CHAPTER 24
... about whether a change in their output price is an increase in the real price or only on the nominal or dollar price • If producers believe demand for their product has fallen, they will cut back production • If this happened throughout the economy, it would lead to a recession ...
... about whether a change in their output price is an increase in the real price or only on the nominal or dollar price • If producers believe demand for their product has fallen, they will cut back production • If this happened throughout the economy, it would lead to a recession ...
Macroeconomic Shocks, Housing Market and Banks` Performance
... find that real house prices only respond to demand fluctuations occurring either at an aggregate or sectorial level. Most significant housing price booms also take place with greater financial exposure to mortgages and real domestic currency depreciations, two factors that potentially magnify rising ...
... find that real house prices only respond to demand fluctuations occurring either at an aggregate or sectorial level. Most significant housing price booms also take place with greater financial exposure to mortgages and real domestic currency depreciations, two factors that potentially magnify rising ...
W What is the Monetary Standard, Or, How Did the Volcker-Greenspan FOMCs
... bank concerned about the “inflationary psychology” of bond markets will naturally possess such concerns. The introduction of a third concern beyond the smoothing of actual and expected changes in the price level, namely, a desire to smooth the interest rate, introduces drift in the price level (rela ...
... bank concerned about the “inflationary psychology” of bond markets will naturally possess such concerns. The introduction of a third concern beyond the smoothing of actual and expected changes in the price level, namely, a desire to smooth the interest rate, introduces drift in the price level (rela ...
Money demand in the euro area
... fluctuations between assets and non-durable goods. In actual fact, the macroeconomic development in the euro area in the 2004-2007 period has been characterised by a very sharp increase in the price of assets, such as real estate or shares, which significantly outpaced GDP growth. In order to gauge ...
... fluctuations between assets and non-durable goods. In actual fact, the macroeconomic development in the euro area in the 2004-2007 period has been characterised by a very sharp increase in the price of assets, such as real estate or shares, which significantly outpaced GDP growth. In order to gauge ...
PLEASE DO NOT QUOTE A Small Estimated Model (SEM) for New Zealand
... from interest rates to inflation is around 8 to 11 quarters (at least 5 quarters from interest rates to the output gap, then a 3 quarter lag between the output gap and inflation). The real TWI gap impacts with a lag of 4 to 7 quarters, with a total coefficient of –0.26 (jointly significant) with the ...
... from interest rates to inflation is around 8 to 11 quarters (at least 5 quarters from interest rates to the output gap, then a 3 quarter lag between the output gap and inflation). The real TWI gap impacts with a lag of 4 to 7 quarters, with a total coefficient of –0.26 (jointly significant) with the ...
Chapter 4: Skating to Where the Puck is Going: Aggregate Supply
... unemployment —layoffs instead of lower wages – in output markets, prices fall due to surpluses, but falling incomes from unemployment in input markets decrease consumption demand (C) ...
... unemployment —layoffs instead of lower wages – in output markets, prices fall due to surpluses, but falling incomes from unemployment in input markets decrease consumption demand (C) ...
Money Supply, Interest Rate, Liquidity and Share Prices
... rates, the yield on equities. Any increase in the supply of money will tend to cause all interest rates across the board in the demand of money to fall. The speed with which yield on other assets respond depends on the rate at which excess holdings of money balances are reduced: this provides a clu ...
... rates, the yield on equities. Any increase in the supply of money will tend to cause all interest rates across the board in the demand of money to fall. The speed with which yield on other assets respond depends on the rate at which excess holdings of money balances are reduced: this provides a clu ...
word 97
... the associated strengthening of domestic demand in western Europe. In Russia, the deep recession has bottomed out and output has started to rise again, although the foundations for a sustained recovery still appear to be rather weak. There has also been an upturn in economic activity in most of the ...
... the associated strengthening of domestic demand in western Europe. In Russia, the deep recession has bottomed out and output has started to rise again, although the foundations for a sustained recovery still appear to be rather weak. There has also been an upturn in economic activity in most of the ...
My lecture
... Review of Long Run • Unemployment is never zero. Full employment implies operating at the natural rate of unemployment. • Increases in the available money in an economic system lead to rising price level. • Inflation pushes up the nominal interest rate while real interest rate is determined as savi ...
... Review of Long Run • Unemployment is never zero. Full employment implies operating at the natural rate of unemployment. • Increases in the available money in an economic system lead to rising price level. • Inflation pushes up the nominal interest rate while real interest rate is determined as savi ...
