Class: AP Bio Unit: Genetics Estimated Date Target Reading
... require use of the rule of multiplication and two probability questions that require use of the rule of addition.) Describe non-mendelian inheritance and human genetic disorders. ...
... require use of the rule of multiplication and two probability questions that require use of the rule of addition.) Describe non-mendelian inheritance and human genetic disorders. ...
LDL receptors
... in a very short time. Denaturation at 94°C : During the denaturation, the double strand melts open to single stranded DNA. Annealing at 50-65°C : The primers are annealed. extension at 72°C : This is the ideal working temperature for the polymerase. The polymerase adds dNTP's from 5' to 3', reading ...
... in a very short time. Denaturation at 94°C : During the denaturation, the double strand melts open to single stranded DNA. Annealing at 50-65°C : The primers are annealed. extension at 72°C : This is the ideal working temperature for the polymerase. The polymerase adds dNTP's from 5' to 3', reading ...
C - TeacherWeb
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... pyrimidine (20.1) a family of nitrogenous bases that are components of nucleic acids and consist of a single six- sided ring. The common pyrimidines of DNA are cytosine and thymine; the common pyrimidines of RNA are cytosine and uracil. pyrimidine dimer (20.7) two adjacent pyrimidine bases in a DNA ...
... pyrimidine (20.1) a family of nitrogenous bases that are components of nucleic acids and consist of a single six- sided ring. The common pyrimidines of DNA are cytosine and thymine; the common pyrimidines of RNA are cytosine and uracil. pyrimidine dimer (20.7) two adjacent pyrimidine bases in a DNA ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... pyrimidine (20.1) a family of nitrogenous bases that are components of nucleic acids and consist of a single six- sided ring. The common pyrimidines of DNA are cytosine and thymine; the common pyrimidines of RNA are cytosine and uracil. pyrimidine dimer (20.7) two adjacent pyrimidine bases in a DNA ...
... pyrimidine (20.1) a family of nitrogenous bases that are components of nucleic acids and consist of a single six- sided ring. The common pyrimidines of DNA are cytosine and thymine; the common pyrimidines of RNA are cytosine and uracil. pyrimidine dimer (20.7) two adjacent pyrimidine bases in a DNA ...
DNA webquest
... Answer the following questions as you move through the animation of Transcription. Before clicking 1. The diagram represents what type of molecule? __________________________________ Click through the animation. 2. What function does the RNA polymerase have? __________________________________ 3. Whe ...
... Answer the following questions as you move through the animation of Transcription. Before clicking 1. The diagram represents what type of molecule? __________________________________ Click through the animation. 2. What function does the RNA polymerase have? __________________________________ 3. Whe ...
DNA Technology
... solely by the sequence of their base pairs. However, because there are so many millions of base pairs, the task would be very time-consuming. Instead, scientists are able to use a shorter method, because of repeating patterns in DNA. These patterns do not, however, give an individual "fingerprint," ...
... solely by the sequence of their base pairs. However, because there are so many millions of base pairs, the task would be very time-consuming. Instead, scientists are able to use a shorter method, because of repeating patterns in DNA. These patterns do not, however, give an individual "fingerprint," ...
Genes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Question: A pair of PCR primers are designed to be complementary to sites 120-135 and 440-465 of the human b-globin gene. What is the expected size of the amplification product if these primers are used with a human DNA template? Answer: 120 - 465 = 345 bp Question: If the template is DNA from a bab ...
... Question: A pair of PCR primers are designed to be complementary to sites 120-135 and 440-465 of the human b-globin gene. What is the expected size of the amplification product if these primers are used with a human DNA template? Answer: 120 - 465 = 345 bp Question: If the template is DNA from a bab ...
Study Island
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
Bio 309F
... 19. The size of a gene is defined by A. start codon B. stop codon C. Introns D. A and B E. A, B, and C are correct 20. Biological functions of proteins/polypeptides (mechanism whereby the genetic information of a gene is carried out by proteins) are determined by A. number of amino acids B. ratio of ...
... 19. The size of a gene is defined by A. start codon B. stop codon C. Introns D. A and B E. A, B, and C are correct 20. Biological functions of proteins/polypeptides (mechanism whereby the genetic information of a gene is carried out by proteins) are determined by A. number of amino acids B. ratio of ...
The first midterm will consist of 20 four
... 7) A SNP is an example of a) a frame shift mutation b) transpositional control c) genetic regulation d) a genetic marker 8) The gene defect for both Huntington's Disease and Fragile-X syndrome consists of a) a series of repeated nucleotide sequences b) a mispairing of base pairs c) a major ...
