Solutions - University of California, Berkeley
... increases. In our IA-AD figure this unfavorable inflation shock shifts the IA curve up from IA ! to IA! . Moving to the IS-MP diagram, remember that the MP curve is given by the interest rate rule r = r(Y, π) and that r is increasing in inflation. In response to the increase in inflation the central ...
... increases. In our IA-AD figure this unfavorable inflation shock shifts the IA curve up from IA ! to IA! . Moving to the IS-MP diagram, remember that the MP curve is given by the interest rate rule r = r(Y, π) and that r is increasing in inflation. In response to the increase in inflation the central ...
Table 12.2 (completed)
... lower aggregate supply and this in turn must be the result of either higher resource prices or lower productivity. The cure for stagflation, some economists believe, is through policies designed to increase competition – thus lowering prices – and though tax-incentive programs to boost incentives an ...
... lower aggregate supply and this in turn must be the result of either higher resource prices or lower productivity. The cure for stagflation, some economists believe, is through policies designed to increase competition – thus lowering prices – and though tax-incentive programs to boost incentives an ...
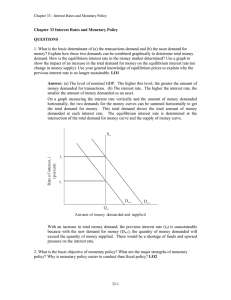
Chapter 33 Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
... Federal funds are loaned overnight, so lenders don’t have to wait long for repayment. The reserves loaned would otherwise generate no interest, so even loaning at the lower Federal funds rate is beneficial to lenders. Interest rates also depend on risk. It is less risky to lend overnight to other ba ...
... Federal funds are loaned overnight, so lenders don’t have to wait long for repayment. The reserves loaned would otherwise generate no interest, so even loaning at the lower Federal funds rate is beneficial to lenders. Interest rates also depend on risk. It is less risky to lend overnight to other ba ...
The ABCs of US savings bonds
... EE savings bonds purchased directly through financial institutions are printed with the words "Patriot Bond" on them. All of these types of United States Savings Bonds accrue interest, and all of them have a “final maturity” date beyond which this interest-accrual will cease. At the time of purchase ...
... EE savings bonds purchased directly through financial institutions are printed with the words "Patriot Bond" on them. All of these types of United States Savings Bonds accrue interest, and all of them have a “final maturity” date beyond which this interest-accrual will cease. At the time of purchase ...
Macro2 Exercise #2
... the button entitled, “Recession” and click to make inflationary expectations constant. After that, click “Continue.” You will see a table entitled, “Initial Conditions: Recession.” Print out this table for future reference. Click “Continue.” You will see a table entitled, “Policy Decisions.” You are ...
... the button entitled, “Recession” and click to make inflationary expectations constant. After that, click “Continue.” You will see a table entitled, “Initial Conditions: Recession.” Print out this table for future reference. Click “Continue.” You will see a table entitled, “Policy Decisions.” You are ...
T7- Bonds
... •Bonds are also called fixed-income securities because the cash flow from them is fixed. •Stocks are equity; bonds are debt. •The key reason to purchase bonds is to diversify your portfolio. •The issuers of bonds are governments and corporations. •A bond is characterized by its face value, coupon ra ...
... •Bonds are also called fixed-income securities because the cash flow from them is fixed. •Stocks are equity; bonds are debt. •The key reason to purchase bonds is to diversify your portfolio. •The issuers of bonds are governments and corporations. •A bond is characterized by its face value, coupon ra ...
Econ 102: Problem Set 1
... From the Classical Dichotomy we know that this change in the money supply will not, in the long run, change any real variables. Therefore real GDP, the real interest rate, and the real exchange rate will be unchanged in the long run, remaining at the levels determined in the open-economy model that ...
... From the Classical Dichotomy we know that this change in the money supply will not, in the long run, change any real variables. Therefore real GDP, the real interest rate, and the real exchange rate will be unchanged in the long run, remaining at the levels determined in the open-economy model that ...
here - Hans-Böckler
... level inertia and also make expected inflation a function of the future price level rather than the current price level. Those modelling changes explain why the central bank cannot raise inflation to lower the real interest rate and circumvent the ZLB. That gives New Keynesian models an escape hatch ...
... level inertia and also make expected inflation a function of the future price level rather than the current price level. Those modelling changes explain why the central bank cannot raise inflation to lower the real interest rate and circumvent the ZLB. That gives New Keynesian models an escape hatch ...
Exercises for Chapter 26
... d. None of the above are correct. ANSWER: d. None of the above are correct. 17. If Turkey increases its budget deficit, it will reduce a. private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left. b. investment and so shift the demand for loanable funds left. c. public saving and so shift the su ...
