THE CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL`S RISK
... that the risk-free rate should match the period of the cash flows, the authors conclude: “for most capital projects and corporate acquisitions, the yield on the US government Treasury bond of ten or more years in maturity would be appropriate.” (p. 26) The yields on risk-free securities are related ...
... that the risk-free rate should match the period of the cash flows, the authors conclude: “for most capital projects and corporate acquisitions, the yield on the US government Treasury bond of ten or more years in maturity would be appropriate.” (p. 26) The yields on risk-free securities are related ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from
... These empirical results have motivated some authors to work with a hybrid Phillips curve: besides the expected inflation term, the equation also contains a lagged term for inflation. In this paper, we do not have a special concern about the specific derivation for the persistence in 8. X = Q period ...
... These empirical results have motivated some authors to work with a hybrid Phillips curve: besides the expected inflation term, the equation also contains a lagged term for inflation. In this paper, we do not have a special concern about the specific derivation for the persistence in 8. X = Q period ...
Inflation Report, August 2016
... economy-wide minimum wage), their aggregate growth rate across the economy accelerated further, significantly exceeding labour productivity dynamics. Looking at consumer prices, the influence of external factors is prevalent for the time being, although the wage cost pressures that have been buildin ...
... economy-wide minimum wage), their aggregate growth rate across the economy accelerated further, significantly exceeding labour productivity dynamics. Looking at consumer prices, the influence of external factors is prevalent for the time being, although the wage cost pressures that have been buildin ...
$doc.title
... property market. House prices doubled between the end of 2001 and the end of 2007. Construction costs form a non-trivial fraction of the CPI in New Zealand and drove a particularly large fraction of inflation over the most recent cycle (Hargreaves et al., 2006). The average household’s debt rose fro ...
... property market. House prices doubled between the end of 2001 and the end of 2007. Construction costs form a non-trivial fraction of the CPI in New Zealand and drove a particularly large fraction of inflation over the most recent cycle (Hargreaves et al., 2006). The average household’s debt rose fro ...
Economics and Political Economy
... 2. Inflation Dynamics and Economic Growth in Tanzania Inflation is one of the key determinants of economic performance, indicating growth, demand conditions, and the levels and trends in monetary and fiscal policy stance (Rutasitara, 2004). Thus, at all times, even when the rate of inflation seems t ...
... 2. Inflation Dynamics and Economic Growth in Tanzania Inflation is one of the key determinants of economic performance, indicating growth, demand conditions, and the levels and trends in monetary and fiscal policy stance (Rutasitara, 2004). Thus, at all times, even when the rate of inflation seems t ...
Supply Constraints Are Not Valid Instrumental Variables for Home
... incomes, to be more creative (higher patents per capita), and to have higher leisure amenities (as measured by the number of tourist visits).” People can move, so if supply-constrained markets are relatively expensive, they should be more pleasant places to live or offer higher wages than other mark ...
... incomes, to be more creative (higher patents per capita), and to have higher leisure amenities (as measured by the number of tourist visits).” People can move, so if supply-constrained markets are relatively expensive, they should be more pleasant places to live or offer higher wages than other mark ...
Monetary Policy with Interest on Reserves
... Why does it matter so much whether the Fed pays interest on reserves with a large balance sheet, or reverts to a traditional very small balance sheet with non-interest-paying reserves? The short answers: optimal quantity of money, and financial stability. Optimal quantity of money Milton Friedman (1 ...
... Why does it matter so much whether the Fed pays interest on reserves with a large balance sheet, or reverts to a traditional very small balance sheet with non-interest-paying reserves? The short answers: optimal quantity of money, and financial stability. Optimal quantity of money Milton Friedman (1 ...
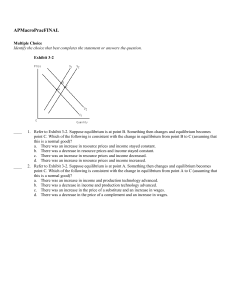
APMacroPracFIN
... ____ 45. The actual change in the money supply as a result of an increase in excess reserves will be less than the maximum change if banks a. do not lend out all of their excess reserves. b. borrow from the Federal Reserve. c. sell some of their government securities to the Federal Reserve. d. lend ...
... ____ 45. The actual change in the money supply as a result of an increase in excess reserves will be less than the maximum change if banks a. do not lend out all of their excess reserves. b. borrow from the Federal Reserve. c. sell some of their government securities to the Federal Reserve. d. lend ...
Chapter 7 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... translated into increased consumption and increased aggregate demand. In contrast, a decrease in consumption would accompany diminished consumer expectations and a decrease in consumer confidence, as happened after the stock market crash of 1929. The same problem has plagued the economies of most We ...
... translated into increased consumption and increased aggregate demand. In contrast, a decrease in consumption would accompany diminished consumer expectations and a decrease in consumer confidence, as happened after the stock market crash of 1929. The same problem has plagued the economies of most We ...
ExamView - CH 28 sample test questions.tst
... b. lowers the price level. c. decreases uncertainty. d. makes it easier to use money as a standard of account. e. makes money function less well as a store of value. ____ 61. During an inflation, a household with savings of $100,000 a. gains because inflation increases the value of their savings. b. ...
... b. lowers the price level. c. decreases uncertainty. d. makes it easier to use money as a standard of account. e. makes money function less well as a store of value. ____ 61. During an inflation, a household with savings of $100,000 a. gains because inflation increases the value of their savings. b. ...
