Business Cycle Theory Fichier
... that require sectoral adjustment processes. The sectoral adjustment processes are accompanied by increased levels of unemployment and lower incomes that reduce the aggregate demand for products for all sectors. The result is reduced labor supply and low movement of workers between sectors, even thou ...
... that require sectoral adjustment processes. The sectoral adjustment processes are accompanied by increased levels of unemployment and lower incomes that reduce the aggregate demand for products for all sectors. The result is reduced labor supply and low movement of workers between sectors, even thou ...
Title goes here – this sample illustrates a two
... “Obviously, it is not possible to draw an explicit link between specific reforms and the recent improvements in Australia’s economic performance. Time lags between reform implementation and impact, the complementary nature of many reform initiatives, the concentration of adjustment costs in the near ...
... “Obviously, it is not possible to draw an explicit link between specific reforms and the recent improvements in Australia’s economic performance. Time lags between reform implementation and impact, the complementary nature of many reform initiatives, the concentration of adjustment costs in the near ...
No: 2012 – 56 Release date: 27 November 2012
... stance deviate significantly from this framework and consequently have an adverse effect on the medium-term inflation outlook. 20. Prudent fiscal policy is crucial for preserving the resilience of our economy against existing global uncertainties. Strengthening the structural reform agenda that woul ...
... stance deviate significantly from this framework and consequently have an adverse effect on the medium-term inflation outlook. 20. Prudent fiscal policy is crucial for preserving the resilience of our economy against existing global uncertainties. Strengthening the structural reform agenda that woul ...
President’s Report Board Directors
... CURRENT ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS - September 2, 2014 Data released since your last Directors' meeting show the economy grew at a faster pace in the second quarter than originally thought. Growth is expected to slow in the third quarter but remain above trend throughout the second half of the year. Rec ...
... CURRENT ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS - September 2, 2014 Data released since your last Directors' meeting show the economy grew at a faster pace in the second quarter than originally thought. Growth is expected to slow in the third quarter but remain above trend throughout the second half of the year. Rec ...
Reading Legitimation Crisis During the Meltdown
... and real estate, inflating asset values. As a measure of these paper "investments," consider the following sequence: in 1956 the Dow Jones Industrial Average reached 500; 16 years later, 1972, it reached 1000; 15 years later, 1987, it hit 2000, then exploded to 8000 ten years later (1997), then to 1 ...
... and real estate, inflating asset values. As a measure of these paper "investments," consider the following sequence: in 1956 the Dow Jones Industrial Average reached 500; 16 years later, 1972, it reached 1000; 15 years later, 1987, it hit 2000, then exploded to 8000 ten years later (1997), then to 1 ...
View/Open
... doing business and in making the system more rigid. These are gradual changes. In the short run, we now have a rigid system and it has been hit with many shocks in the 70's. What are the appropriate policies? Aggregate demand restraint is an obvious policy to deal with the economic system. It is cle ...
... doing business and in making the system more rigid. These are gradual changes. In the short run, we now have a rigid system and it has been hit with many shocks in the 70's. What are the appropriate policies? Aggregate demand restraint is an obvious policy to deal with the economic system. It is cle ...
defense and security effects of the economic crisis
... “a situation in which the economy of a country experiences a sudden downturn brought on by a financial crisis”…with the most likely effects being “a falling GDP, a drying up of liquidity and rising/falling prices due to inflation/deflation.” [1] Referring to the economic crisis, the economists make ...
... “a situation in which the economy of a country experiences a sudden downturn brought on by a financial crisis”…with the most likely effects being “a falling GDP, a drying up of liquidity and rising/falling prices due to inflation/deflation.” [1] Referring to the economic crisis, the economists make ...
the solow productivity paradox in historical perspective
... Continued declines in the prices of information technology capital mean that a constant nominal flow of savings channeled to such investments will bring more and more real investment. As long as information technology capital earns the same rate of return as other capital, then labor productivity gr ...
... Continued declines in the prices of information technology capital mean that a constant nominal flow of savings channeled to such investments will bring more and more real investment. As long as information technology capital earns the same rate of return as other capital, then labor productivity gr ...
