Figure 8-12 Responses of the Inflation Rate (p)
... continuous inflation. Along the SP curve, the economy is not in a long run equilibrium because the price level is constantly racing ahead of the nominal wage rage. There will be continuous pressures for higher wages. As labor contracts fail to anticipate further inflation, and as a result they fai ...
... continuous inflation. Along the SP curve, the economy is not in a long run equilibrium because the price level is constantly racing ahead of the nominal wage rage. There will be continuous pressures for higher wages. As labor contracts fail to anticipate further inflation, and as a result they fai ...
Fiscal Reaction Function: Evidences from CESEE countries 4
... states and countries out of EU. As some of CESEE countries became Eurozone members in recent years, their decisions on primary and budget balance levels were influenced by Maastricht criteria for Eurozone admission (Mencinger and Aristovnik, 2013). In addition, NMS are generally considered to be mor ...
... states and countries out of EU. As some of CESEE countries became Eurozone members in recent years, their decisions on primary and budget balance levels were influenced by Maastricht criteria for Eurozone admission (Mencinger and Aristovnik, 2013). In addition, NMS are generally considered to be mor ...
The Composition of Capital Inflows When Emerging
... firms. Domestic agents take the world interest rate as given. There are two kinds of foreign agents: the aforementioned multinational firms who search to purchase domestic firms and the global credit market of one-period bonds that determines the world real interest rate. Unlike the domestic firms t ...
... firms. Domestic agents take the world interest rate as given. There are two kinds of foreign agents: the aforementioned multinational firms who search to purchase domestic firms and the global credit market of one-period bonds that determines the world real interest rate. Unlike the domestic firms t ...
Exposure to international crises: trade vs. financial contagion
... countries’ recoveries over the 2008-2014 period. The separation of the parameters governing shocks to these channels does not mean that there is no interaction between these two aspects of the economy. The important feature is that the model parameters for each channel can be independently matched ...
... countries’ recoveries over the 2008-2014 period. The separation of the parameters governing shocks to these channels does not mean that there is no interaction between these two aspects of the economy. The important feature is that the model parameters for each channel can be independently matched ...
L7-9InstrumentsMABP
... Suffered recession, but equilibrated BP at point A. ITF-220 - Prof.J.Frankel ...
... Suffered recession, but equilibrated BP at point A. ITF-220 - Prof.J.Frankel ...
Sample
... change, so do the prices of exports and imports. Countries whose exchange rates are depreciating will find their exports becoming more price competitive and their imports relatively more expensive. If a seller of products or services expects payment for exports in any denomination other than their h ...
... change, so do the prices of exports and imports. Countries whose exchange rates are depreciating will find their exports becoming more price competitive and their imports relatively more expensive. If a seller of products or services expects payment for exports in any denomination other than their h ...
Output Response to Government Spending: Evidence from New International Military Spending Data
... observations and to sample-composition issues—qualitatively, our main conclusions remain unaffected. Third, although a country likely increases its geopolitical influence as it becomes richer, we doubt that this channel plays a significant role at an annual frequency. Finally, any remaining endogene ...
... observations and to sample-composition issues—qualitatively, our main conclusions remain unaffected. Third, although a country likely increases its geopolitical influence as it becomes richer, we doubt that this channel plays a significant role at an annual frequency. Finally, any remaining endogene ...
Chapter 11: The Money Market and the LM Curve Copyright MHHE
... How are we going to capture these complexities, and yet still manage to draw simple diagrams? Consider placing the nominal interest rate i on the vertical axis and total income Y on the horizontal axis. For each possible value of Y on the horizontal axis, plot the point whose vertical axis value is ...
... How are we going to capture these complexities, and yet still manage to draw simple diagrams? Consider placing the nominal interest rate i on the vertical axis and total income Y on the horizontal axis. For each possible value of Y on the horizontal axis, plot the point whose vertical axis value is ...
RABE-DISSERTATION-2015 - JScholarship
... Thus, at the heart of mercantilism lies the belief that the exportation of goods and services is intrinsically desirable and should be actively encouraged. In other words, the accumulation of gold that was the principal objective of the “mercantilism” of the 19th century has been supplanted by the ...
... Thus, at the heart of mercantilism lies the belief that the exportation of goods and services is intrinsically desirable and should be actively encouraged. In other words, the accumulation of gold that was the principal objective of the “mercantilism” of the 19th century has been supplanted by the ...
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... • The dynamic model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply (DAD-DAS) determines both – real GDP (Y), and – the inflation rate (π) ...
... • The dynamic model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply (DAD-DAS) determines both – real GDP (Y), and – the inflation rate (π) ...
The Role of Government: Impact on Macroeconomy
... 2.2 Economic growth and public policy What can government do to raise productivity and living standards? 2.2.1 Importance of savings and investment Because capital is a produced factor of production, a society can change the amount of capital it has. One way to raise future productivity is to invest ...
... 2.2 Economic growth and public policy What can government do to raise productivity and living standards? 2.2.1 Importance of savings and investment Because capital is a produced factor of production, a society can change the amount of capital it has. One way to raise future productivity is to invest ...
Mankiw: Brief Principles of Macroeconomics, Second Edition
... The Importance of Interest Rates • For the US economy the interest rate effect on the aggregate demand is more significant than the wealth effect and exchange rate effect. – Money wealth is a very small percentage of total wealth. Price level changes will not affect the total wealth that much. – Ex ...
... The Importance of Interest Rates • For the US economy the interest rate effect on the aggregate demand is more significant than the wealth effect and exchange rate effect. – Money wealth is a very small percentage of total wealth. Price level changes will not affect the total wealth that much. – Ex ...
