Macroeconomic Adjustment Mechanisms in An Oil Based Economy: Saudi Arabia Looney, R.E.
... associated with restoration of equilibrium must, therefore, depend (among other things) on liquidity and the ease of convertibility of other assets. We know that because of Islamic codes and the lack of government debt, there are few financial assets available. Most assets other than cash would be r ...
... associated with restoration of equilibrium must, therefore, depend (among other things) on liquidity and the ease of convertibility of other assets. We know that because of Islamic codes and the lack of government debt, there are few financial assets available. Most assets other than cash would be r ...
A world without inflation
... banks in the late 1970s combined with structural shifts in the global economy, such as globalization, technological innovations and weakening trade union influence, have been key factors behind falling trend inflation in the developed world. Since 2008, this strong disinflationary trend has been com ...
... banks in the late 1970s combined with structural shifts in the global economy, such as globalization, technological innovations and weakening trade union influence, have been key factors behind falling trend inflation in the developed world. Since 2008, this strong disinflationary trend has been com ...
Monetary Policy in Japan: Problems and Solutions
... independence is often cited as a cause for an unusually high inflation rate, about 30%, in 1973-74, in the wake of the first oil crisis. After the inflation of 1973-74, the Bank of Japan had conducted prudent monetary policy, achieving a gradual decline in the inflation rate. Cargill, Hutchison, an ...
... independence is often cited as a cause for an unusually high inflation rate, about 30%, in 1973-74, in the wake of the first oil crisis. After the inflation of 1973-74, the Bank of Japan had conducted prudent monetary policy, achieving a gradual decline in the inflation rate. Cargill, Hutchison, an ...
chapter28
... Some argue that wages do not fall during slack periods and that the economy can get “stuck” at an equilibrium below potential output. In this case, monetary and fiscal policy would be necessary to restore full employment. ...
... Some argue that wages do not fall during slack periods and that the economy can get “stuck” at an equilibrium below potential output. In this case, monetary and fiscal policy would be necessary to restore full employment. ...
File - MCNEIL ECONOMICS
... c. It can raise or lower the discount rate. (1) Raising the discount rate discourages banks from borrowing reserves from the Fed. (2) Lowering the discount rate encourages banks to borrow from the Fed. d. It can auction off to banks the right to borrow reserves for a set period of time (usually 28 d ...
... c. It can raise or lower the discount rate. (1) Raising the discount rate discourages banks from borrowing reserves from the Fed. (2) Lowering the discount rate encourages banks to borrow from the Fed. d. It can auction off to banks the right to borrow reserves for a set period of time (usually 28 d ...
Pre-Test Chap 12 Handout Page
... Macroeconomists believe that the aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped. One explanation for this relationship is that (a) a rising price level increases the value of the money balances, thus inducing consumers to purchase more. (b) interest rates and investment spending are inversely related. ...
... Macroeconomists believe that the aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped. One explanation for this relationship is that (a) a rising price level increases the value of the money balances, thus inducing consumers to purchase more. (b) interest rates and investment spending are inversely related. ...
Answers to questions.
... Inflation can also be caused by increases in costs of major inputs used throughout the economy. This type of inflation is often described as costpush inflation. Increases in costs push prices up. The most common recent examples are inflationary periods caused largely by increases in the price of oil ...
... Inflation can also be caused by increases in costs of major inputs used throughout the economy. This type of inflation is often described as costpush inflation. Increases in costs push prices up. The most common recent examples are inflationary periods caused largely by increases in the price of oil ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... of many LDCs, one characterized by the absence of markets for primary securities (such as government bonds and equity), but flourishing curb markets. Bank credit and loans taken out on the curb market are used to finance firms’ working capital, not consumer expenditure. This model provides a direct ...
... of many LDCs, one characterized by the absence of markets for primary securities (such as government bonds and equity), but flourishing curb markets. Bank credit and loans taken out on the curb market are used to finance firms’ working capital, not consumer expenditure. This model provides a direct ...
