DNA, RNA and Protein
... This process produces two exact DNA molecules (Chromosomes) that are the same DNA never leaves the nucleus ...
... This process produces two exact DNA molecules (Chromosomes) that are the same DNA never leaves the nucleus ...
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS VIRTUAL LAB
... For each section read the question first and then read through the information on the website. As you go through the virtual lab, be sure to read all directions, follow all prompts given to you, and answer all of the following questions. DNA STRAND SIZE ...
... For each section read the question first and then read through the information on the website. As you go through the virtual lab, be sure to read all directions, follow all prompts given to you, and answer all of the following questions. DNA STRAND SIZE ...
Lecture 10: Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA)
... most organisms (humans, animals, bacteria, plants, and some viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is v ...
... most organisms (humans, animals, bacteria, plants, and some viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is v ...
Prepractical demo_SF_Class_2009
... Use another tube for negative control (no DNA) Add primers,nucleotides, Taq DNA polymerase, buffer ...
... Use another tube for negative control (no DNA) Add primers,nucleotides, Taq DNA polymerase, buffer ...
Chapter 20 Notes: DNA Technology
... 2) Isolate plasmid from bacterial cell; 3) cut both DNA samples with the same restriction enzyme to open up bacterial plasmid & create sticky ends on both ...
... 2) Isolate plasmid from bacterial cell; 3) cut both DNA samples with the same restriction enzyme to open up bacterial plasmid & create sticky ends on both ...
Annette Vinther Heydenreich
... Genetic immunization (DNA vaccines) has the potential to both produce neutralizing antibodies (humoral immune response) and cytotoxic T-cells (cellular immune response), which is believed to be essential in viral infections like HIV. In order to stop the viral replication at the site of entry, mucos ...
... Genetic immunization (DNA vaccines) has the potential to both produce neutralizing antibodies (humoral immune response) and cytotoxic T-cells (cellular immune response), which is believed to be essential in viral infections like HIV. In order to stop the viral replication at the site of entry, mucos ...
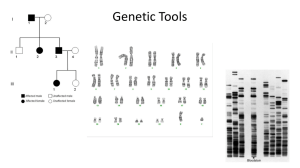
Genetic Tools
... • Genes that are carried on the X chromosome are called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X ...
... • Genes that are carried on the X chromosome are called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X ...
Chapter Outline - Ltcconline.net
... a. 61 code for amino acids and b. 3 are stop codons, instructing the ribosomes to end the polypeptide. 3. Because diverse organisms share a common genetic code, it is possible to program one species to produce a protein from another species by transplanting DNA I. Transcription: From DNA to RNA 1. T ...
... a. 61 code for amino acids and b. 3 are stop codons, instructing the ribosomes to end the polypeptide. 3. Because diverse organisms share a common genetic code, it is possible to program one species to produce a protein from another species by transplanting DNA I. Transcription: From DNA to RNA 1. T ...
Gene Technology Quest – Study Guide KEY What is a genome? A
... enzyme cuts DNA. Their importance is that this allows for DNA from other organisms to join this genome in order to make recombinant DNA. 9. How is recombinant DNA formed? Recombinant DNA is formed when a restriction enzyme cuts the DNA from one organism and DNA from another organism is added to the ...
... enzyme cuts DNA. Their importance is that this allows for DNA from other organisms to join this genome in order to make recombinant DNA. 9. How is recombinant DNA formed? Recombinant DNA is formed when a restriction enzyme cuts the DNA from one organism and DNA from another organism is added to the ...
direct genetic testing
... Genetic testing • testing for a pathogenic mutation in a certain gene in an individual that indicate a person’s risk of developing or transmitting a ...
... Genetic testing • testing for a pathogenic mutation in a certain gene in an individual that indicate a person’s risk of developing or transmitting a ...
Biotechnology
... DNA into a new bacterium. Recombinant DNA: DNA produced by combining DNA from different organisms ...
... DNA into a new bacterium. Recombinant DNA: DNA produced by combining DNA from different organisms ...
DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis
... amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
... amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering - Mrs. Moyer
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
struktur dan fungsi kromosom
... X-ray diffraction analysis DNA does not coil smoothly Base sequences dictate preferred nucleosome positions along DNA Spacing and structure affect genetic function ...
... X-ray diffraction analysis DNA does not coil smoothly Base sequences dictate preferred nucleosome positions along DNA Spacing and structure affect genetic function ...
Genetic Engineering
... organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products. ...
... organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products. ...
Heredity Notes - Madison County Schools / Overview
... Heredity-the passing of traits from parents to offspring. ...
... Heredity-the passing of traits from parents to offspring. ...
1 Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/530 2010 1. The concept of “one gene: one
... d. Removes mis-matched bases during DNA replication 19. A “perfect” molecular marker is one that a. Is tightly linked to the target gene of interest b. Interacts epistatically with the target gene of interest c. Is always monomorphic d. Is located in the target gene of interest 20. All molecular mar ...
... d. Removes mis-matched bases during DNA replication 19. A “perfect” molecular marker is one that a. Is tightly linked to the target gene of interest b. Interacts epistatically with the target gene of interest c. Is always monomorphic d. Is located in the target gene of interest 20. All molecular mar ...
What is DNA Fingerprinting
... the crime scene and one from a suspect -- came from the same individual. Fortunately, the genetic comparison doesn't require that investigators look at all of the DNA found in the tissue samples. That would take months or even years. Instead, by marking a small number of segments of DNA in one sampl ...
... the crime scene and one from a suspect -- came from the same individual. Fortunately, the genetic comparison doesn't require that investigators look at all of the DNA found in the tissue samples. That would take months or even years. Instead, by marking a small number of segments of DNA in one sampl ...
From Gene to Protein Part 2
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.