MONETARY POLICY UNDER A NEW KEYNESIAN PERSPECTIVE
... that when oil is difficult to substitute in production, firms find optimal to charge higher relative prices as a premium in compensation for the risk that oil price volatility generates on their marginal costs. Chapter 3 uses the model laid out chapter 2 to investigate how monetary policy should rea ...
... that when oil is difficult to substitute in production, firms find optimal to charge higher relative prices as a premium in compensation for the risk that oil price volatility generates on their marginal costs. Chapter 3 uses the model laid out chapter 2 to investigate how monetary policy should rea ...
modules 31 to 35
... This does not mean that Monetary or Fiscal policies are ineffective. Short Run changes are important. ...
... This does not mean that Monetary or Fiscal policies are ineffective. Short Run changes are important. ...
Housing and Consumption in Spain Paloma Taltavull de La Paz
... renting. We are not going to tackle any aspects related to this kind of access to the market. It is implicitly considered that demand use to covers their residential necessity owning their house, something which reflect the existing evidence in Spain2. The issue that is raised here is focused to ana ...
... renting. We are not going to tackle any aspects related to this kind of access to the market. It is implicitly considered that demand use to covers their residential necessity owning their house, something which reflect the existing evidence in Spain2. The issue that is raised here is focused to ana ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... raise the capital intensity of an economy through its effect on the demand for liquidity. As nominal interest rates increase, the cost of holding nominal money balances rises, thereby shifting portfolio demand from money to real capital and putting downward pressure on interest rates (dr/dn < 1). Su ...
... raise the capital intensity of an economy through its effect on the demand for liquidity. As nominal interest rates increase, the cost of holding nominal money balances rises, thereby shifting portfolio demand from money to real capital and putting downward pressure on interest rates (dr/dn < 1). Su ...
Inflation dynamics, marginal cost, and the output gap:
... rationalize a disturbance (or “cost-push shock”) term in empirical NKPCs, that is the basis for the existence for a trade-off between price inflation and output gap variability. We will argue that such a shock term can be rationalized even in the absence of labor market rigidities, once one consider ...
... rationalize a disturbance (or “cost-push shock”) term in empirical NKPCs, that is the basis for the existence for a trade-off between price inflation and output gap variability. We will argue that such a shock term can be rationalized even in the absence of labor market rigidities, once one consider ...
Chapter 21(6): Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
... When aggregate demand increases, the AD curve shifts rightward. Three key factors shift the AD curve: ♦ Expectations — higher expected future incomes, higher expected inflation, or higher expected profits increase current aggregate demand. ♦ Fiscal policy and monetary policy — Fiscal policy is gover ...
... When aggregate demand increases, the AD curve shifts rightward. Three key factors shift the AD curve: ♦ Expectations — higher expected future incomes, higher expected inflation, or higher expected profits increase current aggregate demand. ♦ Fiscal policy and monetary policy — Fiscal policy is gover ...
Core Inflation: Concepts, Uses and Measurement
... price indices do not do so. Failure to allow for such substitution effects means that the aggregate price index will be affected by relative price movements. Third, prices may not be fully flexible in the short run. In particular, if there are costs associated with adjusting nominal prices, relative ...
... price indices do not do so. Failure to allow for such substitution effects means that the aggregate price index will be affected by relative price movements. Third, prices may not be fully flexible in the short run. In particular, if there are costs associated with adjusting nominal prices, relative ...
Chapter 36 MC — Five Debates Over Macroeconomic Policy
... 10. The Federal Reserve will tend to tighten monetary policy when a. interest rates are rising too rapidly. b. it thinks the unemployment rate is too high. c. the growth rate of real GDP is quite sluggish. d. it thinks inflation is too high today, or will become too high in the future. ANS: D PTS: 1 ...
... 10. The Federal Reserve will tend to tighten monetary policy when a. interest rates are rising too rapidly. b. it thinks the unemployment rate is too high. c. the growth rate of real GDP is quite sluggish. d. it thinks inflation is too high today, or will become too high in the future. ANS: D PTS: 1 ...
Inflation Inertia in Egypt and its Policy Implications
... Low inflation is a key for macroeconomic stability as evidenced by many country experiences, since high inflation in general hurt macroeconomic stability mainly through lower domestic savings by deeply negative real interest rates, lower capital accumulation due to increased uncertainty, and real ap ...
... Low inflation is a key for macroeconomic stability as evidenced by many country experiences, since high inflation in general hurt macroeconomic stability mainly through lower domestic savings by deeply negative real interest rates, lower capital accumulation due to increased uncertainty, and real ap ...
Kirjallisen työn pohja
... they may confront during an inflationary period. The main aim of this thesis is to clarify the potential effects of inflation on SMEs. In order to achieve this goal, theoretical background of inflation, current context of inflation in Vietnam and information about the Case Company are studied. The m ...
... they may confront during an inflationary period. The main aim of this thesis is to clarify the potential effects of inflation on SMEs. In order to achieve this goal, theoretical background of inflation, current context of inflation in Vietnam and information about the Case Company are studied. The m ...
Quantitative Easing and the Liquidity Channel of Monetary Policy
... and output. Whether this effect has quantitative power will depend on a number of factors, such as the degree of asset market integration, the elasticity of investment with respect to the price of capital, and the wage elasticity of the labor supply. But on the whole, the conclusion is that quantita ...
... and output. Whether this effect has quantitative power will depend on a number of factors, such as the degree of asset market integration, the elasticity of investment with respect to the price of capital, and the wage elasticity of the labor supply. But on the whole, the conclusion is that quantita ...