Histological identifications of lesions
... minutesv. A few modifications were done e.g. the final extension time at 720 C was modified to 35 minutes to reduce stutter bands and the number of cycles was increased from 24 to 30 in the PCR to increase the yield. Since degradation of DNA by formalin fixation limits reproducible amplification of ...
... minutesv. A few modifications were done e.g. the final extension time at 720 C was modified to 35 minutes to reduce stutter bands and the number of cycles was increased from 24 to 30 in the PCR to increase the yield. Since degradation of DNA by formalin fixation limits reproducible amplification of ...
제3회 한국분자세포생물학회 이동성 유전인자분과 학술대회
... The NGS technologies of genome DNA structure, expression profiling and epigenome elements have been used widely as approaches in the expertise of genome biology and genetics. The application to genome study has been particularly developed with the introduction of the nextgeneration DNA sequencer (NG ...
... The NGS technologies of genome DNA structure, expression profiling and epigenome elements have been used widely as approaches in the expertise of genome biology and genetics. The application to genome study has been particularly developed with the introduction of the nextgeneration DNA sequencer (NG ...
2011 - Barley World
... 51. Based on this sequence, you can tell that it came from an exon and not an intron a. T b. F 52. RNA differs from DNA in that a. It is usually single stranded b. It contains triose rather than deoxyribose c. It contains the base adenine rather than thymine d. It is always single stranded 53. tRNA ...
... 51. Based on this sequence, you can tell that it came from an exon and not an intron a. T b. F 52. RNA differs from DNA in that a. It is usually single stranded b. It contains triose rather than deoxyribose c. It contains the base adenine rather than thymine d. It is always single stranded 53. tRNA ...
Genome Sequencing Using a Mapping Approach
... Mapping Approach Ultimately through the use of these techniques a high density physical map of sequence polymorphisms can be generated and used as the basis for squencing the genome. ...
... Mapping Approach Ultimately through the use of these techniques a high density physical map of sequence polymorphisms can be generated and used as the basis for squencing the genome. ...
Lecture 3: Prokaryotes and Protists
... Prokaryotes use specialized infolded regions of the plasma membrane to perform many metabolic functions a. Lack organelles for cellular respiration and photosynthesis Prokaryotes have smaller, simpler genomes than eukaryotes a. Genome usually consists of a ring of DNA with few associated proteins b. ...
... Prokaryotes use specialized infolded regions of the plasma membrane to perform many metabolic functions a. Lack organelles for cellular respiration and photosynthesis Prokaryotes have smaller, simpler genomes than eukaryotes a. Genome usually consists of a ring of DNA with few associated proteins b. ...
Document
... c. The organism that carry the altered gene. d. The organism that carry the normal gene. 47- Phenyl kotonuria is an example of………………………. a. Deletion mutation. b. Null mutation. c. Nonsense mutation. d. Missense mutation. 48- The Sickle cell anemia patient will show ………….genotype. a. Hb AC. ...
... c. The organism that carry the altered gene. d. The organism that carry the normal gene. 47- Phenyl kotonuria is an example of………………………. a. Deletion mutation. b. Null mutation. c. Nonsense mutation. d. Missense mutation. 48- The Sickle cell anemia patient will show ………….genotype. a. Hb AC. ...
Targeted Genome Editing for Gene Containment in
... Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) was introduced into the black ash genome through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation using hypocotyl explants. Adventitious shoots were regenerated from transformed cells showing kanamycinresistance, and the presence of the Bt-gene was confirmed. Once roots are formed o ...
... Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) was introduced into the black ash genome through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation using hypocotyl explants. Adventitious shoots were regenerated from transformed cells showing kanamycinresistance, and the presence of the Bt-gene was confirmed. Once roots are formed o ...
EOC Review Questions
... 69. What disease is caused by uncontrolled, abnormal cell division? a. Leprosy b. cancer c. heart disease d. tuberculosis 70. What is the purpose of DNA polymerase? A) It carries genetic information to the ribosomes. B) It produces a complementary copy of a strand of DNA. C) It constructs RNA chains ...
... 69. What disease is caused by uncontrolled, abnormal cell division? a. Leprosy b. cancer c. heart disease d. tuberculosis 70. What is the purpose of DNA polymerase? A) It carries genetic information to the ribosomes. B) It produces a complementary copy of a strand of DNA. C) It constructs RNA chains ...
Welcome to Comp 665 - UNC Computational Genetics
... Sequence Organization • The DNA sequence is broken into several independent segments organized into structures called chromosomes • Chromosomes vary between different organisms. The DNA molecule may be circular or linear, and can contain from 10,000 to 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. • Simple single-cel ...
... Sequence Organization • The DNA sequence is broken into several independent segments organized into structures called chromosomes • Chromosomes vary between different organisms. The DNA molecule may be circular or linear, and can contain from 10,000 to 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. • Simple single-cel ...
Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens
... aphids; the chlamydiae; and the parasitic spirochetes, such as Borrelia burgdorferi (the agent of Lyme disease). Small genome size in these organisms is associated with other distinctive genetic features, including rapid evolution of polypeptide sequences and low genomic G⫹C content (Figure 1). The ...
... aphids; the chlamydiae; and the parasitic spirochetes, such as Borrelia burgdorferi (the agent of Lyme disease). Small genome size in these organisms is associated with other distinctive genetic features, including rapid evolution of polypeptide sequences and low genomic G⫹C content (Figure 1). The ...
