INFLATION DYNAMICS IN VIETNAM Hien Thi Thu Le
... demand could be because consumers are spending more, perhaps because interest rates have fallen, taxes have been cut or simply because there is a greater level of consumer confidence. Furthermore, it could be because by firms who are investing more under the expectation of future economic growth. It ...
... demand could be because consumers are spending more, perhaps because interest rates have fallen, taxes have been cut or simply because there is a greater level of consumer confidence. Furthermore, it could be because by firms who are investing more under the expectation of future economic growth. It ...
Chapter 11 - Pearson Canada
... that what households and firms expect to see and experience in the future is not affected by what they see and experience today. This is a restrictive assumption. We might expect, for example, that international tensions threatening war in the future may influence trade decisions today. Similarly, n ...
... that what households and firms expect to see and experience in the future is not affected by what they see and experience today. This is a restrictive assumption. We might expect, for example, that international tensions threatening war in the future may influence trade decisions today. Similarly, n ...
modules 31 to 35
... a) Draw an AD/AS model in LR equilibrium b) Draw a money market graph in equilibrium c) Draw a loanable funds market in equilibrium d) List the 3 fiscal policy tools and the 3 monetary policy tools. e) Go back. What should they do to those tools if expansionary policies ...
... a) Draw an AD/AS model in LR equilibrium b) Draw a money market graph in equilibrium c) Draw a loanable funds market in equilibrium d) List the 3 fiscal policy tools and the 3 monetary policy tools. e) Go back. What should they do to those tools if expansionary policies ...
Chapter 29 AS-AD and the Business Cycle
... 2) What is the NBER's definition of recession? Discuss the relationship between the phases of the business cycle, real GDP and unemployment in the context of the United States economy from 1992 to the present. Answer: The NBER defines a recession as a period of significant decline in total output, i ...
... 2) What is the NBER's definition of recession? Discuss the relationship between the phases of the business cycle, real GDP and unemployment in the context of the United States economy from 1992 to the present. Answer: The NBER defines a recession as a period of significant decline in total output, i ...
The Contemporaneous Correlation Between
... The variables included for the United States specification are the natural logs of real GDP, the GDP deflator, the relative price of oil, M1, and the S&P 500; and the levels of the federal funds rate, the ratio of net exports to GDP, the spread between the three month treasury bill rate and ten year ...
... The variables included for the United States specification are the natural logs of real GDP, the GDP deflator, the relative price of oil, M1, and the S&P 500; and the levels of the federal funds rate, the ratio of net exports to GDP, the spread between the three month treasury bill rate and ten year ...
18.6 Problems In Implementing Monetary Policy
... ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Instructors of classes adopting EXPLORING ECONOMICS, Second Edition by Robert L. Sexton as an assigned textbook may reproduce material from this publication for classroom use or in a secure electronic network environment that prevents downloading or reproducing the copyrighted m ...
... ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Instructors of classes adopting EXPLORING ECONOMICS, Second Edition by Robert L. Sexton as an assigned textbook may reproduce material from this publication for classroom use or in a secure electronic network environment that prevents downloading or reproducing the copyrighted m ...
Chapter 25 Aggregate Demand and Supply Analysis
... (b) changes in government spending and taxes, and net exports are important sources of shifts in the aggregate demand curve. (c) changes in consumer or business optimism are not independent sources of shifts in the aggregate demand curve. (d) all of the above are true. Answer: B Question Status: Pre ...
... (b) changes in government spending and taxes, and net exports are important sources of shifts in the aggregate demand curve. (c) changes in consumer or business optimism are not independent sources of shifts in the aggregate demand curve. (d) all of the above are true. Answer: B Question Status: Pre ...
File - MCNEIL ECONOMICS
... that is based on aggregate demand and aggregate supply. This model can be used to explain real domestic output and the level of prices at any point in time and to understand what causes output and the price level to change. The aggregate demand (AD) curve is downsloping. Changes in the price level h ...
... that is based on aggregate demand and aggregate supply. This model can be used to explain real domestic output and the level of prices at any point in time and to understand what causes output and the price level to change. The aggregate demand (AD) curve is downsloping. Changes in the price level h ...
Money, Central Banking in India and International Financial Institutions - I
... had planted and harvested more corn that what he would need.. Goods used in barter are generally in their natural state, in line with the environment conditions and activities developed by the group, corresponding to elementary needs of the group's members. This exchange, however, is not free from d ...
... had planted and harvested more corn that what he would need.. Goods used in barter are generally in their natural state, in line with the environment conditions and activities developed by the group, corresponding to elementary needs of the group's members. This exchange, however, is not free from d ...
Chapter 29(14)
... order to spend their money more rapidly (by shopping more frequently). At still higher anticipated inflation rates, people incur costs by using alternatives for money to conduct transactions. ♦ Tax consequences — anticipated inflation reduces the after-tax return from saving, which decreases saving ...
... order to spend their money more rapidly (by shopping more frequently). At still higher anticipated inflation rates, people incur costs by using alternatives for money to conduct transactions. ♦ Tax consequences — anticipated inflation reduces the after-tax return from saving, which decreases saving ...
chapter 6 - McGraw
... then look at some of the economics that underlie the mechanics. The price-output relation along the aggregate supply curve is built up from the links among wages, prices, employment, and output. The link between unemployment and inflation is called the Phillips curve. We translate between unemployme ...
