BIO 110 Survey of Biology QZM 3 QA 150701.1
... b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the following do nucleic acids and proteins have in common? a. They are both made of amino acids. b. Their ...
... b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the following do nucleic acids and proteins have in common? a. They are both made of amino acids. b. Their ...
Fetal Psychology
... strongly of curry, cumin, garlic, onion and other essences from a mother's diet. Whether fetuses can taste these flavors isn't yet known, but scientists have found that a 33-week-old preemie will suck harder on a sweetened nipple than on a plain rubber one. "During the last trimester, the fetus is ...
... strongly of curry, cumin, garlic, onion and other essences from a mother's diet. Whether fetuses can taste these flavors isn't yet known, but scientists have found that a 33-week-old preemie will suck harder on a sweetened nipple than on a plain rubber one. "During the last trimester, the fetus is ...
PPT presentation - Yavapai College
... DNA is transcribed and translated to make proteins that run cell metabolism • DNA is transcribed to mRNA • mRNA is translated to amino acid sequence • Amino acid sequence folds up into protein • Proteins catalyze reactions of cell metabolism • This process is called “gene expression”—the informatio ...
... DNA is transcribed and translated to make proteins that run cell metabolism • DNA is transcribed to mRNA • mRNA is translated to amino acid sequence • Amino acid sequence folds up into protein • Proteins catalyze reactions of cell metabolism • This process is called “gene expression”—the informatio ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET
... The first step of protein synthesis is __________________. This step occurs in the _________________ of the cell. During this step the enzyme __________________________ makes a copy of a gene out of RNA. This is called a _________________ RNA or mRNA. Some parts of mRNA called ______________ have to ...
... The first step of protein synthesis is __________________. This step occurs in the _________________ of the cell. During this step the enzyme __________________________ makes a copy of a gene out of RNA. This is called a _________________ RNA or mRNA. Some parts of mRNA called ______________ have to ...
Lecture_note_463BI
... 60 to 90 tRNA isoacceptors (Lin and Agris, 1980). The studies by McBride et al. (1989) as well as studies by others (see, e.g., 180620, 189930, 189920, 180640, 189880) indicated that tRNA genes and pseudogenes are dispersed on at least 7 human chromosomes and suggested that these sequences would pro ...
... 60 to 90 tRNA isoacceptors (Lin and Agris, 1980). The studies by McBride et al. (1989) as well as studies by others (see, e.g., 180620, 189930, 189920, 180640, 189880) indicated that tRNA genes and pseudogenes are dispersed on at least 7 human chromosomes and suggested that these sequences would pro ...
IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT TO THE ENGLISH SPRINGER
... It is important to note that there are a large number of dogs that have tested as genetically affected, but are reported as clinically normal by their owners. This is also similar to the situation in Miniature Longhaired Dachshunds. With the wide range of age of onset observed for PRA in ESS, it may ...
... It is important to note that there are a large number of dogs that have tested as genetically affected, but are reported as clinically normal by their owners. This is also similar to the situation in Miniature Longhaired Dachshunds. With the wide range of age of onset observed for PRA in ESS, it may ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 32. In the pedigree you just completed, explain why you know the genotype of one female in the third generation, but are unsure of the other. ...
... 32. In the pedigree you just completed, explain why you know the genotype of one female in the third generation, but are unsure of the other. ...
CHAPTER 14: DNA: THE GENETIC MATERIAL
... experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand served as a template for the production of a new one and each old and new strand then intertwined to become a new helix. Double-stranded DNA replication is complicated since new nucleotide ...
... experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand served as a template for the production of a new one and each old and new strand then intertwined to become a new helix. Double-stranded DNA replication is complicated since new nucleotide ...
Guidelines for Diagnostic Imaging During Pregnancy
... animals exposed to large doses of radiation (ie, 100–200 rad). However, in humans, growth restriction, microcephaly, and mental retardation are the most common adverse effects from high-dose radiation (3, 6, 7). Based on data from atomic bomb survivors, it appears that the risk of central nervous sy ...
... animals exposed to large doses of radiation (ie, 100–200 rad). However, in humans, growth restriction, microcephaly, and mental retardation are the most common adverse effects from high-dose radiation (3, 6, 7). Based on data from atomic bomb survivors, it appears that the risk of central nervous sy ...
Using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy, DNA
... membranes [5-6], but these early TIRFM experiments were not yet able to resolve individual molecules. The use of TIRFM for visualizing single fluorescent molecules was brought about through significant advances in charge-coupled device (CCD) technologies that greatly enhanced the ability of these ca ...
... membranes [5-6], but these early TIRFM experiments were not yet able to resolve individual molecules. The use of TIRFM for visualizing single fluorescent molecules was brought about through significant advances in charge-coupled device (CCD) technologies that greatly enhanced the ability of these ca ...
Genetics - nimitz163
... heterozygous individuals, ONLY the dominant allele achieves expression. The recessive allele is present but remains unexpressed. In order to express a recessive allele, one has to be homozygous for the trait (they must have 2 recessive alleles) pg. 119 #5 ...
