Genetics: The Information Broker
... In genetic crosses the re-current quantitative ratio of 3:1 among offspring supports the presence of ____ copy/copies of each gene in an organism of all species of eukaryotes. ...
... In genetic crosses the re-current quantitative ratio of 3:1 among offspring supports the presence of ____ copy/copies of each gene in an organism of all species of eukaryotes. ...
Lab 6: Electrophoresis
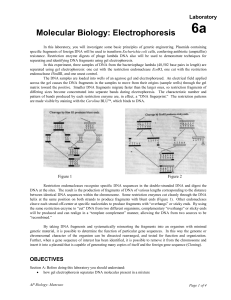
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
2.4 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... –Genetic code – universal language of genetics used by virtually all living organisms •Works in three nucleotide units of mRNA called codons •Each codon codes for a single amino acid •One amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon –There are 64 codons and only 20 amino acids – degeneracy of ...
... –Genetic code – universal language of genetics used by virtually all living organisms •Works in three nucleotide units of mRNA called codons •Each codon codes for a single amino acid •One amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon –There are 64 codons and only 20 amino acids – degeneracy of ...
Lecture_8
... • They are then broken again to allow the technology to sequence each within a reasonable array. ...
... • They are then broken again to allow the technology to sequence each within a reasonable array. ...
Activation of Transcription
... genetic information needed to create an adult is in our genome. Embryonic cells undergo differentiation to produce specific cell types such as muscle, nerve, and blood cells. Different cell types are the consequence of differential gene expression. ...
... genetic information needed to create an adult is in our genome. Embryonic cells undergo differentiation to produce specific cell types such as muscle, nerve, and blood cells. Different cell types are the consequence of differential gene expression. ...
Describe the central dogma of molecular biology.
... information in cells is from DNA, to RNA, to proteins. Basically, genes control the traits of organisms by controlling which proteins are made. Although there are exceptions, in general, each gene codes for the production of one polypeptide. ...
... information in cells is from DNA, to RNA, to proteins. Basically, genes control the traits of organisms by controlling which proteins are made. Although there are exceptions, in general, each gene codes for the production of one polypeptide. ...
All information is taken from open sources, mostly wikipedia Flu
... Marburg virus (believed to be under development as of 1992) Machupo virus (believed to be under development as of 1992) Veepox (hybrid of Venezuelan equine encephalitis with smallpox)[citation needed] Ebolapox (hybrid of ebola with smallpox)[citation needed] Annual production capacities for many of ...
... Marburg virus (believed to be under development as of 1992) Machupo virus (believed to be under development as of 1992) Veepox (hybrid of Venezuelan equine encephalitis with smallpox)[citation needed] Ebolapox (hybrid of ebola with smallpox)[citation needed] Annual production capacities for many of ...
Whose DNA was sequenced for the Human Genome Project?
... Although humans appear to have stopped accumulating repeated DNA over 50 million years ago, there seems to be no such decline in rodents. This may account for some of the fundamental differences between hominids and rodents, although gene estimates are similar in these species. Scientists have propo ...
... Although humans appear to have stopped accumulating repeated DNA over 50 million years ago, there seems to be no such decline in rodents. This may account for some of the fundamental differences between hominids and rodents, although gene estimates are similar in these species. Scientists have propo ...
Chapter 8 Human Genetics and Biotechnology Worksheets
... think of female as the default sex of the human species. Can you think of a reason why the Y chromosome is so much smaller than the X chromosome? Human Genes Humans have an estimated 20,000 to 22,000 genes. This may sound like a lot, but it really isn’t. Far simpler species have almost as many genes ...
... think of female as the default sex of the human species. Can you think of a reason why the Y chromosome is so much smaller than the X chromosome? Human Genes Humans have an estimated 20,000 to 22,000 genes. This may sound like a lot, but it really isn’t. Far simpler species have almost as many genes ...
Genetic engineering of human FSH (Gonal
... proteins must also follow a set of instructions. These instructions are carried by another macromolecule called DNA which, in mammalian cells, is found in the chromosomes which are located in the nucleus. The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide, comprising a base, a sugar and a phosphate gro ...
... proteins must also follow a set of instructions. These instructions are carried by another macromolecule called DNA which, in mammalian cells, is found in the chromosomes which are located in the nucleus. The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide, comprising a base, a sugar and a phosphate gro ...
