large separations (see inset). ...
... are well defined. At larger energies above the plasmon cutoff, one recovers the same rate as in undoped graphene, characterized by a 1/z 6 dependence at large separations (see inset). ...
Quantum key distribution
Quantum key distribution (QKD) uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure communication. It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is often incorrectly called quantum cryptography, as it is the most well known example of the group of quantum cryptographic tasks.An important and unique property of quantum key distribution is the ability of the two communicating users to detect the presence of any third party trying to gain knowledge of the key. This results from a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the process of measuring a quantum system in general disturbs the system. A third party trying to eavesdrop on the key must in some way measure it, thus introducing detectable anomalies. By using quantum superpositions or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be implemented which detects eavesdropping. If the level of eavesdropping is below a certain threshold, a key can be produced that is guaranteed to be secure (i.e. the eavesdropper has no information about it), otherwise no secure key is possible and communication is aborted.The security of encryption that uses quantum key distribution relies on the foundations of quantum mechanics, in contrast to traditional public key cryptography which relies on the computational difficulty of certain mathematical functions, and cannot provide any indication of eavesdropping at any point in the communication process, or any mathematical proof as to the actual complexity of reversing the one-way functions used. QKD has provable security based on information theory, and forward secrecy.Quantum key distribution is only used to produce and distribute a key, not to transmit any message data. This key can then be used with any chosen encryption algorithm to encrypt (and decrypt) a message, which can then be transmitted over a standard communication channel. The algorithm most commonly associated with QKD is the one-time pad, as it is provably secure when used with a secret, random key. In real world situations, it is often also used with encryption using symmetric key algorithms like the Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm. In the case of QKD this comparison is based on the assumption of perfect single-photon sources and detectors, that cannot be easily implemented.