Spherical Mirrors
... the path (2) that passes through the focal point F of the concave mirror, or appears to pass through the focal point of the convex mirror. This is because the incident and reflected rays make equal angles with the radius of curvature at the point of incidence. 3. Ray (3) passes through the focal poi ...
... the path (2) that passes through the focal point F of the concave mirror, or appears to pass through the focal point of the convex mirror. This is because the incident and reflected rays make equal angles with the radius of curvature at the point of incidence. 3. Ray (3) passes through the focal poi ...
optical properties of dielectric mirrors, produced by large area glass
... The production of highly reflective surfaces used as mirrors could be classified into wet coating and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. In case of wet coating, the metal used as reflective substrate is silver. It is deposited onto the glass surface, via certain chemical process as result of c ...
... The production of highly reflective surfaces used as mirrors could be classified into wet coating and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. In case of wet coating, the metal used as reflective substrate is silver. It is deposited onto the glass surface, via certain chemical process as result of c ...
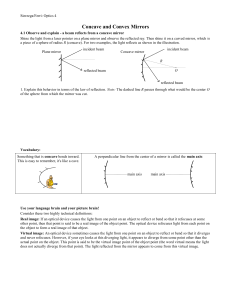
Concave and Convex Mirrors
... Point the beams of the lasers parallel to the main axis of the mirror (a horizontal axis through the center of the mirror). After reflection, they all pass through the same point exactly in the middle between the mirror and the center of the sphere from which the mirror was cut. This point is called ...
... Point the beams of the lasers parallel to the main axis of the mirror (a horizontal axis through the center of the mirror). After reflection, they all pass through the same point exactly in the middle between the mirror and the center of the sphere from which the mirror was cut. This point is called ...
Chapter Notes
... Only two incident rays are needed to find the image but you can use another by drawing the incident ray through the vertex and measuring the angle of incidence, this in turn tells you the angle of reflection that gives you the reflected ray. Three different images are produced in the concave mirror ...
... Only two incident rays are needed to find the image but you can use another by drawing the incident ray through the vertex and measuring the angle of incidence, this in turn tells you the angle of reflection that gives you the reflected ray. Three different images are produced in the concave mirror ...
Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine optical tools to extend vision far into space. As you will see, some ...
... tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine optical tools to extend vision far into space. As you will see, some ...
Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... Mirrors, lenses, and other optical inventions are called optical tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine opt ...
... Mirrors, lenses, and other optical inventions are called optical tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine opt ...
lecture23
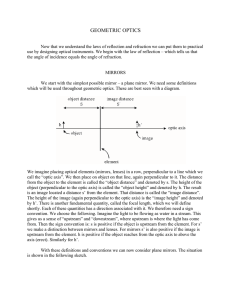
... Object Distance. When the object is on the same side as the incoming light, the object distance is positive (otherwise is negative). Image Distance. When the image is on the same side as the outgoing light, the image distance is positive (otherwise is negative). (negative image distance virtual im ...
... Object Distance. When the object is on the same side as the incoming light, the object distance is positive (otherwise is negative). Image Distance. When the image is on the same side as the outgoing light, the image distance is positive (otherwise is negative). (negative image distance virtual im ...
Physics 221 – Lab 7 Spherical mirrors
... Materials: optics bench, incandescent light source, 50 mm concave mirror, viewing screen, crossed arrow target, and three component holders. Set up the light source at the far left end of the optics bench. Somewhere near the middle of the bench, place the crossed arrow target (on a component holder) ...
... Materials: optics bench, incandescent light source, 50 mm concave mirror, viewing screen, crossed arrow target, and three component holders. Set up the light source at the far left end of the optics bench. Somewhere near the middle of the bench, place the crossed arrow target (on a component holder) ...
MIRRORS reflect light and obey the law
... The image can be seen on a __________________________ or a piece of paper. This image is called a _________________ ___________________. ...
... The image can be seen on a __________________________ or a piece of paper. This image is called a _________________ ___________________. ...
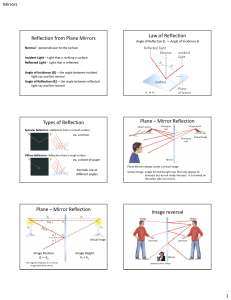
Reflection from Plane Mirrors Law of Reflection Types of Reflection
... 2. Next, Follow the rules of reflection for concave mirrors. – The ray that went through the focal point then reflects parallel to the principle axis – The ray that moved parallel will then reflect through the focal point. ...
... 2. Next, Follow the rules of reflection for concave mirrors. – The ray that went through the focal point then reflects parallel to the principle axis – The ray that moved parallel will then reflect through the focal point. ...
