Lab 1 Artificial Selection The purpose of a particular investigation
... DNA has an overall (-) and it is inserted in a wells on a gel made of aragose. Agarose is porous and DNA fragments can move through the gel. The size of pores can be regulated by adjusting the concentration of agarose used. The gel is inserted into an electrophoresis box and covered with a buffer. T ...
... DNA has an overall (-) and it is inserted in a wells on a gel made of aragose. Agarose is porous and DNA fragments can move through the gel. The size of pores can be regulated by adjusting the concentration of agarose used. The gel is inserted into an electrophoresis box and covered with a buffer. T ...
Advanced Genetics
... • Potentially fatal blood disease caused by a parasite that is transmitted to humans and animal hosts by the mosquito. • Human parasite digests the red blood cell’s hemoglobin and changes the properties of the cell ...
... • Potentially fatal blood disease caused by a parasite that is transmitted to humans and animal hosts by the mosquito. • Human parasite digests the red blood cell’s hemoglobin and changes the properties of the cell ...
Transmission & maternal effects
... female gametes, depending upon the specific system Drive systems can be located on autosomes or sex chromosomes Drive occurs through a variety of molecular genetic mechanisms, each a unique story ...
... female gametes, depending upon the specific system Drive systems can be located on autosomes or sex chromosomes Drive occurs through a variety of molecular genetic mechanisms, each a unique story ...
Chapter 12 Notes
... 1. Do you think that cells produce all the proteins for which the DNA (genes) code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the typ ...
... 1. Do you think that cells produce all the proteins for which the DNA (genes) code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the typ ...
human_growth_la
... Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell penetrates an egg cell and the two haploid cells combine to form a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes in a human. There are numerous obstacles and challenges for a sperm and egg cell to combine starting with the fact that many sperm cells do not even make it to t ...
... Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell penetrates an egg cell and the two haploid cells combine to form a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes in a human. There are numerous obstacles and challenges for a sperm and egg cell to combine starting with the fact that many sperm cells do not even make it to t ...
Chapter 6 - Lemon Bay High School
... Addition, deletion, or rearrangement of individual genes ...
... Addition, deletion, or rearrangement of individual genes ...
Inborn Errors of Metabolism BCH 451
... X –Linked Inheritance • The gene is present on the X -chromosome. • Each son has a 50% chance of receiving the mutant gene from the mother • Daughters also have a 50% chance, but will also inherit a normal X from the father . • Variable phenotype in carrier daughters, because of random X inactivati ...
... X –Linked Inheritance • The gene is present on the X -chromosome. • Each son has a 50% chance of receiving the mutant gene from the mother • Daughters also have a 50% chance, but will also inherit a normal X from the father . • Variable phenotype in carrier daughters, because of random X inactivati ...
Structure-Function Relationship in DNA sequence Recognition by
... where mab is the number of pairs, amino acid a and base b observed, w is the weight given to each observation, f(s) is the relative frequency of occurrence of any amino acids at grid point s, and gab(s) is the equivalent relative frequency of occurrence of amino acid a against base b. R and T are ga ...
... where mab is the number of pairs, amino acid a and base b observed, w is the weight given to each observation, f(s) is the relative frequency of occurrence of any amino acids at grid point s, and gab(s) is the equivalent relative frequency of occurrence of amino acid a against base b. R and T are ga ...
Homologous Recombination (Introductory Concepts
... chromosome, which is a lethal event (unless fixed by repair). Two exchanges will leave the chromosome in its circular viable state. Hence, in most instances of homologous recombination in bacteria, we are considering a minimum of two exchanges, or higher even number of ex ...
... chromosome, which is a lethal event (unless fixed by repair). Two exchanges will leave the chromosome in its circular viable state. Hence, in most instances of homologous recombination in bacteria, we are considering a minimum of two exchanges, or higher even number of ex ...
Deception Through Terminology - Part 1 of 7
... Thus, we could analyze the DNA structure of thousands of animals (without seeing the animals themselves, only their DNA) and determine which animals are in the same "species." Ditto for plants. For example, in order for a Chihuahua and a Great Dane to be in the same "species" their DNA must be the s ...
... Thus, we could analyze the DNA structure of thousands of animals (without seeing the animals themselves, only their DNA) and determine which animals are in the same "species." Ditto for plants. For example, in order for a Chihuahua and a Great Dane to be in the same "species" their DNA must be the s ...
book ppt - Castle High School
... Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that are passed on from one cell, or organism, to another. Mutations occur by a variety of processes. ...
... Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that are passed on from one cell, or organism, to another. Mutations occur by a variety of processes. ...
1) From DNA to protein 2) Gene mutation
... Mutations may have benefits: • Provide the raw material for evolution in the form of genetic diversity • Diversity may benefit the organism immediately—if mutation is in somatic cells • Or may cause an advantageous change in offspring ...