Annotation Practice Activity [Based on materials from the GEP
... A genome is the total genetic content of an organism. In order to study a genome, DNA is isolated from a convenient tissue source, digested with a battery of restriction enzymes or physically broken into 1-2 kb DNA fragments and cloned into appropriate vectors. The total of all the cloned fragments ...
... A genome is the total genetic content of an organism. In order to study a genome, DNA is isolated from a convenient tissue source, digested with a battery of restriction enzymes or physically broken into 1-2 kb DNA fragments and cloned into appropriate vectors. The total of all the cloned fragments ...
Assignment 2
... 3. Circle coding codons; cross-out non-coding areas 4. Draw a diagram showing the sequence of mRNA before and after splicing as well as complementary tRNA in a proper order carrying proper aminoacids. 5. Suggest 3 different point mutations in the DNA sequence that could happen inside the coding area ...
... 3. Circle coding codons; cross-out non-coding areas 4. Draw a diagram showing the sequence of mRNA before and after splicing as well as complementary tRNA in a proper order carrying proper aminoacids. 5. Suggest 3 different point mutations in the DNA sequence that could happen inside the coding area ...
Metagenomics: DNA sequencing of environmental samples
... be greatly accelerated by microbes that derive energy from the reaction (chemolithotrophs)46. Microbial communities flourish under these seemingly hostile conditions, forming extensive underwater streamers and floating biofilms anchored in pyritic sediments, but are typically of relatively low diver ...
... be greatly accelerated by microbes that derive energy from the reaction (chemolithotrophs)46. Microbial communities flourish under these seemingly hostile conditions, forming extensive underwater streamers and floating biofilms anchored in pyritic sediments, but are typically of relatively low diver ...
Name ______ Date ______ Must be completed by March 13, 2015
... What is a protein? 17. Our bodies contain about 100 _________________ cells. In these cells the machines that do work are molecules called _____________. 18. Animals feel pain because cells called n_________ send messages to the brain. Draw one of these cells. R ___________ proteins on the cells ena ...
... What is a protein? 17. Our bodies contain about 100 _________________ cells. In these cells the machines that do work are molecules called _____________. 18. Animals feel pain because cells called n_________ send messages to the brain. Draw one of these cells. R ___________ proteins on the cells ena ...
Protein Synthesis Webquest
... A. Go to: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 ...
... A. Go to: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 ...
Transcription and translation ppt
... DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand It does this by covalently bonding ribonucleoside triphosphates that align opposite their exposed complementary partner (using the energ ...
... DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand It does this by covalently bonding ribonucleoside triphosphates that align opposite their exposed complementary partner (using the energ ...
Chapter 3 Proteins: - California State University San Marcos
... using integrase also encoded by transposon ...
... using integrase also encoded by transposon ...
Real Cats Wear Pink
... specialists, who, she said, were interested in the prospect of creating a genetic model for fighting diseases. A tool to spot cystic-fibrosis The Audubon scientists want to use their technique to develop a gene-therapy treatment for cystic fibrosis, an incurable hereditary disease for which, Gomez s ...
... specialists, who, she said, were interested in the prospect of creating a genetic model for fighting diseases. A tool to spot cystic-fibrosis The Audubon scientists want to use their technique to develop a gene-therapy treatment for cystic fibrosis, an incurable hereditary disease for which, Gomez s ...
Lab 08-Bacterial Transformation
... In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for one or more trai ...
... In this activity, you will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria naturally contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for one or more trai ...
9.3 – Blueprint of Life - Resource Centre / FrontPage
... accompanied by selection, allow change over many generations: Outline the impact on the evolution of plants and animals of: Changes in the physical conditions in the environment: Changes in the chemical condition in the environment: Competition for resources: – Evolutionary theory states tha ...
... accompanied by selection, allow change over many generations: Outline the impact on the evolution of plants and animals of: Changes in the physical conditions in the environment: Changes in the chemical condition in the environment: Competition for resources: – Evolutionary theory states tha ...
Ahmad Shah Blueprint of Life
... accompanied by selection, allow change over many generations: Outline the impact on the evolution of plants and animals of: Changes in the physical conditions in the environment: Changes in the chemical condition in the environment: Competition for resources: – Evolutionary theory states tha ...
... accompanied by selection, allow change over many generations: Outline the impact on the evolution of plants and animals of: Changes in the physical conditions in the environment: Changes in the chemical condition in the environment: Competition for resources: – Evolutionary theory states tha ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.