6th grade reflection lab final
... absorb any of the light but instead bounces it back off the surface. A mirror is flat, smooth, and polished. When light hits a mirror it is not absorbed but is reflected off at a very predictable angle. The angle that the light hits the mirror is called the angle of incidence. The angle of light tha ...
... absorb any of the light but instead bounces it back off the surface. A mirror is flat, smooth, and polished. When light hits a mirror it is not absorbed but is reflected off at a very predictable angle. The angle that the light hits the mirror is called the angle of incidence. The angle of light tha ...
Optics
... 2. The term ‘virtual” is chosen to distinguish this type of image from a “real” image, in which the rays do not pass through a point of intersection ...
... 2. The term ‘virtual” is chosen to distinguish this type of image from a “real” image, in which the rays do not pass through a point of intersection ...
Parallel-plate MEMS Mirror Design for Large On
... and allows for easy fabrication, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. ...
... and allows for easy fabrication, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. ...
Quiz 9
... *1. (5pts) A person walks into a room that has, on opposite walls, two plane mirrors producing multiple images. Find the distance from the person to the third image seen in the left-hand mirror when the person is 1.50 m away from the mirror on the left wall and 2.50 m away from the mirror on the rig ...
... *1. (5pts) A person walks into a room that has, on opposite walls, two plane mirrors producing multiple images. Find the distance from the person to the third image seen in the left-hand mirror when the person is 1.50 m away from the mirror on the left wall and 2.50 m away from the mirror on the rig ...
File - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... • Light can be regarded as a group of rays. • Light travels in reasonably ...
... • Light can be regarded as a group of rays. • Light travels in reasonably ...
Physics 91170 (2.3) Exam
... Explain what Sandy would notice about the coin once she pours water in the beaker to the level indicated in the diagram above. In your answer, you should give reasons for Sandy’s observation of the coin once the water is poured into the beaker. Sketch on the diagram provided below to support your ex ...
... Explain what Sandy would notice about the coin once she pours water in the beaker to the level indicated in the diagram above. In your answer, you should give reasons for Sandy’s observation of the coin once the water is poured into the beaker. Sketch on the diagram provided below to support your ex ...
Document
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
Grade 10 Academic Science – Optics (Physics) Laboratory
... 6. Use the ray box with the single opening of the slit, direct a ray of light through O1. 7. Mark at least three points on the Incident Ray and three points on the Reflected Ray 8. Use the ruler, connect the points and draw both the Incident Ray and Reflected Ray 9. Send a second ray of light throug ...
... 6. Use the ray box with the single opening of the slit, direct a ray of light through O1. 7. Mark at least three points on the Incident Ray and three points on the Reflected Ray 8. Use the ruler, connect the points and draw both the Incident Ray and Reflected Ray 9. Send a second ray of light throug ...
Ray Diagrams
... Light reflected off the mirror converges to form an image in the eye. The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabr ...
... Light reflected off the mirror converges to form an image in the eye. The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabr ...
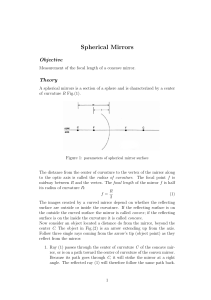
Spherical Mirrors
... it is easier to move the mirror than the source, which should remain near the end of the bench. You can measure the object distance using the scale built in to the bench. The mirror holder has a small pointer that indicates the location of the mirror’s vertex. It may be more convenient to hold the m ...
... it is easier to move the mirror than the source, which should remain near the end of the bench. You can measure the object distance using the scale built in to the bench. The mirror holder has a small pointer that indicates the location of the mirror’s vertex. It may be more convenient to hold the m ...
urved - St. Thomas Aquinas Catholic Secondary School
... Mirrors with a single curvature find many uses in our homes ...
... Mirrors with a single curvature find many uses in our homes ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... Now that we understand the laws of reflection and refraction we can put them to practical use by designing optical instruments. We begin with the law of reflection – which tells us that the angle of incidence equals the angle of refraction. MIRRORS We start with the simplest possible mirror – a plan ...
... Now that we understand the laws of reflection and refraction we can put them to practical use by designing optical instruments. We begin with the law of reflection – which tells us that the angle of incidence equals the angle of refraction. MIRRORS We start with the simplest possible mirror – a plan ...
Curved Mirrors - Mr Linseman`s wiki
... Parts of the concave mirror: • Vertex (V) – the centre of the mirror • Principal Axis (PA) — line that goes through V • Focus (F)—where the reflected rays of parallel incident rays intersect • Centre of Curvature (C)—the centre of the sphere from which the mirror was cut ...
... Parts of the concave mirror: • Vertex (V) – the centre of the mirror • Principal Axis (PA) — line that goes through V • Focus (F)—where the reflected rays of parallel incident rays intersect • Centre of Curvature (C)—the centre of the sphere from which the mirror was cut ...