... heterozygous individuals, ONLY the dominant allele achieves expression. The recessive allele is present but remains unexpressed. In order to express a recessive allele, one has to be homozygous for the trait (they must have 2 recessive alleles) pg. 119 #5 ...
Chemical Structure of Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Evidences, DNA is
... The nucleic acids are the hereditary determinants of living organisms. They are the macromolecules present in most living cells either in the free state or bound to proteins as nucleoproteins. There are two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Both are pres ...
... The nucleic acids are the hereditary determinants of living organisms. They are the macromolecules present in most living cells either in the free state or bound to proteins as nucleoproteins. There are two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Both are pres ...
2.2 Genetics, advanced
... nucleic acid sequence that was made in the cytoplasm, every group of three nucleic acids is called a CODON. Each codon codes for one amino acid. For example, if the first three nucleic acids are G, C, T, when you check that code in a manual, you find that means the first amino acid is Alanine. If ...
... nucleic acid sequence that was made in the cytoplasm, every group of three nucleic acids is called a CODON. Each codon codes for one amino acid. For example, if the first three nucleic acids are G, C, T, when you check that code in a manual, you find that means the first amino acid is Alanine. If ...
Gene transfer from organelles to the nucleus: Frequent and in big
... monas reinhardtii. C. reinhardtii has one (and only one) chloroplast per cell. They examined ⬇13 billion homoplastomic transformants looking for a single stable nuclear transfer, and found none at all. Of course, that negative result could be due to any number of things, so they checked to see wheth ...
... monas reinhardtii. C. reinhardtii has one (and only one) chloroplast per cell. They examined ⬇13 billion homoplastomic transformants looking for a single stable nuclear transfer, and found none at all. Of course, that negative result could be due to any number of things, so they checked to see wheth ...
LP - Columbia University
... Some enzymes recognize relatively short sequences. For example, an enzyme may be a "4 cutter" = enzyme that recognizes a 4 base pair site. (See handout.) Short sites (sequences) are found more often, and enzymes that cut them produce many relatively short fragments. Some enzymes recognize longer seq ...
... Some enzymes recognize relatively short sequences. For example, an enzyme may be a "4 cutter" = enzyme that recognizes a 4 base pair site. (See handout.) Short sites (sequences) are found more often, and enzymes that cut them produce many relatively short fragments. Some enzymes recognize longer seq ...
Full-Text PDF
... is an essential step in population analysis, especially for next generation sequencing applications. Many nanoparticles as well as naturally occurring clay minerals contain charged surfaces or edges that capture negatively charged DNA molecules after cell lysis within DNA extraction. Depending on th ...
... is an essential step in population analysis, especially for next generation sequencing applications. Many nanoparticles as well as naturally occurring clay minerals contain charged surfaces or edges that capture negatively charged DNA molecules after cell lysis within DNA extraction. Depending on th ...
Quantitative analysis to assess the performance of the
... chromosomal changes in cancer. As cancerous cells multiply, they can undergo dramatic chromosomal changes, including chromosome loss, duplication, and the translocation of DNA from one chromosome to another. Chromosome aberrations have previously been detected using optical imaging of whole chromoso ...
... chromosomal changes in cancer. As cancerous cells multiply, they can undergo dramatic chromosomal changes, including chromosome loss, duplication, and the translocation of DNA from one chromosome to another. Chromosome aberrations have previously been detected using optical imaging of whole chromoso ...
Uniparental Disomy (UPD)
... The 46 chromosomes in each cell of the human body can be divided into 23 pairs.1 Normally, one chromosome of each pair is inherited from the mother and one from the father. Uniparental disomy (UPD) is an atypical inheritance pattern in which both members of a single pair of chromosomes are inherited ...
... The 46 chromosomes in each cell of the human body can be divided into 23 pairs.1 Normally, one chromosome of each pair is inherited from the mother and one from the father. Uniparental disomy (UPD) is an atypical inheritance pattern in which both members of a single pair of chromosomes are inherited ...
chapter 17 and 18 study guide
... repressor’s shape so that it cannot bind to the operator thus switching the operon on. Enhancer? A segment of eukaryotic DNA containing multiple control elements usually located far from the gene whose transcription it regulates Activators? Proteins that bind to certain mediator proteins and general ...
... repressor’s shape so that it cannot bind to the operator thus switching the operon on. Enhancer? A segment of eukaryotic DNA containing multiple control elements usually located far from the gene whose transcription it regulates Activators? Proteins that bind to certain mediator proteins and general ...
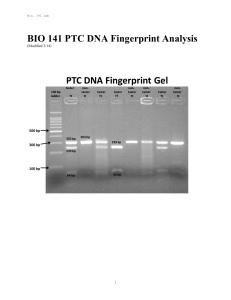
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA Fingerprinting and its Role in Forensics Genetic uniqueness is a fact of life. From generation to generation, characteristics are inherited, combined, and assorted among individuals through a common denominator: the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. No two individuals have identical DNA seq ...
... DNA Fingerprinting and its Role in Forensics Genetic uniqueness is a fact of life. From generation to generation, characteristics are inherited, combined, and assorted among individuals through a common denominator: the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. No two individuals have identical DNA seq ...