Keynesian interpretation of the quantity theory of money
... amount of money in the economy. Monetarists believe that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply. ...
... amount of money in the economy. Monetarists believe that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply. ...
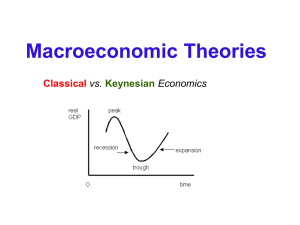
Classical versus Keynesian Economics
... Classical economists were the 1st school of economic thought starting in 1776 Adam Smith was the founder and they believed: ...
... Classical economists were the 1st school of economic thought starting in 1776 Adam Smith was the founder and they believed: ...
Problem Set 7 FE312 Fall 2011 Rahman Some Answers 1
... then it should increase aggregate demand by increasing the money supply. This policy response shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward. In this case, the economy immediately reaches a new equilibrium – the price level is permanently higher, but there is no loss in output associated with the adver ...
... then it should increase aggregate demand by increasing the money supply. This policy response shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward. In this case, the economy immediately reaches a new equilibrium – the price level is permanently higher, but there is no loss in output associated with the adver ...
Chapter Goals
... • Sometimes called supply-side economics • Issues of growth are considered in a long-run framework • The short-run business cycle focuses on demand • Sometimes called demand-side economics • Business cycles are generally considered in a short-run framework • Inflation and unemployment fall within bo ...
... • Sometimes called supply-side economics • Issues of growth are considered in a long-run framework • The short-run business cycle focuses on demand • Sometimes called demand-side economics • Business cycles are generally considered in a short-run framework • Inflation and unemployment fall within bo ...
The Backing of the Currency and Economic Stability
... Eventually, this necessitated a change in the official ratio, accomplished by the Coinage Act of 1834, which raised the ratio to sixteen-to-one (Leavens 20). As Leavens states, “the market ratio in 1834 was between 15.5 and 16.0 to 1, so that the 16-to-1 coinage ratio intentionally overvalued gold,” ...
... Eventually, this necessitated a change in the official ratio, accomplished by the Coinage Act of 1834, which raised the ratio to sixteen-to-one (Leavens 20). As Leavens states, “the market ratio in 1834 was between 15.5 and 16.0 to 1, so that the 16-to-1 coinage ratio intentionally overvalued gold,” ...
AP Macro The Quantity Theory of Money
... Assume on average a dollar bill does ten transactions (buying and selling of goods and services) per year. Thus velocity of circulation "V" in this case is 10. Here, a one dollar bill does the equivalent of ten dollars’ worth of transactions. So, M x V=1x10=10 dollars ...
... Assume on average a dollar bill does ten transactions (buying and selling of goods and services) per year. Thus velocity of circulation "V" in this case is 10. Here, a one dollar bill does the equivalent of ten dollars’ worth of transactions. So, M x V=1x10=10 dollars ...
Raising Economic Growth in Japan (22 Oct 02).
... had a long association with the Bank of Japan, as a visiting scholar in the 1980s and as an honorary foreign adviser in the 1990s—a job that I regret I had to resign from when I joined President Bush’s Administration last year. I lived in Tokyo for a short time in 1987—in the Aoyama neighborhood. My ...
... had a long association with the Bank of Japan, as a visiting scholar in the 1980s and as an honorary foreign adviser in the 1990s—a job that I regret I had to resign from when I joined President Bush’s Administration last year. I lived in Tokyo for a short time in 1987—in the Aoyama neighborhood. My ...
Economic Growth - Leon County Schools
... • Growth is a widely held economic goal. • When a nation can expand its output relative to its population, ...
... • Growth is a widely held economic goal. • When a nation can expand its output relative to its population, ...
Economic_growth - YSU
... • One key to productivity growth is growth in nation’s capital stock – With more capital, a given number of workers can produce more output than before ...
... • One key to productivity growth is growth in nation’s capital stock – With more capital, a given number of workers can produce more output than before ...