... d. None of the above are correct. ANSWER: d. None of the above are correct. 17. If Turkey increases its budget deficit, it will reduce a. private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left. b. investment and so shift the demand for loanable funds left. c. public saving and so shift the su ...
Robbins-inflation
... (M) what will happen to prices (P)? Ex: Assume money supply is $5 and it is being used to buy 10 products with a price of $2 each. 1. How much is the velocity of money? 2. If the velocity and output stay the same, what will happen if the amount of money is increase to $10? Notice, doubling the money ...
... (M) what will happen to prices (P)? Ex: Assume money supply is $5 and it is being used to buy 10 products with a price of $2 each. 1. How much is the velocity of money? 2. If the velocity and output stay the same, what will happen if the amount of money is increase to $10? Notice, doubling the money ...
March 12, 2004
... (III) bonds with higher interest rates are worth more, increasing wealth and spending; by the transactions demand, the public will want to hold more money to conduct this higher level of transactions; (IV) when interest rates are low, the public is likely to believe they cannot go lower; the fear of ...
... (III) bonds with higher interest rates are worth more, increasing wealth and spending; by the transactions demand, the public will want to hold more money to conduct this higher level of transactions; (IV) when interest rates are low, the public is likely to believe they cannot go lower; the fear of ...
Will higher national saving lead to higher GDP
... insignificant in terms of raising living standards in an economy. But more importantly, investment probably contributes to faster multi-factor productivity growth (e.g. through the adoption of a new technology) which would lift the growth rate permanently.2 But the question remains as to whether dom ...
... insignificant in terms of raising living standards in an economy. But more importantly, investment probably contributes to faster multi-factor productivity growth (e.g. through the adoption of a new technology) which would lift the growth rate permanently.2 But the question remains as to whether dom ...
Slide 1 - Porterville College Home
... Because of increasing population and productivity, the nation’s natural or potential GDP increases steadily over time. As it does so, actual real output is sometimes above and sometimes below the natural level. The difference is called the output gap ...
... Because of increasing population and productivity, the nation’s natural or potential GDP increases steadily over time. As it does so, actual real output is sometimes above and sometimes below the natural level. The difference is called the output gap ...
201200505 Sample Final Exam FINAL Problem Answers
... important to explain why potential output is a good goal--or why your preferred alternative is a better goal. b. Suppose that the President-Elect’s political advisors say that it is very important, politically, to cut government spending. What do you say in response? Here are three possibilities: (i ...
... important to explain why potential output is a good goal--or why your preferred alternative is a better goal. b. Suppose that the President-Elect’s political advisors say that it is very important, politically, to cut government spending. What do you say in response? Here are three possibilities: (i ...
Dr William Muhairwe
... Interest rate subsidised compared to market rate (i.e. 8% compared to market rate of 14% Interest rate included hedge costs against foreign exchange risk. ...
... Interest rate subsidised compared to market rate (i.e. 8% compared to market rate of 14% Interest rate included hedge costs against foreign exchange risk. ...
Chapter 26 Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
... nominal and real interest rates? How does deflation differ from inflation? LO3 Answer: The CPI is constructed from a “market basket” sampling of goods that consumers typically purchase. Prices for goods in the market basket are collected each month, weighted by the importance of the good in the bask ...
... nominal and real interest rates? How does deflation differ from inflation? LO3 Answer: The CPI is constructed from a “market basket” sampling of goods that consumers typically purchase. Prices for goods in the market basket are collected each month, weighted by the importance of the good in the bask ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... versa for negative price changes.This observation has stoked considerable interest amongst researchers because, normally, we expect asset prices to adjust immediately to reflect new information about fundamental value, not gradually over time (see Meese and Wallace 1994 for some important empirical ...
... versa for negative price changes.This observation has stoked considerable interest amongst researchers because, normally, we expect asset prices to adjust immediately to reflect new information about fundamental value, not gradually over time (see Meese and Wallace 1994 for some important empirical ...
problem set 1 - Shepherd Webpages
... resource productivity (or technological change in the broad sense), what will happen to the “growth rate” (defined as an increase in output per worker or per ...
... resource productivity (or technological change in the broad sense), what will happen to the “growth rate” (defined as an increase in output per worker or per ...
Public Debt: Private Asset
... checks, called discount checks, to the successful bidders on the issue date. The amount of the checks, determined by the auction process, represents interest on the bill. (In contrast, buyers of T-notes and T-bonds receive semi-annual interest payments.) All T-bills, notes, and bonds are held in boo ...
... checks, called discount checks, to the successful bidders on the issue date. The amount of the checks, determined by the auction process, represents interest on the bill. (In contrast, buyers of T-notes and T-bonds receive semi-annual interest payments.) All T-bills, notes, and bonds are held in boo ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.