Chapter 6 | Thermochemistry
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
- Philsci
... in the whole of physics when one takes into account the range, immense diversity, and accuracy of its predictions. But not only does it fail to solve the great quantum mystery of what sort of entities electrons and atoms can be in view of their apparently contradictory particle and wave properties. ...
... in the whole of physics when one takes into account the range, immense diversity, and accuracy of its predictions. But not only does it fail to solve the great quantum mystery of what sort of entities electrons and atoms can be in view of their apparently contradictory particle and wave properties. ...
Powerpoint 8/12
... correct theory of quantum gravity, Therefore Preskill offers, and Hawking/Thorne accept, a wager that: When an initial pure quantum state undergoes gravitational collapse to form a black hole, the final state at the end of black hole evaporation will always be a pure quantum state. The loser(s) will ...
... correct theory of quantum gravity, Therefore Preskill offers, and Hawking/Thorne accept, a wager that: When an initial pure quantum state undergoes gravitational collapse to form a black hole, the final state at the end of black hole evaporation will always be a pure quantum state. The loser(s) will ...
The Copenhagen Interpretation
... multiplied by its complex conjugate to give the predicted transition probability. In a more sophisticated calculation one might use density matrices pA(x';x") and PB(y'',y") instead of *A(J;) and ¥s(y) to represent the prepared system and the possible result. This would allow for preparations and me ...
... multiplied by its complex conjugate to give the predicted transition probability. In a more sophisticated calculation one might use density matrices pA(x';x") and PB(y'',y") instead of *A(J;) and ¥s(y) to represent the prepared system and the possible result. This would allow for preparations and me ...
Document
... “Matter from light” CERN Courier, Nov. 1997 “E=mc2, really” Scientific American, Dec. 1997 “Let there be matter” Discover, Dec. 1997 “Gamma rays create matter by plowing into laser light” Phys. Today, Feb 1998 ...
... “Matter from light” CERN Courier, Nov. 1997 “E=mc2, really” Scientific American, Dec. 1997 “Let there be matter” Discover, Dec. 1997 “Gamma rays create matter by plowing into laser light” Phys. Today, Feb 1998 ...
Quantum nanophotonic phase switch with a single atom.
... where g 5 (2g)2/kc is the cooperativity, 2g is the single-photon Rabi frequency, d is the atom–photon detuning and the cavity is taken to be resonant with the driving laser. In our apparatus, the cavity intensity and atomic population decay rates are given by k 5 2p 3 25 GHz and c 5 2p 3 6 MHz, resp ...
... where g 5 (2g)2/kc is the cooperativity, 2g is the single-photon Rabi frequency, d is the atom–photon detuning and the cavity is taken to be resonant with the driving laser. In our apparatus, the cavity intensity and atomic population decay rates are given by k 5 2p 3 25 GHz and c 5 2p 3 6 MHz, resp ...
phase stability - CERN Accelerator School
... writing of Ωs is directly related to the RF angular frequency. Moreover in a linac the equivallent h will be equal to 1. CAS ...
... writing of Ωs is directly related to the RF angular frequency. Moreover in a linac the equivallent h will be equal to 1. CAS ...
Completely Quantized Collapse and Consequences
... The usual quantum rule for probabilities (the squared norm of a state in the superposition) gives the CSL probability of realization of that state. The measurement (reality) problem in standard quantum theory has often been phrased in terms of difficulties associated with the ill-defined collapse po ...
... The usual quantum rule for probabilities (the squared norm of a state in the superposition) gives the CSL probability of realization of that state. The measurement (reality) problem in standard quantum theory has often been phrased in terms of difficulties associated with the ill-defined collapse po ...
No Slide Title
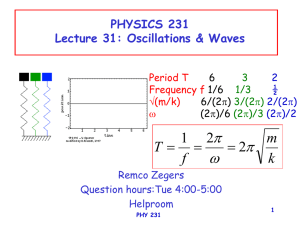
... of 2m between a maximum and the nearest minimum and vertical height of 2m. If it moves with 1m/s, what is its: a) amplitude b) period c) frequency ...