... then look at some of the economics that underlie the mechanics. The price-output relation along the aggregate supply curve is built up from the links among wages, prices, employment, and output. The link between unemployment and inflation is called the Phillips curve. We translate between unemployme ...
How Has Globalization Affected Inflation?
... currency areas. Is this situation sustainable or does it foreshadow unwelcome inflation surprises in the near future? Some analysts have argued that low and stable inflation reflects more intense global competition, which prevents firms from raising prices and puts downward pressures on wages in man ...
... currency areas. Is this situation sustainable or does it foreshadow unwelcome inflation surprises in the near future? Some analysts have argued that low and stable inflation reflects more intense global competition, which prevents firms from raising prices and puts downward pressures on wages in man ...
12INFLATION*
... 12. If the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward less than expected, a. expectations could not be rational expectations. b. real GDP will be less than potential GDP. c. the real interest rate will be lower than expected. d. the real wage rate will be lower than expected. 13. Which of the following ...
... 12. If the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward less than expected, a. expectations could not be rational expectations. b. real GDP will be less than potential GDP. c. the real interest rate will be lower than expected. d. the real wage rate will be lower than expected. 13. Which of the following ...
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... 17) How does an increase in the price level affect the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded? Answer: An increase in the price level decreases the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded for three reasons. First, it decreases the buying power of money. As a result, people decr ...
... 17) How does an increase in the price level affect the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded? Answer: An increase in the price level decreases the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded for three reasons. First, it decreases the buying power of money. As a result, people decr ...
What Explains Inflation in China?
... Central to current monetary policy in the major advanced economies is price stability, where an increase in the general price level is termed inflation and a decrease deflation. Inflation and deflation distort price signals, leading to inefficient allocation of resources; they also undermine the cre ...
... Central to current monetary policy in the major advanced economies is price stability, where an increase in the general price level is termed inflation and a decrease deflation. Inflation and deflation distort price signals, leading to inefficient allocation of resources; they also undermine the cre ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION II SEMESTER BA ECONOMICS
... regularities must go beyond what is obvious to the producers, consumers, and exchangers themselves. Only in the eighteenth century, most clearly illustrated by the work of Cantillon (1755), the physiocrats, David Hume, and especially Adam Smith, does one find the idea that there are laws to be disco ...
... regularities must go beyond what is obvious to the producers, consumers, and exchangers themselves. Only in the eighteenth century, most clearly illustrated by the work of Cantillon (1755), the physiocrats, David Hume, and especially Adam Smith, does one find the idea that there are laws to be disco ...
NATIONAL
... consumption function with a Bawuol-Tobin model of money demand. Suppose, for example, that consumers receive a constant flow of real income and desire a Income flows to bank accounts, where it is constant flow of consumption. protected from inflation, and consumers withdraw cash at discrete interval ...
... consumption function with a Bawuol-Tobin model of money demand. Suppose, for example, that consumers receive a constant flow of real income and desire a Income flows to bank accounts, where it is constant flow of consumption. protected from inflation, and consumers withdraw cash at discrete interval ...
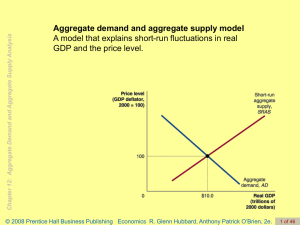
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O'Brien, 2e.
... buy more U.S. goods. •If the dollar depreciates, foreign firms and households will buy more U.S. goods and U.S. firms and households will buy fewer foreign goods. Net exports will rise and the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. ...
... buy more U.S. goods. •If the dollar depreciates, foreign firms and households will buy more U.S. goods and U.S. firms and households will buy fewer foreign goods. Net exports will rise and the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. ...
ECS1601 –SECTION A 1.16 Which of the following statements are
... 2.10 The correct alternative is (2 [2] Correct. Since the gold price is quoted in dollars, an increase in the price of gold means that more dollars will be earned – the supply of dollar increases. 2.11 Which one of the following is most likely to increase the demand for US dollar on the South Afric ...
... 2.10 The correct alternative is (2 [2] Correct. Since the gold price is quoted in dollars, an increase in the price of gold means that more dollars will be earned – the supply of dollar increases. 2.11 Which one of the following is most likely to increase the demand for US dollar on the South Afric ...
Inflation Targeting
... price stability supports economic growth because it allows households and businesses (including export enterprises) to plan ahead and arrive at betterinformed decisions about their consumption, investment, savings and production needs. In the case of export firms, price stability allows them to pric ...
... price stability supports economic growth because it allows households and businesses (including export enterprises) to plan ahead and arrive at betterinformed decisions about their consumption, investment, savings and production needs. In the case of export firms, price stability allows them to pric ...
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... level between periods t − 1 and t. Similarly, t +1 is the percentage change in the p price level that will occur between periods t and t + 1. As of time period t, t +1 p represents a future inflation rate and therefore is not yet known. Note that the subscript on a variable tells us when the variabl ...
... level between periods t − 1 and t. Similarly, t +1 is the percentage change in the p price level that will occur between periods t and t + 1. As of time period t, t +1 p represents a future inflation rate and therefore is not yet known. Note that the subscript on a variable tells us when the variabl ...