Surrey seminar on CQP - School of Computing Science
... and now measuring the first qubit gives us the desired information about f , and we only used the quantum black box once. Quantum parallelism was used to calculate f(0) and f(1) ; a global property of f ended up being encoded in a single place so that it could be extracted by a measurement. Developi ...
... and now measuring the first qubit gives us the desired information about f , and we only used the quantum black box once. Quantum parallelism was used to calculate f(0) and f(1) ; a global property of f ended up being encoded in a single place so that it could be extracted by a measurement. Developi ...
THE MINIMUM-UNCERTAINTY SQUEEZED STATES FOR ATOMS
... harmonic oscillators, which are important in these applications, in the most simple closed form. Our approach reveals the quantum numbers/integrals of motion of the squeezed states in terms of solution of certain Ermakov-type system [104], [105]. The corresponding generalizations of Fock states, whi ...
... harmonic oscillators, which are important in these applications, in the most simple closed form. Our approach reveals the quantum numbers/integrals of motion of the squeezed states in terms of solution of certain Ermakov-type system [104], [105]. The corresponding generalizations of Fock states, whi ...
Basic Fluorescence Principles I
... alkali brought it back. Hence Boyle was the first to use fluorescence as a pH indicator! Galileo (1612) described the emission of light (phosphorescence) from the famous Bolognian stone, discovered by Vincenzo Casciarolo, a Bolognian shoemaker. Galileo wrote: "It must be explained how it happens tha ...
... alkali brought it back. Hence Boyle was the first to use fluorescence as a pH indicator! Galileo (1612) described the emission of light (phosphorescence) from the famous Bolognian stone, discovered by Vincenzo Casciarolo, a Bolognian shoemaker. Galileo wrote: "It must be explained how it happens tha ...
Liquid State NMR Quantum Computing
... viewed as a logic gate (Figure 1) which flips one spin conditioned upon the orientation of a neighboring spin. If we arbitrarily assign “0” to a spin up and “1” to a spin down, we can think of spin-1/2 nuclei as bits in a digital computer. We remind the reader that bits (“0” or “1”) can be used to r ...
... viewed as a logic gate (Figure 1) which flips one spin conditioned upon the orientation of a neighboring spin. If we arbitrarily assign “0” to a spin up and “1” to a spin down, we can think of spin-1/2 nuclei as bits in a digital computer. We remind the reader that bits (“0” or “1”) can be used to r ...
Coupled-mode theory for general free-space resonant scattering of waves
... the scatterer’s size or radial composition. Hence, only one multipole component of the incident plane wave was scattered at resonance. Now, if we consider an arbitrary resonant scatterer 共not necessarily of spherical or cylindrical symmetry兲, such that its size is much smaller than the wavelength of ...
... the scatterer’s size or radial composition. Hence, only one multipole component of the incident plane wave was scattered at resonance. Now, if we consider an arbitrary resonant scatterer 共not necessarily of spherical or cylindrical symmetry兲, such that its size is much smaller than the wavelength of ...
Proton- [Proton - lambda] correlations in central Pb + Pb
... pairs. For each pair, it is required that the tracks have an average separation of at least 3.0 cm. This average is determined as the arithmetic mean of the track distances determined in planes perpendicular to the beam axis. For each TPC, two planes are taken into account. Their distances to the ta ...
... pairs. For each pair, it is required that the tracks have an average separation of at least 3.0 cm. This average is determined as the arithmetic mean of the track distances determined in planes perpendicular to the beam axis. For each TPC, two planes are taken into account. Their distances to the ta ...
CERN Teacher Programmes: Welcome to CERN!
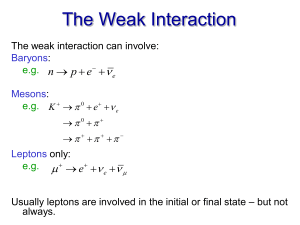
... exchange speculations: physicists looked at various combinations of charge exchange and spin exchange between nucleons with varying degrees of success, but none could produce complete and satisfactory quantitative explanations of observed nuclear phenomena. The way out of the difficulties was provid ...