... of 2m between a maximum and the nearest minimum and vertical height of 2m. If it moves with 1m/s, what is its: a) amplitude b) period c) frequency ...
Nonlinear quantum mechanics, the superposition principle, and the
... If the principle does hold for objects of arbitrarily large size, as would be the case in standard quantum theory, then how does one understand the apparent breakdown of superposition during a quantum measurement? One possible answer, within linear quantum theory, is that indeed the breakdown of sup ...
... If the principle does hold for objects of arbitrarily large size, as would be the case in standard quantum theory, then how does one understand the apparent breakdown of superposition during a quantum measurement? One possible answer, within linear quantum theory, is that indeed the breakdown of sup ...
Crystallization of strongly interacting photons in a nonlinear optical fiber
... but, knowing the position of one, other photons are likely to follow at well-defined distances determined by the average photon density. These correlations are predicted to decay relatively slowly in space. We emphasize that the oscillation period depends only on the density of photons nph inside th ...
... but, knowing the position of one, other photons are likely to follow at well-defined distances determined by the average photon density. These correlations are predicted to decay relatively slowly in space. We emphasize that the oscillation period depends only on the density of photons nph inside th ...
12 Quantum Electrodynamics
... In this chapter we want to couple electrons and photons with each other by an appropriate interaction and study the resulting interacting field theory, the famous quantum electrodynamics (QED). Since the coupling should not change the two physical degrees of freedom described by the four-component p ...
... In this chapter we want to couple electrons and photons with each other by an appropriate interaction and study the resulting interacting field theory, the famous quantum electrodynamics (QED). Since the coupling should not change the two physical degrees of freedom described by the four-component p ...
PPT
... We’ll understand why this is as we go forward. For example, a freely expanding gas is not in equilibrium until the density is the same everywhere. ...
... We’ll understand why this is as we go forward. For example, a freely expanding gas is not in equilibrium until the density is the same everywhere. ...
- Philsci
... Later, Bell derived in 1964 an inequality from the distant correlations encoded by the singlet state and some natural locality assumptions. For various orientations quantum theory predicts the violation of this inequality; and in a host of experiments since systems have vindicated this prediction. T ...
... Later, Bell derived in 1964 an inequality from the distant correlations encoded by the singlet state and some natural locality assumptions. For various orientations quantum theory predicts the violation of this inequality; and in a host of experiments since systems have vindicated this prediction. T ...
1 The Fourier Transform
... The wave-particle duality problem can be somewhat reconciled by thinking about particles as localized wave packets. Waves of different frequencies are superposed so that they interfere completely (or nearly so) outside of a small spatial region. Clearly, both the amplitudes (magnitude of waves of di ...
... The wave-particle duality problem can be somewhat reconciled by thinking about particles as localized wave packets. Waves of different frequencies are superposed so that they interfere completely (or nearly so) outside of a small spatial region. Clearly, both the amplitudes (magnitude of waves of di ...
Course Pack ISP 209L Mystery of the Physical World Lab
... the probability of both coins giving heads, or the probability of both coins giving tails is 25%, but the probability of getting one head and one tail is 50%. The factor of 2 larger probability is due to the fact that there are two possible ways of getting this combination. These same basic ideas ap ...
... the probability of both coins giving heads, or the probability of both coins giving tails is 25%, but the probability of getting one head and one tail is 50%. The factor of 2 larger probability is due to the fact that there are two possible ways of getting this combination. These same basic ideas ap ...
Measurement of the transverse electric field profile of light by a self
... phase-front, which is the surface of constant phase of the propagating light beam. One such method is using a Shack-Hartmann sensor, which consists of a lenslet array in front on an imaging detector [4]. This sensor measures the phase gradient at a grid of points which intersect the beam. It has an ...
... phase-front, which is the surface of constant phase of the propagating light beam. One such method is using a Shack-Hartmann sensor, which consists of a lenslet array in front on an imaging detector [4]. This sensor measures the phase gradient at a grid of points which intersect the beam. It has an ...