History of Climate Change
... 1. Changes in solar luminosity - Our young sun shone 25 – 30% less brightly than it does today. But, climate during early earth’s history was generally warmer than today. 2. The long-term carbon cycle Over long periods of time, the carbon cycle alters the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. ...
... 1. Changes in solar luminosity - Our young sun shone 25 – 30% less brightly than it does today. But, climate during early earth’s history was generally warmer than today. 2. The long-term carbon cycle Over long periods of time, the carbon cycle alters the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. ...
History of Climate Change
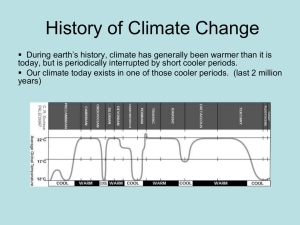
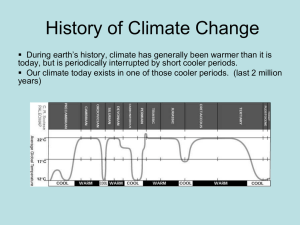
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
1) THIS IS THE WARMEST CLIMATE ZONE ON EARTH, AND THE
... a) precipitation, temperature, & humidity c) vegetation, temperature, & precipitation ...
... a) precipitation, temperature, & humidity c) vegetation, temperature, & precipitation ...
Climate: Causes and World Climates
... The Bonneville Salt Flats are part of the very dry Great Basin of the Sierra Nevada of California. The region receives little rainfall. ...
... The Bonneville Salt Flats are part of the very dry Great Basin of the Sierra Nevada of California. The region receives little rainfall. ...
7th Grade Weather and Climate Vocabulary Terms Weather
... 2) Radiation – transfer of heat energy through empty space. ...
... 2) Radiation – transfer of heat energy through empty space. ...
Unit 2 Review Guide
... 1. Define the following terms: earthquake, tsunami, tornado, volcano, hurricane, tropical depression, typhoon, Climate, weather, crust, plate tectonics, fold, fault, high-low-middle latitude belts, pangea 2. Where geographically is one most likely to find the following in the US and around the world ...
... 1. Define the following terms: earthquake, tsunami, tornado, volcano, hurricane, tropical depression, typhoon, Climate, weather, crust, plate tectonics, fold, fault, high-low-middle latitude belts, pangea 2. Where geographically is one most likely to find the following in the US and around the world ...
Climate Verses Weather
... -The physical climate system involves the earth's atmosphere, land surfaces, and oceans, along with the snow and ice that is so prominent in much of Canada. These components interact with one another and with aspects of the earth's biosphere to determine not only the day-to-day weather, but also the ...
... -The physical climate system involves the earth's atmosphere, land surfaces, and oceans, along with the snow and ice that is so prominent in much of Canada. These components interact with one another and with aspects of the earth's biosphere to determine not only the day-to-day weather, but also the ...
Climate Notes How are climates described?
... -Temperature generally decreases as elevation increases. How do we study Climate change? -Climatologist a scientist who gathers data to study and compare past and present climates and to predict future climate change. -Fossils of a plant or animal may show adaptations to a particular environment and ...
... -Temperature generally decreases as elevation increases. How do we study Climate change? -Climatologist a scientist who gathers data to study and compare past and present climates and to predict future climate change. -Fossils of a plant or animal may show adaptations to a particular environment and ...
... Dr. Alex Hall is a professor in UCLA’s Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences and a member of UCLA’s Institute of the Environment and Sustainability, where he is the faculty director of the UCLA Center for Climate Change Solutions. He is also a member of the executive committee of the UCLA-J ...
Climate - Moodle
... The conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time: _____________________ __________________ , ______________ , _______________________ May __________________ day to day ...
... The conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time: _____________________ __________________ , ______________ , _______________________ May __________________ day to day ...
Climate

Climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area. It is measured by assessing the patterns of variation in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological variables in a given region over long periods of time. Climate is different from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region.A region's climate is generated by the climate system, which has five components: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere.The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and the typical ranges of different variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used classification scheme was originally developed by Wladimir Köppen. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature and precipitation information and is used in studying animal species diversity and potential effects of climate changes. The Bergeron and Spatial Synoptic Classification systems focus on the origin of air masses that define the climate of a region.Paleoclimatology is the study of ancient climates. Since direct observations of climate are not available before the 19th century, paleoclimates are inferred from proxy variables that include non-biotic evidence such as sediments found in lake beds and ice cores, and biotic evidence such as tree rings and coral. Climate models are mathematical models of past, present and future climates. Climate change may occur over long and short timescales from a variety of factors; recent warming is discussed in global warming.