Wages Behaviour and Unemployment in Keynes and New
... Keynes’s view, workers are concerned not only with real wages but also with relative wages, that is with how their pay compares with the pay of those to whom they regard themselves at least equal in merit and status. However, if labour markets are disaggregated and desynchronised, a nominal wage cut ...
... Keynes’s view, workers are concerned not only with real wages but also with relative wages, that is with how their pay compares with the pay of those to whom they regard themselves at least equal in merit and status. However, if labour markets are disaggregated and desynchronised, a nominal wage cut ...
inertial inflation and the cruzado plan - Bresser
... heterodox shock. An orthodox shock, inspired by monetarist or Keynesian economics, is based on a cut in state spending and an increase in taxes, on a drastic reduction in the money supply, on an increase in the interest rate and on a recession which would have indirectly led to a reduction in wages ...
... heterodox shock. An orthodox shock, inspired by monetarist or Keynesian economics, is based on a cut in state spending and an increase in taxes, on a drastic reduction in the money supply, on an increase in the interest rate and on a recession which would have indirectly led to a reduction in wages ...
An Index of Coincident Economic Indicators for
... quarters of decline during the 2001 recession, though it involved a loss of nearly three million jobs – the biggest recessionary job loss in the post-World War II period until that time. During the 2007-09 recession, which officially lasted from December 2007 to June 2009, GDP data was especially mi ...
... quarters of decline during the 2001 recession, though it involved a loss of nearly three million jobs – the biggest recessionary job loss in the post-World War II period until that time. During the 2007-09 recession, which officially lasted from December 2007 to June 2009, GDP data was especially mi ...
Package `pwt`
... rgdpl2th real GDP per hour worked by employees (Laspeyres 2 index, US dollars in 2005 prices). grgdpch growth rate of real GDP per capita (chain-weighted index). grgdpl2 growth rate of real GDP per capita (Laspeyres 2 index). ...
... rgdpl2th real GDP per hour worked by employees (Laspeyres 2 index, US dollars in 2005 prices). grgdpch growth rate of real GDP per capita (chain-weighted index). grgdpl2 growth rate of real GDP per capita (Laspeyres 2 index). ...
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... Economists have generally believed that falling oil prices will benefit the U.S. economy and lead to higher economic growth. Falling oil prices should lead to falling gasoline and heating oil prices and put more money in the pockets of consumers that will lead to increases in aggregate demand. Since ...
... Economists have generally believed that falling oil prices will benefit the U.S. economy and lead to higher economic growth. Falling oil prices should lead to falling gasoline and heating oil prices and put more money in the pockets of consumers that will lead to increases in aggregate demand. Since ...
An alternative approach to measuring the output gap
... method is less reliable just at the end of the monitored period, and therefore data on gap achieved by SVAR method are more reliable, which is free of similarly biased estimates. In consequence of expansionary fiscal policy during the period of 1994-98 the economy occurred in substantial inner and e ...
... method is less reliable just at the end of the monitored period, and therefore data on gap achieved by SVAR method are more reliable, which is free of similarly biased estimates. In consequence of expansionary fiscal policy during the period of 1994-98 the economy occurred in substantial inner and e ...
Special Topic 6: Lessons from the Great Depression
... • Sixty countries responded with higher tariffs on American exports and the volume of trade fell by more than 50%. ...
... • Sixty countries responded with higher tariffs on American exports and the volume of trade fell by more than 50%. ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... The previous edition’s presentation of the derivation of aggregate demand from the AE model has been moved to the appendix of the chapter so that instructors can use or ignore this material as warranted. The discussion of “Determinants of Aggregate Demand” now distinguishes between the “initial chan ...
... The previous edition’s presentation of the derivation of aggregate demand from the AE model has been moved to the appendix of the chapter so that instructors can use or ignore this material as warranted. The discussion of “Determinants of Aggregate Demand” now distinguishes between the “initial chan ...
Lecture 13
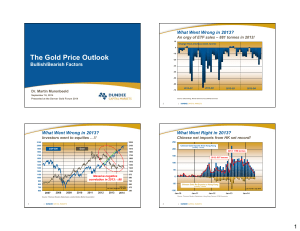
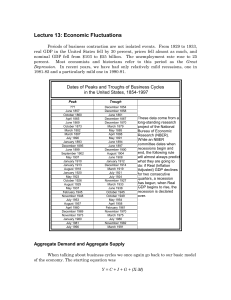
... Lecture 13: Economic Fluctuations Periods of business contraction are not isolated events. From 1929 to 1933, real GDP in the United States fell by 30 percent, prices fell almost as much, and nominal GDP fell from $103 to $55 billion. The unemployment rate rose to 25 percent. Most economists and his ...