Copyright © 2001 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
... Inflation tends to change relatively slowly as long as the economy is at full employment and there are no external shocks to the price level ...
... Inflation tends to change relatively slowly as long as the economy is at full employment and there are no external shocks to the price level ...
Faculty of Islamic Economics and Business
... The rate of return for constant growth stock consists of two components which are dividend yield and capital gains yield. The former can be thought of as the rate of return for a stock whose dividend is constant, an investor who purchased a share of common stock for price , and who received constant ...
... The rate of return for constant growth stock consists of two components which are dividend yield and capital gains yield. The former can be thought of as the rate of return for a stock whose dividend is constant, an investor who purchased a share of common stock for price , and who received constant ...
CHAPTER 16: Monetary Policy
... Why Did Homebuilder Toll Brothers, Inc. Prosper during the 2001 Recession? ...
... Why Did Homebuilder Toll Brothers, Inc. Prosper during the 2001 Recession? ...
Demand-Pull Inflation
... Lower than anticipated inflation raises the real wage rate and workers gain at the expense of employers. Higher than anticipated inflation lowers the real wage rate, increases the quantity of labor demanded, makes jobs easier to find, and lowers the unemployment rate. Lower than anticipated inflatio ...
... Lower than anticipated inflation raises the real wage rate and workers gain at the expense of employers. Higher than anticipated inflation lowers the real wage rate, increases the quantity of labor demanded, makes jobs easier to find, and lowers the unemployment rate. Lower than anticipated inflatio ...
Fiscal and monetary coordination, Reserve Bank of New Zealand
... monetary and fiscal policy include that: • the Reserve Bank, as the monetary authority, has ‘operational’ independence to pursue its statutorily imposed goal of price stability; • the Reserve Bank, therefore, is required to respond to developments in the economy – including changes in fiscal policy ...
... monetary and fiscal policy include that: • the Reserve Bank, as the monetary authority, has ‘operational’ independence to pursue its statutorily imposed goal of price stability; • the Reserve Bank, therefore, is required to respond to developments in the economy – including changes in fiscal policy ...
Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation
... (d) Increase union strength in the economy. Answer: C Level of difficulty: 1 Section: 12.2 ...
... (d) Increase union strength in the economy. Answer: C Level of difficulty: 1 Section: 12.2 ...
Chapter 16 - Central Web Server 2
... A major change in monetary policy allowed the Bank of England to be free to pursue its policy goals without direct political control. An economist studied how the British bond market reacted to the policy change by comparing the interest rates changes on two types of long-term bonds: bonds that are ...
... A major change in monetary policy allowed the Bank of England to be free to pursue its policy goals without direct political control. An economist studied how the British bond market reacted to the policy change by comparing the interest rates changes on two types of long-term bonds: bonds that are ...
Money and Inflation
... Friedman) concludes that changes in aggregate spending are determined primarily by the money supply. • Keynesian analysis indicates that high inflation cannot be driven by fiscal policy only. • But both viewpoints tell us that high inflation can occur only with a high rate of money growth. ...
... Friedman) concludes that changes in aggregate spending are determined primarily by the money supply. • Keynesian analysis indicates that high inflation cannot be driven by fiscal policy only. • But both viewpoints tell us that high inflation can occur only with a high rate of money growth. ...
Document
... (a) in the interest of the United States as a whole and in the interest of computer producing regions of the country. (b) in the interest of United States as a whole but not in the interest of computer producing regions of the country. (c) not in the interest of the United States as a whole but in t ...
... (a) in the interest of the United States as a whole and in the interest of computer producing regions of the country. (b) in the interest of United States as a whole but not in the interest of computer producing regions of the country. (c) not in the interest of the United States as a whole but in t ...
Reflating Japan: Time to Get Unconventional?
... Monetary policy responded with a delay to the recession that followed the real estate crisis of the early 1990s (McCallum, 2003). The BoJ reduced its policy rate so slowly, that real interest rates rose, as inflation turned negative. By the turn of the century the BoJ had cut the policy rate to zero ...
... Monetary policy responded with a delay to the recession that followed the real estate crisis of the early 1990s (McCallum, 2003). The BoJ reduced its policy rate so slowly, that real interest rates rose, as inflation turned negative. By the turn of the century the BoJ had cut the policy rate to zero ...
IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance (IOSR-JEF)
... Another avenue that monetary authorities can fight deflation is to devalue the domestic currency via large open market sales of the domestic currency in order to generate sufficient import price inflation and raising foreign demand for domestic goods and services. However, in Zimbabwe monetary autho ...
... Another avenue that monetary authorities can fight deflation is to devalue the domestic currency via large open market sales of the domestic currency in order to generate sufficient import price inflation and raising foreign demand for domestic goods and services. However, in Zimbabwe monetary autho ...
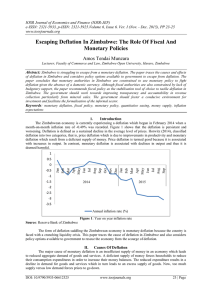
DPEco2.3.4 Low and Stable Rates of Inflation DPEco2.3.4 The
... 2. Monetary policy: mainly in the short run to control demand-pull inflationary pressures higher interest rates to reduce consumer and investment spending. Monetary policy has an effect on costs through the effect of changes in interest rates on the value of the currency. 3. Supply side economic pol ...
... 2. Monetary policy: mainly in the short run to control demand-pull inflationary pressures higher interest rates to reduce consumer and investment spending. Monetary policy has an effect on costs through the effect of changes in interest rates on the value of the currency. 3. Supply side economic pol ...