... 7) A SNP is an example of a) a frame shift mutation b) transpositional control c) genetic regulation d) a genetic marker 8) The gene defect for both Huntington's Disease and Fragile-X syndrome consists of a) a series of repeated nucleotide sequences b) a mispairing of base pairs c) a major ...
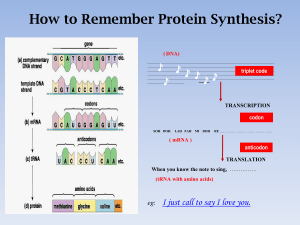
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Practice MC Questions
... Which of the following statements regarding the DNA of a gene being expressed is true? A. After unwinding, both of the DNA strands act as ...
... Which of the following statements regarding the DNA of a gene being expressed is true? A. After unwinding, both of the DNA strands act as ...
PCR - share1
... (such as skin used in burn treatment). - Therapeutic cloning, (the creation of an embryo to supply embryonic stem cells for medical use) is only allowed to the blastocyst stage in most places: uses? pros and cons? - The race is on to reprogram ...
... (such as skin used in burn treatment). - Therapeutic cloning, (the creation of an embryo to supply embryonic stem cells for medical use) is only allowed to the blastocyst stage in most places: uses? pros and cons? - The race is on to reprogram ...
DNA switches
... microscopic nucleus of a cell — that it fits only because it is tightly wound and coiled around itself. When they looked at the three-dimensional structure — the hairball — Encode researchers discovered that small segments of dark-matter DNA are often quite close to genes they control. In the past, ...
... microscopic nucleus of a cell — that it fits only because it is tightly wound and coiled around itself. When they looked at the three-dimensional structure — the hairball — Encode researchers discovered that small segments of dark-matter DNA are often quite close to genes they control. In the past, ...
Key concepts_Regulation of transcription in
... gene expression. Certain modifications, like lysine acetylation, correlate strongly with gene activity. Others are associated with gene silencing. Histone replacement variants also play a role in gene regulation. For example, H2A.Z is often found in nucleosomes that flank nucleosome-free regions, wh ...
... gene expression. Certain modifications, like lysine acetylation, correlate strongly with gene activity. Others are associated with gene silencing. Histone replacement variants also play a role in gene regulation. For example, H2A.Z is often found in nucleosomes that flank nucleosome-free regions, wh ...
Name: “Berry Full of DNA” DNA Extraction Lab Question: What
... opportunity to examine the DNA closely. ...
... opportunity to examine the DNA closely. ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY - Bishop Amat Memorial High School
... Genetic Engineering Techniques Definition: Technology that uses genetic and recombinant DNA methods to devise new combinations of genes to produce improved pharmaceutical and agricultural products. ...
... Genetic Engineering Techniques Definition: Technology that uses genetic and recombinant DNA methods to devise new combinations of genes to produce improved pharmaceutical and agricultural products. ...
下載 - 國立高雄師範大學
... (A) they are both present in pairs in all diploid cells (B) they both undergo segregation during meiosos (C) they both pair up with their homologous during prophase of mitosis (D) their copy number in the dell decrease after meiosis, and increase during fertilization (E) they are both copied during ...
... (A) they are both present in pairs in all diploid cells (B) they both undergo segregation during meiosos (C) they both pair up with their homologous during prophase of mitosis (D) their copy number in the dell decrease after meiosis, and increase during fertilization (E) they are both copied during ...
DNA Methylation studies
... DNA methylation is one of the several post-synthetic modifications that normal DNA goes through after each replication. Methylation does not alter the DNA sequence but alters its function, and it plays an important role by interfering DNA-protein interactions such as during transcription. DNA methyl ...
... DNA methylation is one of the several post-synthetic modifications that normal DNA goes through after each replication. Methylation does not alter the DNA sequence but alters its function, and it plays an important role by interfering DNA-protein interactions such as during transcription. DNA methyl ...
Y13 Biology Y2 PLCs Student Teacher 1
... Epigenetics involves heritable changes in gene function, without changes to the base sequence of DNA. These changes are caused by changes in the environment that inhibit transcription by: increased methylation of the DNA or decreased acetylation of associated histones. The relevance of epigeneti ...
... Epigenetics involves heritable changes in gene function, without changes to the base sequence of DNA. These changes are caused by changes in the environment that inhibit transcription by: increased methylation of the DNA or decreased acetylation of associated histones. The relevance of epigeneti ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.