... Lecture 13: Economic Fluctuations Periods of business contraction are not isolated events. From 1929 to 1933, real GDP in the United States fell by 30 percent, prices fell almost as much, and nominal GDP fell from $103 to $55 billion. The unemployment rate rose to 25 percent. Most economists and his ...
Synthetic Commodity Money
... offers some exceptions to Irving Fisher’s (1920, p. 131) claim that “Irredeemable paper money has almost invariably proven a curse to the country employing it,” that experience nevertheless supplies many further instances of the reckless, if not disastrous, mismanagement of fiat standards. Commodit ...
... offers some exceptions to Irving Fisher’s (1920, p. 131) claim that “Irredeemable paper money has almost invariably proven a curse to the country employing it,” that experience nevertheless supplies many further instances of the reckless, if not disastrous, mismanagement of fiat standards. Commodit ...
“When Did the Swiss Get so Rich?” Comparing Living
... achieved in the first half of the twentieth century and followed by constant expansion of Swiss financial institutions, is believed to have brought prosperity not only to an ever growing service sector, but, by its sheer size and its links to other sectors, to the Swiss economy as a whole.7 To prese ...
... achieved in the first half of the twentieth century and followed by constant expansion of Swiss financial institutions, is believed to have brought prosperity not only to an ever growing service sector, but, by its sheer size and its links to other sectors, to the Swiss economy as a whole.7 To prese ...
short-run aggregate supply curve
... The Aggregate Supply Curve • The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output in the economy. ...
... The Aggregate Supply Curve • The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output in the economy. ...
Money Still Matters
... shocks to actual money holdings or the determinants of long-run money demand cause deviations of actual and desired money balances and therefore “the agent will attempt to move towards his long-run target demand for money by altering his current rate of flow of expenditures on goods, services, and a ...
... shocks to actual money holdings or the determinants of long-run money demand cause deviations of actual and desired money balances and therefore “the agent will attempt to move towards his long-run target demand for money by altering his current rate of flow of expenditures on goods, services, and a ...
Economic Forecasting in the Great Recession
... horizons of one to nine months. Horizons one through three refer to the current quarter; four to six are forecasts made with a one quarter lead; etc. The actual data that are used to evaluate these forecasts were the real time numbers available 90 days after the end or the quarter to which they refe ...
... horizons of one to nine months. Horizons one through three refer to the current quarter; four to six are forecasts made with a one quarter lead; etc. The actual data that are used to evaluate these forecasts were the real time numbers available 90 days after the end or the quarter to which they refe ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INFLATION: THEORY AND EVIDENCE Bennett 1. McCallum
... demonstrates that the principal conclusions of theoretical analysis are not highly sensitive to details of model specification, provided that the latter posits rational agents free of money illusion. Whether one assumes finite—lived or infinite—lived agents, such models suggest that steady—state inf ...
... demonstrates that the principal conclusions of theoretical analysis are not highly sensitive to details of model specification, provided that the latter posits rational agents free of money illusion. Whether one assumes finite—lived or infinite—lived agents, such models suggest that steady—state inf ...
Long Depression

The Long Depression was a worldwide price recession, beginning in 1873 and running through the spring of 1879. It was the most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing strong economic growth fueled by the Second Industrial Revolution in the decade following the American Civil War. The episode was labeled the ""Great Depression"" at the time, and it held that designation until the Great Depression of the 1930s. Though a period of general deflation and a general contraction, it did not have the severe economic retrogression of the Great Depression.It was most notable in Western Europe and North America, at least in part because reliable data from the period are most readily available in those parts of the world. The United Kingdom is often considered to have been the hardest hit; during this period it lost some of its large industrial lead over the economies of Continental Europe. While it was occurring, the view was prominent that the economy of the United Kingdom had been in continuous depression from 1873 to as late as 1896 and some texts refer to the period as the Great Depression of 1873–96.In the United States, economists typically refer to the Long Depression as the Depression of 1873–79, kicked off by the Panic of 1873, and followed by the Panic of 1893, book-ending the entire period of the wider Long Depression. The National Bureau of Economic Research dates the contraction following the panic as lasting from October 1873 to March 1879. At 65 months, it is the longest-lasting contraction identified by the NBER, eclipsing the Great Depression's 43 months of contraction.In the US, from 1873–1879, 18,000 businesses went bankrupt, including 89 railroads. Ten states and hundreds of banks went bankrupt. Unemployment peaked in 1878, long after the panic ended. Different sources peg the peak unemployment rate anywhere from 8.25% to 14%.