... Mutations may have benefits: • Provide the raw material for evolution in the form of genetic diversity • Diversity may benefit the organism immediately—if mutation is in somatic cells • Or may cause an advantageous change in offspring ...
DNA and Its Role in Heredity
... Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that are passed on from one cell, or organism, to another. Mutations occur by a variety of processes. ...
... Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that are passed on from one cell, or organism, to another. Mutations occur by a variety of processes. ...
DNA - An overview - World of Teaching
... The Hershey – Chase Experiment • Additional direct evidence indicating that DNA is the genetic material was published in 1952 by A.D. Hershey (1969 Nobel Prize winner) and M.Chase. • These experiments showed that the genetic information of a particular bacterial virus (bacteriophage T2) was presen ...
... The Hershey – Chase Experiment • Additional direct evidence indicating that DNA is the genetic material was published in 1952 by A.D. Hershey (1969 Nobel Prize winner) and M.Chase. • These experiments showed that the genetic information of a particular bacterial virus (bacteriophage T2) was presen ...
Fuggles
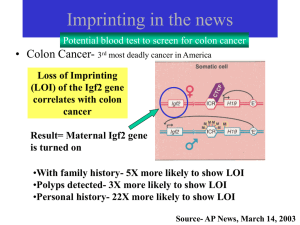
... location where the gene can be found on the chromosome is referred to as the gene locus. The gene “pair” is technically referred to as a gene, as both members of the pair code for the same trait. A gene could consist of a variety of different forms, but only two forms are ever present per gene (one ...
... location where the gene can be found on the chromosome is referred to as the gene locus. The gene “pair” is technically referred to as a gene, as both members of the pair code for the same trait. A gene could consist of a variety of different forms, but only two forms are ever present per gene (one ...
PowerPoint
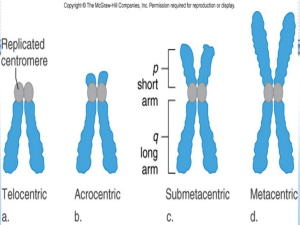
... • Karyotyping has shown that not all of chromosome 21 has to be present in triplicate to produce Down syndrome • In a few rare individuals, the only extra chromosomal material is the distal half of the long arm of chromosome 21. • This region houses most of the genes including a gene for an enzyme i ...
... • Karyotyping has shown that not all of chromosome 21 has to be present in triplicate to produce Down syndrome • In a few rare individuals, the only extra chromosomal material is the distal half of the long arm of chromosome 21. • This region houses most of the genes including a gene for an enzyme i ...
Using Molecular Markers in Plant Genetics
... the discovery and detection of important genes in crops. Just as the name indicates, SNPs are identified by a single nucleotide base change in the genetic code at a specific location on the chromosome. Once ...
... the discovery and detection of important genes in crops. Just as the name indicates, SNPs are identified by a single nucleotide base change in the genetic code at a specific location on the chromosome. Once ...
Science League Biology I Exam January 2014 Choose the answer
... 52. Cytokinesis usually, but not always, follows mitosis. If a cell completed mitosis but not cytokinesis, the result would be a cell with a. a single large nucleus b. high concentrations of actin and myosin c. two abnormally small nuclei d. two nuclei e. two nuclei but with half the amount of DNA 5 ...
... 52. Cytokinesis usually, but not always, follows mitosis. If a cell completed mitosis but not cytokinesis, the result would be a cell with a. a single large nucleus b. high concentrations of actin and myosin c. two abnormally small nuclei d. two nuclei e. two nuclei but with half the amount of DNA 5 ...
Physicochemical studies on interactions between DNA and RNA
... mixing was 0.425, corresponding to a concentration of 48.3 yg/ml. The DNA was mixed with equal volume of RNA polymerase with a concentration of 207 yg/ml before mixing. The absorbance difference measured at 4°C is given by the triangles. The filled circles give the absorbance difference measured at ...
... mixing was 0.425, corresponding to a concentration of 48.3 yg/ml. The DNA was mixed with equal volume of RNA polymerase with a concentration of 207 yg/ml before mixing. The absorbance difference measured at 4°C is given by the triangles. The filled circles give the absorbance difference measured at ...
No Origin, No Problem for Yeast DNA Replication
... during each cell cycle. In budding yeast, DNA replication initiates from well-defined origins called autonomously replicating sequences (ARSs), while in multicellular organisms replication it is thought to initiate from broader, less well-defined zones. Interestingly, some recent work has suggested ...
... during each cell cycle. In budding yeast, DNA replication initiates from well-defined origins called autonomously replicating sequences (ARSs), while in multicellular organisms replication it is thought to initiate from broader, less well-defined zones. Interestingly, some recent work has suggested ...