Activity Name - Science4Inquiry.com
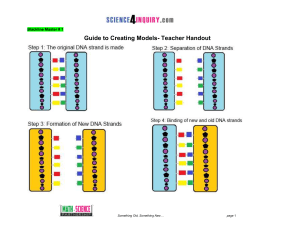
... Something Old, Something New… You are a Molecular Biologist who is studying the process of DNA replication. Your task is to build a model that represents this process. Next you will investigate where DNA replication took place in the human body and explain why it occurred. This activity is divided u ...
... Something Old, Something New… You are a Molecular Biologist who is studying the process of DNA replication. Your task is to build a model that represents this process. Next you will investigate where DNA replication took place in the human body and explain why it occurred. This activity is divided u ...
From father From mother
... hair, so he will definitely have straight hair (regardless of if his genotype is CC or Cc.) ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... hair, so he will definitely have straight hair (regardless of if his genotype is CC or Cc.) ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Lab Section_____________ Prelab questions for Lab 8 1. For each
... developed and it cannot be treated effectively. Because the onset is typically late in life, individuals bear offspring and pass this gene on before they realize they carry it. Consequently this disease is easily transmitted to later generations. A diagnostic test has been developed using DNA analys ...
... developed and it cannot be treated effectively. Because the onset is typically late in life, individuals bear offspring and pass this gene on before they realize they carry it. Consequently this disease is easily transmitted to later generations. A diagnostic test has been developed using DNA analys ...
Selection of Candidate Genes for Population Studies
... prostate cancer cases and controls. We will explore the independent effect of those SNPs on the risk of prostate cancer. We will also add the haplotype tagging SNPs of the DSBR pathways in order to identify haplotypes associated with prostate cancer risk. Those additional studies will have a greater ...
... prostate cancer cases and controls. We will explore the independent effect of those SNPs on the risk of prostate cancer. We will also add the haplotype tagging SNPs of the DSBR pathways in order to identify haplotypes associated with prostate cancer risk. Those additional studies will have a greater ...
Mutations and Evolution
... mRNA. In RNA the nucleic acid base uracil (U) replaces the thymine in DNA, so investigations have found that many uracil pairs with the adenine in DNA during copying. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules of the ‘frequent mutations’ in the attached to each of the amino acids each have complementary triplet ...
... mRNA. In RNA the nucleic acid base uracil (U) replaces the thymine in DNA, so investigations have found that many uracil pairs with the adenine in DNA during copying. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules of the ‘frequent mutations’ in the attached to each of the amino acids each have complementary triplet ...
Unit 10.1.4 - Measuring Genetic Variation using Molecular Markers
... enzyme coded by different alleles at one gene locus. Isozymes are different molecular forms of an enzyme coded by more than one gene locus. However, the term ‘isozymes’ is freely used for both situations. Polymorphisms in DNA DNA can be compared in many different ways in order to identify polymorphi ...
... enzyme coded by different alleles at one gene locus. Isozymes are different molecular forms of an enzyme coded by more than one gene locus. However, the term ‘isozymes’ is freely used for both situations. Polymorphisms in DNA DNA can be compared in many different ways in order to identify polymorphi ...
MUTATIONS
... codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain the wrong amino acids. It will most likely not be functional. Frameshift mutations frequently result in se ...
... codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain the wrong amino acids. It will most likely not be functional. Frameshift mutations frequently result in se ...
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays
... CTX-M-2 Group, AAC(6′)-lb-cr and aadA1. For each Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate, results from the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array were confirmed by pyrosequencing. Representative pyrograms for [A] SHV-156G, [B] SHV-238/240, [C] KPC and [D] CTX-M-1 group are shown. For SHV variant ...
... CTX-M-2 Group, AAC(6′)-lb-cr and aadA1. For each Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate, results from the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array were confirmed by pyrosequencing. Representative pyrograms for [A] SHV-156G, [B] SHV-238/240, [C] KPC and [D] CTX-M-1 group are shown. For SHV variant ...
