Biological Diversity Topic 5
... • The arrangement of these four bases form the entire genetic code • The backbone of the ladder is always the same Sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar • The structure is similar to a ladder that has been twisted into a spiral – it is known as a double helix • James Watson and Francis Crick were th ...
... • The arrangement of these four bases form the entire genetic code • The backbone of the ladder is always the same Sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar • The structure is similar to a ladder that has been twisted into a spiral – it is known as a double helix • James Watson and Francis Crick were th ...
-1- Biophysics 204 Graphics problem set - nucleic acid
... two zinc finger-DNA complexes, Zif268 and GLI. Throughout the exercise, you should keep a few general principles in mind: 1) many proteins use α-helices, sometimes called "recognition helices" to make contacts in the DNA major groove, 2) the orientation of the recognition helix is determined largely ...
... two zinc finger-DNA complexes, Zif268 and GLI. Throughout the exercise, you should keep a few general principles in mind: 1) many proteins use α-helices, sometimes called "recognition helices" to make contacts in the DNA major groove, 2) the orientation of the recognition helix is determined largely ...
DNA Technology
... pick up naked foreign DNA wherever it may be hanging out have surface transport proteins that are ...
... pick up naked foreign DNA wherever it may be hanging out have surface transport proteins that are ...
document
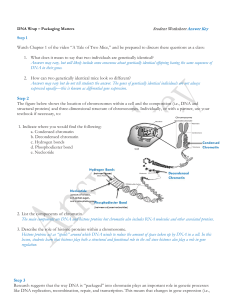
... The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of space taken up by DNA in a cell. In ...
... The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of space taken up by DNA in a cell. In ...
Genomes
... Because strands in a DNA double helix run in opposite directions, the new strands must be made in different ways. Therefore, one daughter strand ( leading strand) is synthesized continuously, in the direction of fork movement, while the strand synthesized in the opposite direction ( the lagging stra ...
... Because strands in a DNA double helix run in opposite directions, the new strands must be made in different ways. Therefore, one daughter strand ( leading strand) is synthesized continuously, in the direction of fork movement, while the strand synthesized in the opposite direction ( the lagging stra ...
Next lectures: Differential Gene expression
... • A-T rich DNA sequences which associate with the nuclear matrix • Hypothesized to define domains of regulatory influence in chromatin • MARs that affect gene expression are often next to defined enhancers (Igm heavy chain) • Improve transgene expression – Limiting influence of integration site – Tr ...
... • A-T rich DNA sequences which associate with the nuclear matrix • Hypothesized to define domains of regulatory influence in chromatin • MARs that affect gene expression are often next to defined enhancers (Igm heavy chain) • Improve transgene expression – Limiting influence of integration site – Tr ...
Genomes 1
... Fragments pass through a detector in size order The colour of the last base inserted is determined Remember, each of the four ddNTPs has a different colour fluorescent dye attached ...
... Fragments pass through a detector in size order The colour of the last base inserted is determined Remember, each of the four ddNTPs has a different colour fluorescent dye attached ...
Name SIS # 1 Introductory Biochemistry BI 28 Third Midterm
... (b) List two problems in E. coli that might arise in producing a protein identical to that isolated from mammalian cells and describe each problem in no more than two sentences. ...
... (b) List two problems in E. coli that might arise in producing a protein identical to that isolated from mammalian cells and describe each problem in no more than two sentences. ...
Bioethics Lesson Plan
... person (except identical twins) has a unique DNA fingerprint. DNA fingerprints are used to identify organisms Identify the parents of child Identify a rapist or murder in a criminal case DNA fingerprint technique is very to a Southern Blot test. Summarize two major goals of the Human Genome ...
... person (except identical twins) has a unique DNA fingerprint. DNA fingerprints are used to identify organisms Identify the parents of child Identify a rapist or murder in a criminal case DNA fingerprint technique is very to a Southern Blot test. Summarize two major goals of the Human Genome ...
*J5JT*_§JJU: ~$f4~*
... A) For a linkage map, markers are spaced by recombination frequency, whereas for a physical map they are spaced by numbers of base pairs (bp). B) There is no difference between the two except in the type of pictorial representation. C) For a linkage map, it is shown how each gene is linked to every ...
... A) For a linkage map, markers are spaced by recombination frequency, whereas for a physical map they are spaced by numbers of base pairs (bp). B) There is no difference between the two except in the type of pictorial representation. C) For a linkage map, it is shown how each gene is linked to every ...
Biotechnology
... Certain disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are linked to speci c genes. Some scientists would like to use gene therapy to cure such disorders. Gene therapy involves replacing the nonworking cells with cells that have been genetically altered. Which of these is a logical argument against gene the ...
