PROBLEM SET 3 14.02 Introductory Macroeconomics March 9, 2005 Due March 16, 2005
... (c) Suppose the economy described by these equations is in medium run equilibrium, and then it is perturbed by the following policy mix : an increase in taxes (say from T0 to T1 ) and an increase in money supply (say from M0 to M1 ). This policy mix may give rise to more than one outcome in the shor ...
... (c) Suppose the economy described by these equations is in medium run equilibrium, and then it is perturbed by the following policy mix : an increase in taxes (say from T0 to T1 ) and an increase in money supply (say from M0 to M1 ). This policy mix may give rise to more than one outcome in the shor ...
Economic Activity - Conneaut Area City Schools
... Prolonged period of high unemployment, weak consumer sales, and business failure. GDP falls rapidly Great Depression of U.S. history (1930-1940) • 25% of all U.S. labor force was unemployed • Many people could not afford to satisfy even their basic needs. • Doesn’t go on forever ...
... Prolonged period of high unemployment, weak consumer sales, and business failure. GDP falls rapidly Great Depression of U.S. history (1930-1940) • 25% of all U.S. labor force was unemployed • Many people could not afford to satisfy even their basic needs. • Doesn’t go on forever ...
Macroeconomics
... What is a Depression? • Depression: severe economic downturn lasting several years—last one was the Great Depression • Many experts say that the Great Depression was aggravated by contractionary monetary policy. The Federal Reserve rightly sought to slow down the stock market bubble in the late 1 ...
... What is a Depression? • Depression: severe economic downturn lasting several years—last one was the Great Depression • Many experts say that the Great Depression was aggravated by contractionary monetary policy. The Federal Reserve rightly sought to slow down the stock market bubble in the late 1 ...
The Industrial Revolution
... • Workers are wage-laborers; i.e., they do not own the product of their labor • The workers’ character is adversely affected by this system ...
... • Workers are wage-laborers; i.e., they do not own the product of their labor • The workers’ character is adversely affected by this system ...
Money, output and Prices in LR Macro_Module_32 money
... based on the next slide. 1. Increasing the money supply is _________________________ policy. 2. The interest rate would __________. 3. A __________ interest rate shifts AD _____. 4. In SR, real GDP ________ and aggregate P level __________. 5. Nominal wages ______________, shifting SRAS _______. 6. ...
... based on the next slide. 1. Increasing the money supply is _________________________ policy. 2. The interest rate would __________. 3. A __________ interest rate shifts AD _____. 4. In SR, real GDP ________ and aggregate P level __________. 5. Nominal wages ______________, shifting SRAS _______. 6. ...
... From January to August 2015, total government revenue fell by 19% compared with the year-earlier period. While there was a small increase in indirect taxes, direct taxes and non-tax revenue fell by 28% and 38%, respectively. Total expenditure, by contrast, was down by just 0.2%. This decrease is att ...
content/teaching outline
... time period. Training workers or providing incentives can increase productivity. If workers are more productive, a company’s profits can increase. For example, training employees to perform a specific task such as packaging computers in a box can allow the worker to complete this one task more effic ...
... time period. Training workers or providing incentives can increase productivity. If workers are more productive, a company’s profits can increase. For example, training employees to perform a specific task such as packaging computers in a box can allow the worker to complete this one task more effic ...
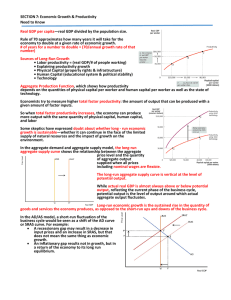
SECTION 7: Economic Growth & Productivity Need to Know —real GDP divided by the population size.
... depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
... depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
Chap 5
... If investors leave due to U.S. falling rates, the Fed may believe it should act to prevent rates from falling lower. ...
... If investors leave due to U.S. falling rates, the Fed may believe it should act to prevent rates from falling lower. ...
Ch. 12 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... D. mild expansion. 2. GDP expressed in constant, or unchanging, prices is called A. real GDP. C. nominal GDP. B. price level. D. net national product. 3. When GDP levels off and begins to decline, the economy is entering A. a peak part of the business cycle. B. an economic boom. C. the contraction p ...
... D. mild expansion. 2. GDP expressed in constant, or unchanging, prices is called A. real GDP. C. nominal GDP. B. price level. D. net national product. 3. When GDP levels off and begins to decline, the economy is entering A. a peak part of the business cycle. B. an economic boom. C. the contraction p ...
Causes Of Recession - School
... In Western economies, recessions are unusual. Take the world’s largest economy the United States - it has suffered only two official downturns, in 1990-91 and 2001. When they happen, they tend to be short-lived lasting perhaps no more than two or three years. If a country fails to emerge from a down ...
... In Western economies, recessions are unusual. Take the world’s largest economy the United States - it has suffered only two official downturns, in 1990-91 and 2001. When they happen, they tend to be short-lived lasting perhaps no more than two or three years. If a country fails to emerge from a down ...
Macroeconomic Concepts
... Occurs when people _________, get laid off from their current jobs, take some time to find the right job after they finish their schooling, or take time off from working for a variety of other reasons ___________ Unemployment ...
... Occurs when people _________, get laid off from their current jobs, take some time to find the right job after they finish their schooling, or take time off from working for a variety of other reasons ___________ Unemployment ...