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays
... CTX-M-2 Group, AAC(6′)-lb-cr and aadA1. For each Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate, results from the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array were confirmed by pyrosequencing. Representative pyrograms for [A] SHV-156G, [B] SHV-238/240, [C] KPC and [D] CTX-M-1 group are shown. For SHV variant ...
... CTX-M-2 Group, AAC(6′)-lb-cr and aadA1. For each Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate, results from the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array were confirmed by pyrosequencing. Representative pyrograms for [A] SHV-156G, [B] SHV-238/240, [C] KPC and [D] CTX-M-1 group are shown. For SHV variant ...
what is mutation?
... during replication, base pairing gets altered leading to mutation. In their rare imino or enol states, they can form adenine-cytosine and guanine-thymine base pairing. ...
... during replication, base pairing gets altered leading to mutation. In their rare imino or enol states, they can form adenine-cytosine and guanine-thymine base pairing. ...
BlastLecture8
... • If query is a coding gene: translate and search protein database • Search PDB if you want a 3-D structure • Search NR if you want any hit • Search UniProt if you want to know what the hits ...
... • If query is a coding gene: translate and search protein database • Search PDB if you want a 3-D structure • Search NR if you want any hit • Search UniProt if you want to know what the hits ...
Smith, GF and Warren, ST: The biology of Down syndrome. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 450: 1-9 (1985).
... is quite unusual in normal newborn infants. Thus, it has long been considered that on the chromosome 21 there resides a gene or genes involved in hemopoiesis or that, in some fashion, predisposes trisomic individuals toward leukemia. Some support for this idea may be drawn from cytogenetic studies i ...
... is quite unusual in normal newborn infants. Thus, it has long been considered that on the chromosome 21 there resides a gene or genes involved in hemopoiesis or that, in some fashion, predisposes trisomic individuals toward leukemia. Some support for this idea may be drawn from cytogenetic studies i ...
FnrP interactions with the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin promoter
... of the translational start site of lktC di¡ers from the consensus site by ¢ve additional bases in the central variable region. Overlapping the palindromic sequence is a known IHF binding site located 281^268 bp upstream of the translational start site of lktC [7]. The 3P end of the IHF binding site ...
... of the translational start site of lktC di¡ers from the consensus site by ¢ve additional bases in the central variable region. Overlapping the palindromic sequence is a known IHF binding site located 281^268 bp upstream of the translational start site of lktC [7]. The 3P end of the IHF binding site ...
Molecular phylogeny, part B
... between DNA sequences to be inferred by making comparisons between those sequences. Multigene family: A group of genes, clustered or dispersed, with related nucleotide sequences. Multiple alignment: An alignment of three or more nucleotide sequences. Multiple hit or multiple substitution: The situat ...
... between DNA sequences to be inferred by making comparisons between those sequences. Multigene family: A group of genes, clustered or dispersed, with related nucleotide sequences. Multiple alignment: An alignment of three or more nucleotide sequences. Multiple hit or multiple substitution: The situat ...
Microsatellite Repeat Variation Within the y1 Gene of Maize and
... Mexico and Guatemala that exhibits various plant forms (annual and perennial), ploidy levels (2N and AN) and cytogenetic characteristics [reviewed by Galinat (1988)]. Three of the four annual teosintes are classified as two subspecies of Zea mays (i.e., ssp. mexicana and ssp. parviglumis) and the Z ...
... Mexico and Guatemala that exhibits various plant forms (annual and perennial), ploidy levels (2N and AN) and cytogenetic characteristics [reviewed by Galinat (1988)]. Three of the four annual teosintes are classified as two subspecies of Zea mays (i.e., ssp. mexicana and ssp. parviglumis) and the Z ...
Karyotype Lab information
... The Role of DNA and Chromosomes 1. During cell division, DNA condenses and coils to form chromosomes. 2. Each chromosome contains millions of nitrogen base pairs which serve as genes. 3. Each gene controls the production of a protein in the organism which creates a trait (characteristic). ...