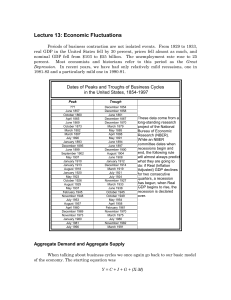
Lecture 13
... The Recession at the End of World War I Following the end of World War I, the economy went into a brief recession. If fact there were two: 1918-19, and 1920-21. The 1920-21 recession saw a significant decline in prices. But the decline in output was relatively mild. The end of World War I brought an ...
... The Recession at the End of World War I Following the end of World War I, the economy went into a brief recession. If fact there were two: 1918-19, and 1920-21. The 1920-21 recession saw a significant decline in prices. But the decline in output was relatively mild. The end of World War I brought an ...
EC 102.07-08-09 Exercises for Chapter 33 SPRING 2006 1. Ceteris
... 1. Explain how an increase in the price level changes interest rates. How does this change in interest rates lead to changes in investment and net exports? ANSWER: When the price level increases, the purchasing power of money held in purses and bank accounts declines. This decline makes people feel ...
... 1. Explain how an increase in the price level changes interest rates. How does this change in interest rates lead to changes in investment and net exports? ANSWER: When the price level increases, the purchasing power of money held in purses and bank accounts declines. This decline makes people feel ...
PART I: Multiple Choice/Fill-In
... level, would it initiate contractionary or expansionary monetary policy? If it did so successfully, would the price level increase or decrease from its level in the original long-run equilibrium? (2 points) Referring to the graph below, if the economy is in long-run equilibrium, then aggregate outpu ...
... level, would it initiate contractionary or expansionary monetary policy? If it did so successfully, would the price level increase or decrease from its level in the original long-run equilibrium? (2 points) Referring to the graph below, if the economy is in long-run equilibrium, then aggregate outpu ...
lesson 6
... With the decrease in interest rates because of the expansionary monetary policy, the interest rate sensitive components of aggregate demand (consumption and investment) will increase, thereby increasing output. (B) In the short run, what happens to the price level? Explain why. The price level incre ...
... With the decrease in interest rates because of the expansionary monetary policy, the interest rate sensitive components of aggregate demand (consumption and investment) will increase, thereby increasing output. (B) In the short run, what happens to the price level? Explain why. The price level incre ...
Worksheet 17.1: Intro to AD
... The demand curve for apples is downward sloping because all else equal, if the price of apples goes up, consumers will switch to a substitute fruit like bananas. With AD, we are talking about the aggregate price level rising for all goods and services in the economy. 1. Wealth or real balances effec ...
... The demand curve for apples is downward sloping because all else equal, if the price of apples goes up, consumers will switch to a substitute fruit like bananas. With AD, we are talking about the aggregate price level rising for all goods and services in the economy. 1. Wealth or real balances effec ...
DEMAND
... Mexico, Vietnam affected interdependency on foreign governments, products, and services? How has free trade with India and China affected the prices of goods and wages sold in America? ...
... Mexico, Vietnam affected interdependency on foreign governments, products, and services? How has free trade with India and China affected the prices of goods and wages sold in America? ...
Chapter 16 Money in macroeconomics
... This indirect gold-exchange standard broke down in 1971-73, and nowadays money in most countries is unbacked paper money (including electronic entries in banks’ accounts). This feature of modern money makes its valuation very di¤erent from that of other assets. A piece of paper money in a modern pay ...
... This indirect gold-exchange standard broke down in 1971-73, and nowadays money in most countries is unbacked paper money (including electronic entries in banks’ accounts). This feature of modern money makes its valuation very di¤erent from that of other assets. A piece of paper money in a modern pay ...
The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macroeconomic
... • The IS-LM model relates the real interest rate to output. • The AD-AS model relates the price level to output. ...
... • The IS-LM model relates the real interest rate to output. • The AD-AS model relates the price level to output. ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... in this index is a measure of inflation. Experts suggest that the CPI overstates inflation because it does not take into account the fact that people make substitutions in the goods and services they buy when prices change. To address this problem (called “substitution bias”) the BLS now changes the ...
... in this index is a measure of inflation. Experts suggest that the CPI overstates inflation because it does not take into account the fact that people make substitutions in the goods and services they buy when prices change. To address this problem (called “substitution bias”) the BLS now changes the ...