From budget-cutting to `bubblenomics`
... averages. Real hourly wages for production and non-supervisory workers, about 80% of the labour force, have stayed roughly flat, languishing at about their level of 1979. Nor has the economic expansion been significantly stronger in either western Europe or Japan. The declining economic dynamism of ...
... averages. Real hourly wages for production and non-supervisory workers, about 80% of the labour force, have stayed roughly flat, languishing at about their level of 1979. Nor has the economic expansion been significantly stronger in either western Europe or Japan. The declining economic dynamism of ...
The Business Cycle
... The letter E represents a recovery. During a recovery, the economy is improving. As people begin spending more, producers are encouraged to increase production. This means more jobs and, in turn, even more ...
... The letter E represents a recovery. During a recovery, the economy is improving. As people begin spending more, producers are encouraged to increase production. This means more jobs and, in turn, even more ...
CHAPTER 17: TEST BANK
... greater R&D will enable greater economic growth. 4. Assuming that the prices of food and other necessities do rise (since many countries have exempted these products from price decontrol), the government might assist low income-people through welfare payments, food stamps, and the like. 5. Despite p ...
... greater R&D will enable greater economic growth. 4. Assuming that the prices of food and other necessities do rise (since many countries have exempted these products from price decontrol), the government might assist low income-people through welfare payments, food stamps, and the like. 5. Despite p ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
... The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
... The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
Chapter 04
... Three basic command economy questions – dictators or governments decide what products are needed. Government owns all means of production. Government decides who will get what is produced. Explain why all economies are mixed – elements of both market and command economies can be found in both. Compa ...
... Three basic command economy questions – dictators or governments decide what products are needed. Government owns all means of production. Government decides who will get what is produced. Explain why all economies are mixed – elements of both market and command economies can be found in both. Compa ...
Global Financial Crisis: The Aftermath
... Slashed interest rates Expanded the money supply Governments provided bailouts for major financial institutions to avert their collapse or took them over outright Governments also cut taxes and raised spending to prevent the economy from falling into a deep recession or even depression ...
... Slashed interest rates Expanded the money supply Governments provided bailouts for major financial institutions to avert their collapse or took them over outright Governments also cut taxes and raised spending to prevent the economy from falling into a deep recession or even depression ...
Comparative Static Analysis of the Keynesian Model
... Simple IS-LM, Continued Applying Cramer’s rule for solution: ...
... Simple IS-LM, Continued Applying Cramer’s rule for solution: ...
2.2.
... Deflation means a decrease in the general level of prices. Usually occurs in recession and depression. Even though prices drop, people tend to have less money to ...
... Deflation means a decrease in the general level of prices. Usually occurs in recession and depression. Even though prices drop, people tend to have less money to ...
PDF
... markets but also by the decrease in risk premiums on corporate bonds and on the government bonds of the emerging economies. In the real economy the positive effects of government stimulus programmes are also being felt. However, experience with past phases of weak economies shows that recovery is us ...
... markets but also by the decrease in risk premiums on corporate bonds and on the government bonds of the emerging economies. In the real economy the positive effects of government stimulus programmes are also being felt. However, experience with past phases of weak economies shows that recovery is us ...
Name:
... The four phases of a typical business cycle, starting at the bottom, are trough, recovery, peak, and recession. As seen in Table 9.1, the length of a complete cycle varies from about 2 to 3 years to as long as 15 years. There is a pre-Christmas spurt in production and sales and a January slackening. ...
... The four phases of a typical business cycle, starting at the bottom, are trough, recovery, peak, and recession. As seen in Table 9.1, the length of a complete cycle varies from about 2 to 3 years to as long as 15 years. There is a pre-Christmas spurt in production and sales and a January slackening. ...
Macroeconomics: Relating to the economy as a whole rather than
... Reflect fully what our nation’s businesses have produced GDP not sole figure for calculating annual production. ...
... Reflect fully what our nation’s businesses have produced GDP not sole figure for calculating annual production. ...
Long Depression

The Long Depression was a worldwide price recession, beginning in 1873 and running through the spring of 1879. It was the most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing strong economic growth fueled by the Second Industrial Revolution in the decade following the American Civil War. The episode was labeled the ""Great Depression"" at the time, and it held that designation until the Great Depression of the 1930s. Though a period of general deflation and a general contraction, it did not have the severe economic retrogression of the Great Depression.It was most notable in Western Europe and North America, at least in part because reliable data from the period are most readily available in those parts of the world. The United Kingdom is often considered to have been the hardest hit; during this period it lost some of its large industrial lead over the economies of Continental Europe. While it was occurring, the view was prominent that the economy of the United Kingdom had been in continuous depression from 1873 to as late as 1896 and some texts refer to the period as the Great Depression of 1873–96.In the United States, economists typically refer to the Long Depression as the Depression of 1873–79, kicked off by the Panic of 1873, and followed by the Panic of 1893, book-ending the entire period of the wider Long Depression. The National Bureau of Economic Research dates the contraction following the panic as lasting from October 1873 to March 1879. At 65 months, it is the longest-lasting contraction identified by the NBER, eclipsing the Great Depression's 43 months of contraction.In the US, from 1873–1879, 18,000 businesses went bankrupt, including 89 railroads. Ten states and hundreds of banks went bankrupt. Unemployment peaked in 1878, long after the panic ended. Different sources peg the peak unemployment rate anywhere from 8.25% to 14%.