... The Role of DNA and Chromosomes 1. During cell division, DNA condenses and coils to form chromosomes. 2. Each chromosome contains millions of nitrogen base pairs which serve as genes. 3. Each gene controls the production of a protein in the organism which creates a trait (characteristic). ...
definitive non definitive non-invasive invasive prenatal diagnosis
... Aneuploidy Detection (+21) • Determine total chromosome 21 transcripts (maternal and fetal) in trisomic and nonnon-trisomic pregnancy • If 10% of cell free DNA in maternal blood is fetal,, trisomic p pregnancies g should provide 5% greater chromosome 21 fetal transcripts than disomic pregnancies ...
... Aneuploidy Detection (+21) • Determine total chromosome 21 transcripts (maternal and fetal) in trisomic and nonnon-trisomic pregnancy • If 10% of cell free DNA in maternal blood is fetal,, trisomic p pregnancies g should provide 5% greater chromosome 21 fetal transcripts than disomic pregnancies ...
Biology 120 Lab Exam 2 Review Session
... Identify whether each of the following is True or False. If it is false, correct the statement. _____ The Y chromosome is smaller than the X chromosome . _____ Interphase is the longest phase in the cell cycle. _____ Meiosis produces two genetically identical offspring. _____ In animals, gametes are ...
... Identify whether each of the following is True or False. If it is false, correct the statement. _____ The Y chromosome is smaller than the X chromosome . _____ Interphase is the longest phase in the cell cycle. _____ Meiosis produces two genetically identical offspring. _____ In animals, gametes are ...
Types of mutation
... genome that sit between genes, and usually they have no effect. When variations occur within genes, there is more often a consequence, but even then mutation only rarely causes death or disease. Mutation also generates new variations that can give an individual a survival ...
... genome that sit between genes, and usually they have no effect. When variations occur within genes, there is more often a consequence, but even then mutation only rarely causes death or disease. Mutation also generates new variations that can give an individual a survival ...
Sequence Alignment - Faculty of Science at Bilkent University
... binds to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript. The target site (blue) is cleaved followed by reverse transcription, with the 3' end of the target site as the primer. Newly synthesized cDNA is shown in pale green. Ligation of the cDNA occurs at the 5' end, and the second strand is synthesized using the ...
... binds to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript. The target site (blue) is cleaved followed by reverse transcription, with the 3' end of the target site as the primer. Newly synthesized cDNA is shown in pale green. Ligation of the cDNA occurs at the 5' end, and the second strand is synthesized using the ...
Identification of a Novel Streptococcal Gene
... promotes the spread of antibiotic resistance. In S. aureus, antibiotic-induced SOS responses affect virulence by modulating mobile genetic elements and affecting chromosomal virulence gene expression (4, 25, 37, 67). Remarkably, SOS-induced error-prone DnaE2 polymerase, by its mutagenic activity, co ...
... promotes the spread of antibiotic resistance. In S. aureus, antibiotic-induced SOS responses affect virulence by modulating mobile genetic elements and affecting chromosomal virulence gene expression (4, 25, 37, 67). Remarkably, SOS-induced error-prone DnaE2 polymerase, by its mutagenic activity, co ...
The Sexual Nature of the Eukaryote Genome
... This paper supports a previous conjecture that the sexual cycle of eukaryotes arose from the infection of cells by genome parasites. The finding are as follows. (1) In prokaryotes, conjugative plasmids ensure their own spread by directing partial cell fusion. (2) Conjugative plasmids permit gene tra ...
... This paper supports a previous conjecture that the sexual cycle of eukaryotes arose from the infection of cells by genome parasites. The finding are as follows. (1) In prokaryotes, conjugative plasmids ensure their own spread by directing partial cell fusion. (2) Conjugative plasmids permit gene tra ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.