... Certain disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are linked to speci c genes. Some scientists would like to use gene therapy to cure such disorders. Gene therapy involves replacing the nonworking cells with cells that have been genetically altered. Which of these is a logical argument against gene the ...
DNA cloning yields multiple copies of a gene or
... 30. In your own words, what is ‘DNA sequencing’ (do not give me the uses of sequencing data obtained through DNA sequencing, but explain to me what this sequencing data is that you get from performing ...
... 30. In your own words, what is ‘DNA sequencing’ (do not give me the uses of sequencing data obtained through DNA sequencing, but explain to me what this sequencing data is that you get from performing ...
BACTERIA TRANSFORMATION LAB (ACTIVITY)
... basic transformation process is to first select the desired gene to be inserted into the organism and select a bacterial plasmid, and then cut these two DNA molecules into fragments using special enzymes called restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments are spliced together with an enzyme called ligase. ...
... basic transformation process is to first select the desired gene to be inserted into the organism and select a bacterial plasmid, and then cut these two DNA molecules into fragments using special enzymes called restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments are spliced together with an enzyme called ligase. ...
Mutations - TeacherWeb
... What do mutations do to the protein? Are they all bad or all good? The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called ...
... What do mutations do to the protein? Are they all bad or all good? The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called ...
Metabolic Processes
... y These complexes do the folds of mitochondria. y The electron transport chain passes each electron along gradually lowering the electron’s energy level. ...
... y These complexes do the folds of mitochondria. y The electron transport chain passes each electron along gradually lowering the electron’s energy level. ...
Modern Genetics Notes
... Every cell does not constantly synthesize every polypeptide it has the ability to make. For example, cells in the pancreas are not always producing tons of insulin because it is not always needed in that quantity That means that every gene in a cell is not turned on all the time. How does a cell kno ...
... Every cell does not constantly synthesize every polypeptide it has the ability to make. For example, cells in the pancreas are not always producing tons of insulin because it is not always needed in that quantity That means that every gene in a cell is not turned on all the time. How does a cell kno ...
Chapter 16 Recombination DNA and Genetic Engineering
... • 2. An underground stem sends up new shoots that are clones • 3. Members of a bacterial colony on a petri dish are clones because • they all came from division of the same cell. • 4. Human identical twins are clones; the original single embryo separate to become two individuals. • 5. Gene cloning i ...
... • 2. An underground stem sends up new shoots that are clones • 3. Members of a bacterial colony on a petri dish are clones because • they all came from division of the same cell. • 4. Human identical twins are clones; the original single embryo separate to become two individuals. • 5. Gene cloning i ...
Organic Compounds Worksheet
... _________________________________________________________________ 14. Give an example of a starch. ________________________________________ 15. Give an example of a place where you would find glycogen. ________________ 16. Where do you find phospholipids? ____________________________________ 17. Whe ...
... _________________________________________________________________ 14. Give an example of a starch. ________________________________________ 15. Give an example of a place where you would find glycogen. ________________ 16. Where do you find phospholipids? ____________________________________ 17. Whe ...
Ch. 12 Notes
... These mutations are not passed down to offspring Sex cell: If the mutations occurs in the sex cells it will be passed down to the offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutation may or may not affect the offspring. ...
... These mutations are not passed down to offspring Sex cell: If the mutations occurs in the sex cells it will be passed down to the offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutation may or may not affect the offspring. ...
Document
... addition to the basic medium that supports growth of wild-type. 7. The function of a protein is strongly dependent upon its __tertiary__________ structure that consists of prominent foldings of the polypeptide chain that are stabilized by non-covalent and, sometime, covalent interactions. 8. __eukar ...
... addition to the basic medium that supports growth of wild-type. 7. The function of a protein is strongly dependent upon its __tertiary__________ structure that consists of prominent foldings of the polypeptide chain that are stabilized by non-covalent and, sometime, covalent interactions. 8. __eukar ...
INTEGRATED MICROSYSTEM FOR FORENSIC DNA
... are slow and labor-intensive. Federal and state crime laboratories have a large number of DNA samples waiting for STR analysis. To address this backlog, and prevent a recurring backlog, the FBI Laboratory has recently sought new technologies that enable rapid STR typing. STR typing has been demonstr ...
... are slow and labor-intensive. Federal and state crime laboratories have a large number of DNA samples waiting for STR analysis. To address this backlog, and prevent a recurring backlog, the FBI Laboratory has recently sought new technologies that enable rapid STR typing. STR typing has been demonstr ...
What is the Structure of DNA?
... the pathogenic strain with living cells of the harmless strain, some living ...
... the pathogenic strain with living cells of the harmless strain, some living ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.