Slide 1
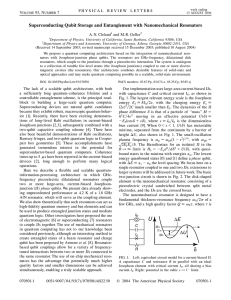
... 2) The proposed single-qubit operations and local measurements should allow testing Bell’s inequality with a pair of capacitively coupled Josephson qubits. ...
... 2) The proposed single-qubit operations and local measurements should allow testing Bell’s inequality with a pair of capacitively coupled Josephson qubits. ...
Distances in Probability Space and the Statistical Complexity
... considerations in describing dynamic features. Why is this of importance? Because (i) usually, statistical approaches are easier to implement than solving equations of motion and (ii) in many cases, they offer the only way of dealing with otherwise intractable problems. 1.1. Meaning of the Concept C ...
... considerations in describing dynamic features. Why is this of importance? Because (i) usually, statistical approaches are easier to implement than solving equations of motion and (ii) in many cases, they offer the only way of dealing with otherwise intractable problems. 1.1. Meaning of the Concept C ...
Topological quantum memory
... is put to optimal use, error recovery succeeds with a probability that approaches one in the limit of a large code block, if and only if both phase errors and bit-flip errors occur with a probability per qubit less than about 11%. In the more realistic case where syndrome measurements are imperfect, ...
... is put to optimal use, error recovery succeeds with a probability that approaches one in the limit of a large code block, if and only if both phase errors and bit-flip errors occur with a probability per qubit less than about 11%. In the more realistic case where syndrome measurements are imperfect, ...
1 Invariance and quantization of charges and currents
... But there is yet another sense in which electromagnetism and quantum mechanics can combine to produce effects – sometimes surprising and beautiful effects – at the macroscopic scale, especially for insulating systems. The quintessential example of this is the quantum Hall effect, discovered in 1980, ...
... But there is yet another sense in which electromagnetism and quantum mechanics can combine to produce effects – sometimes surprising and beautiful effects – at the macroscopic scale, especially for insulating systems. The quintessential example of this is the quantum Hall effect, discovered in 1980, ...
Read PDF - Physics (APS) - American Physical Society
... can further perturb the system [1]. In optomechanics [2], coherent light fields serve as the intermediary between the fragile mechanical states and our inherently classical world by exerting radiation pressure forces and extracting mechanical information. Here, we engineer a microwave cavity optomec ...
... can further perturb the system [1]. In optomechanics [2], coherent light fields serve as the intermediary between the fragile mechanical states and our inherently classical world by exerting radiation pressure forces and extracting mechanical information. Here, we engineer a microwave cavity optomec ...
Quantum control of a Landau-quantized two
... discussed above, i.e., π difference in the arrival phase, which is again described well via optical Bloch equations. The agreement between experiment and theory highlights the striking fact that a Landau-quantized 2DEG in a weak coherent THz field behaves in exactly the same manner as a two-level at ...
... discussed above, i.e., π difference in the arrival phase, which is again described well via optical Bloch equations. The agreement between experiment and theory highlights the striking fact that a Landau-quantized 2DEG in a weak coherent THz field behaves in exactly the same manner as a two-level at ...
Topological quantum computation
... more) spatial dimensions and also in one dimension. But in between these two dull cases, in two dimensions, a remarkably rich variety of types of particle statistics are possible, so rich that we have far to go before we can give a useful classification of all of the possibilities. Indistinguishable ...
... more) spatial dimensions and also in one dimension. But in between these two dull cases, in two dimensions, a remarkably rich variety of types of particle statistics are possible, so rich that we have far to go before we can give a useful classification of all of the possibilities. Indistinguishable ...
Quantum key distribution
Quantum key distribution (QKD) uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure communication. It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is often incorrectly called quantum cryptography, as it is the most well known example of the group of quantum cryptographic tasks.An important and unique property of quantum key distribution is the ability of the two communicating users to detect the presence of any third party trying to gain knowledge of the key. This results from a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the process of measuring a quantum system in general disturbs the system. A third party trying to eavesdrop on the key must in some way measure it, thus introducing detectable anomalies. By using quantum superpositions or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be implemented which detects eavesdropping. If the level of eavesdropping is below a certain threshold, a key can be produced that is guaranteed to be secure (i.e. the eavesdropper has no information about it), otherwise no secure key is possible and communication is aborted.The security of encryption that uses quantum key distribution relies on the foundations of quantum mechanics, in contrast to traditional public key cryptography which relies on the computational difficulty of certain mathematical functions, and cannot provide any indication of eavesdropping at any point in the communication process, or any mathematical proof as to the actual complexity of reversing the one-way functions used. QKD has provable security based on information theory, and forward secrecy.Quantum key distribution is only used to produce and distribute a key, not to transmit any message data. This key can then be used with any chosen encryption algorithm to encrypt (and decrypt) a message, which can then be transmitted over a standard communication channel. The algorithm most commonly associated with QKD is the one-time pad, as it is provably secure when used with a secret, random key. In real world situations, it is often also used with encryption using symmetric key algorithms like the Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm. In the case of QKD this comparison is based on the assumption of perfect single-photon sources and detectors, that cannot be easily implemented.