Macro_online_chapter_10_13e
... Generally, if AD increases, then SRAS will eventually decrease Generally, if AD decreases, then SRAS will eventually increase Sometimes a change in AD is temporary and will quickly move back to its original position so SRAS need not change ...
... Generally, if AD increases, then SRAS will eventually decrease Generally, if AD decreases, then SRAS will eventually increase Sometimes a change in AD is temporary and will quickly move back to its original position so SRAS need not change ...
File
... Domestic Resource Prices • A good example of the major effect that changing resource prices can have on aggregate supply is the oil price hikes of the 1970s. At that time, a group of oil-producing nations called the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) worked in concert to decrease ...
... Domestic Resource Prices • A good example of the major effect that changing resource prices can have on aggregate supply is the oil price hikes of the 1970s. At that time, a group of oil-producing nations called the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) worked in concert to decrease ...
Unit 8
... during a period of one year. Graphically it is shown by an outward shift of the country’s production possibilities curve. It is caused by increased productive capabilities that are made possible by either an increase in inputs (production factors) such as labour, capital or technological innovations ...
... during a period of one year. Graphically it is shown by an outward shift of the country’s production possibilities curve. It is caused by increased productive capabilities that are made possible by either an increase in inputs (production factors) such as labour, capital or technological innovations ...
Demand - Bank of England
... Sources: Bank of England, BCC, CBI, CBI/PwC and ONS. (a) Chained-volume measure. (b) Data are to 2011 Q4. Includes survey measures of investment intentions from the Bank’s Agents (companies’ intended changes in investment over the next twelve months), BCC (net percentage balance of companies who say ...
... Sources: Bank of England, BCC, CBI, CBI/PwC and ONS. (a) Chained-volume measure. (b) Data are to 2011 Q4. Includes survey measures of investment intentions from the Bank’s Agents (companies’ intended changes in investment over the next twelve months), BCC (net percentage balance of companies who say ...
PRESS RELEASE SUMMARY OF THE MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MEETING No: 2015-50
... in June. Accordingly, industrial production grew by 1.6 percent quarter-on-quarter and 3.9 percent year-on-year in the second quarter of 2015. The strong production growth in June does not signify an acceleration in economic activity and is rather a result of compensating for the output loss led by ...
... in June. Accordingly, industrial production grew by 1.6 percent quarter-on-quarter and 3.9 percent year-on-year in the second quarter of 2015. The strong production growth in June does not signify an acceleration in economic activity and is rather a result of compensating for the output loss led by ...
L12 - UKM
... GDP growth averages 3–3.5 percent per year over the long run with large fluctuations in the short run. ...
... GDP growth averages 3–3.5 percent per year over the long run with large fluctuations in the short run. ...
Long Depression

The Long Depression was a worldwide price recession, beginning in 1873 and running through the spring of 1879. It was the most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing strong economic growth fueled by the Second Industrial Revolution in the decade following the American Civil War. The episode was labeled the ""Great Depression"" at the time, and it held that designation until the Great Depression of the 1930s. Though a period of general deflation and a general contraction, it did not have the severe economic retrogression of the Great Depression.It was most notable in Western Europe and North America, at least in part because reliable data from the period are most readily available in those parts of the world. The United Kingdom is often considered to have been the hardest hit; during this period it lost some of its large industrial lead over the economies of Continental Europe. While it was occurring, the view was prominent that the economy of the United Kingdom had been in continuous depression from 1873 to as late as 1896 and some texts refer to the period as the Great Depression of 1873–96.In the United States, economists typically refer to the Long Depression as the Depression of 1873–79, kicked off by the Panic of 1873, and followed by the Panic of 1893, book-ending the entire period of the wider Long Depression. The National Bureau of Economic Research dates the contraction following the panic as lasting from October 1873 to March 1879. At 65 months, it is the longest-lasting contraction identified by the NBER, eclipsing the Great Depression's 43 months of contraction.In the US, from 1873–1879, 18,000 businesses went bankrupt, including 89 railroads. Ten states and hundreds of banks went bankrupt. Unemployment peaked in 1878, long after the panic ended. Different sources peg the peak unemployment rate anywhere from 8.25% to 14%.