... exchange speculations: physicists looked at various combinations of charge exchange and spin exchange between nucleons with varying degrees of success, but none could produce complete and satisfactory quantitative explanations of observed nuclear phenomena. The way out of the difficulties was provid ...
Quantum Chemistry - Eric R. Bittner
... ever have, never be shy about holding forth with bags of authority about subatomic particles and the quantum realm without having done any science whatsoever. Jack Klaff –Bluff Your Way in the Quantum Universe The field of quantum chemistry seeks to provide a rigorous description of chemical process ...
... ever have, never be shy about holding forth with bags of authority about subatomic particles and the quantum realm without having done any science whatsoever. Jack Klaff –Bluff Your Way in the Quantum Universe The field of quantum chemistry seeks to provide a rigorous description of chemical process ...
Quantum cryptography
... Quantum physics deals with fundamental entities of physics – particles like • protons, electrons and neutrons (from which matter is built); • photons (which carry electromagnetic radiation) • various “elementary particles” which mediate other interactions in physics. •We call them particles in spite ...
... Quantum physics deals with fundamental entities of physics – particles like • protons, electrons and neutrons (from which matter is built); • photons (which carry electromagnetic radiation) • various “elementary particles” which mediate other interactions in physics. •We call them particles in spite ...
Schumacher Compression
... Given access to many uses of a noiseless classical channel, what is the best that a sender and receiver can make of this resource for compressed data transmission? Shannon’s compression theorem demonstrates that the Shannon entropy is the fundamental limit for the compression rate in the IID setting ...
... Given access to many uses of a noiseless classical channel, what is the best that a sender and receiver can make of this resource for compressed data transmission? Shannon’s compression theorem demonstrates that the Shannon entropy is the fundamental limit for the compression rate in the IID setting ...
appendix 2 - School of Physics
... to assist students who were not familiar with or had not previously drawn a concept map, a ‘concept map answer cover sheet’, a ‘concept map answer sheet’ and were given 20 minutes to prepare a response. The concept mapping exercise required the construction of a concept map using the nineteen labels ...
... to assist students who were not familiar with or had not previously drawn a concept map, a ‘concept map answer cover sheet’, a ‘concept map answer sheet’ and were given 20 minutes to prepare a response. The concept mapping exercise required the construction of a concept map using the nineteen labels ...
Quantum cryptography
... An important difference between classical and quantum systems A state of a compound classical (quantum) system can be (cannot be) always composed from the states of the subsystem. ...
... An important difference between classical and quantum systems A state of a compound classical (quantum) system can be (cannot be) always composed from the states of the subsystem. ...
A Priori Probability and Localized Observers
... particle is fundamental. In interacting relativistic quantum field theories, however, local particle number becomes indefinite, because of the possibility of particle (or particle-antiparticle) creation. Only in scattering theories are particle states clearly definable. In other words, either we dea ...
... particle is fundamental. In interacting relativistic quantum field theories, however, local particle number becomes indefinite, because of the possibility of particle (or particle-antiparticle) creation. Only in scattering theories are particle states clearly definable. In other words, either we dea ...
Probing charge fluctuator correlations using quantum dot pairs Purohit, er, tt
... detector i originate from QD i only. The QDs in a typical experimental setup would be quite closely spaced and so a Hanbury Brown–Twiss apparatus [21] could be used. In this experiment, the photons from the QDs are passed through a beam splitter so that there are two paths that each lead to a detect ...
... detector i originate from QD i only. The QDs in a typical experimental setup would be quite closely spaced and so a Hanbury Brown–Twiss apparatus [21] could be used. In this experiment, the photons from the QDs are passed through a beam splitter so that there are two paths that each lead to a detect ...










![Proton- [Proton - lambda] correlations in central Pb + Pb](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000062586_1-405b2c192ec461a8bbe310795549777f-300x300.png)