Chapter 18 Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
... mutagens do not become mutations because cells have repair mechanisms called nucleotide excision repair (NER). • NER can prevent mutations by cutting out damaged areas and resynthesizing the proper sequence. ...
... mutagens do not become mutations because cells have repair mechanisms called nucleotide excision repair (NER). • NER can prevent mutations by cutting out damaged areas and resynthesizing the proper sequence. ...
Scientific Process Chapter 1
... _______________Does my dog eat better when exposed to a particular color of light? _______________ Observe the dog’s feeding habits for seven days, using a regular light and then for seven days with a colored light. _______________My dog ate his entire meal each of the 14 days in just under 3 minute ...
... _______________Does my dog eat better when exposed to a particular color of light? _______________ Observe the dog’s feeding habits for seven days, using a regular light and then for seven days with a colored light. _______________My dog ate his entire meal each of the 14 days in just under 3 minute ...
Αρχές Ιατρικής Γενετικής - e
... syndrome. Note his coarse facial features, crouched stance, thickened digits, and protuberant abdomen. B, Transgenic mice with a targeted disruption of α-liduronidase. Progressive coarsening of the face is apparent as 8-week-old mice (left) grow to become 52-week-old mice ...
... syndrome. Note his coarse facial features, crouched stance, thickened digits, and protuberant abdomen. B, Transgenic mice with a targeted disruption of α-liduronidase. Progressive coarsening of the face is apparent as 8-week-old mice (left) grow to become 52-week-old mice ...
Monster Central Dogma - Lincoln Park High School
... 5. Suggest a substitution mutation in the DNA that would cause the first amino acid in the “# of Eyes” gene to change from alanine (Ala) to valine (Val). Write the original DNA codon, then the mutated DNA codon. (1) 6. There is a substitution mutation in the gene for Fangs in which the first DNA bas ...
... 5. Suggest a substitution mutation in the DNA that would cause the first amino acid in the “# of Eyes” gene to change from alanine (Ala) to valine (Val). Write the original DNA codon, then the mutated DNA codon. (1) 6. There is a substitution mutation in the gene for Fangs in which the first DNA bas ...
Chromosomal changes associated with changes in development
... trying to establish the concept of the karyotype; again one of constancy but in this case it is of number, shape and size of mitotic chromosomes. These structurally static visions of a constant genotype fitted in with the emerging information about how genes could be regulated and it became possible ...
... trying to establish the concept of the karyotype; again one of constancy but in this case it is of number, shape and size of mitotic chromosomes. These structurally static visions of a constant genotype fitted in with the emerging information about how genes could be regulated and it became possible ...
NAR Breakthrough Article Identification of a mismatch
... (14), alkyl transfer (15), damage reversion (16) and translesion synthesis (17) pathways, which are more similar to their eukaryal than bacterial counterparts, as also observed in DNA replication and recombination. Biochemical studies of the repair-related proteins in Archaea have been reported, but ...
... (14), alkyl transfer (15), damage reversion (16) and translesion synthesis (17) pathways, which are more similar to their eukaryal than bacterial counterparts, as also observed in DNA replication and recombination. Biochemical studies of the repair-related proteins in Archaea have been reported, but ...
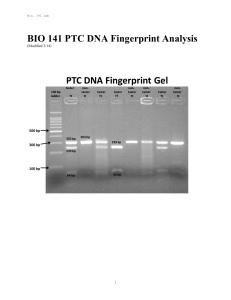
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
documentation dates
... teachers may want to supplement this information as long as all local and State standards from the following pages are completely met by the end of the thirty-six week course. The science teachers are also required to cover the State Department wellness objectives. The suggested teaching schedule mu ...
... teachers may want to supplement this information as long as all local and State standards from the following pages are completely met by the end of the thirty-six week course. The science teachers are also required to cover the State Department wellness objectives. The suggested teaching schedule mu ...
File
... diploid cells – similar in shape, structure, and size and have the same genes, but not necessarily the same alleles. ...
... diploid cells – similar in shape, structure, and size and have the same genes, but not necessarily the same alleles. ...
Full-Text PDF
... dilution of the extracts resulted in amplification of DNA. Through dilution there was a decreased amount of inhibitors, but also less DNA molecules in the sample. The aim of the dilution series was to find at least one dilution for each method to obtain a PCR product. There was no method in which al ...
... dilution of the extracts resulted in amplification of DNA. Through dilution there was a decreased amount of inhibitors, but also less DNA molecules in the sample. The aim of the dilution series was to find at least one dilution for each method to obtain a PCR product. There was no method in which al ...
Dot plot - TeachLine
... Compare new genes to known ones Compare genes from different species information about evolution ...
... Compare new genes to known ones Compare genes from different species information about evolution ...
Document
... •No DNA synthesis occurs –Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, but with two main differences •1. Haploid set of chromosomes •2. Sister chromatids are not identical ...
... •No DNA synthesis occurs –Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, but with two main differences •1. Haploid set of chromosomes •2. Sister chromatids are not identical ...
LESSON 17.4 LESSON 17.4
... neutral mutations tend to accumulate in the DNA of different species at about the same rate. Researchers can compare such DNA sequences in two species. The comparison can reveal how many mutations have occurred independently in each group, as shown in Figure 17–18. The more differences there are bet ...
... neutral mutations tend to accumulate in the DNA of different species at about the same rate. Researchers can compare such DNA sequences in two species. The comparison can reveal how many mutations have occurred independently in each group, as shown in Figure 17–18. The more differences there are bet ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.