Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... However this was not to be. Conflicts and inconsistencies soon arose due to the fundamental differences between relativity and quantum mechanics, which will be elaborated on in later pages. One fundamental difference is that general relativity says that spacetime is warped due to the presence of mas ...
... However this was not to be. Conflicts and inconsistencies soon arose due to the fundamental differences between relativity and quantum mechanics, which will be elaborated on in later pages. One fundamental difference is that general relativity says that spacetime is warped due to the presence of mas ...
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory
... Quantum – ch 12 11. An electron is excited from the ground state to the n = 3 state in a hydrogen atom. Which of the following statements is/are true? a. It takes more energy to ionize the electron from n= 3 than from the ground state. b. The electron is farther from the nucleus on average in the n ...
... Quantum – ch 12 11. An electron is excited from the ground state to the n = 3 state in a hydrogen atom. Which of the following statements is/are true? a. It takes more energy to ionize the electron from n= 3 than from the ground state. b. The electron is farther from the nucleus on average in the n ...
"Material universe" yields surprising new particle An international
... certain rule-set, or symmetry, known as Lorentz symmetry, which is characteristic of highenergy particles. However, Lorentz symmetry does not apply in condensed matter because typical electron velocities in solids are very small compared to the speed of light, making condensed matter physics an in ...
... certain rule-set, or symmetry, known as Lorentz symmetry, which is characteristic of highenergy particles. However, Lorentz symmetry does not apply in condensed matter because typical electron velocities in solids are very small compared to the speed of light, making condensed matter physics an in ...
Multi-electron atoms have interactions between electrons, not just
... descriptions of the behavior or electrons. - The wavefunction describes the probability of finding an electron in a given space - For larger objects, the wave behavior isn't very important .... and quantum mechanics becomes traditional Newtonian physics. ...
... descriptions of the behavior or electrons. - The wavefunction describes the probability of finding an electron in a given space - For larger objects, the wave behavior isn't very important .... and quantum mechanics becomes traditional Newtonian physics. ...
Quantum Field Theory - Institut für Theoretische Physik
... physics in the guise of critical behavior of statistical systems confined to surfaces. ...
... physics in the guise of critical behavior of statistical systems confined to surfaces. ...
Quantum Computing
... (you knew it was coming) Quantum mechanics: “Probability theory with minus signs” (Nature seems to prefer it that way) ...
... (you knew it was coming) Quantum mechanics: “Probability theory with minus signs” (Nature seems to prefer it that way) ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • H is set of mathematical instructions called an operator that produce the total energy of the atom when they are applied to the wave function. • E is the total energy of the atom (the sum of the potential energy due to the attraction between the proton and electron and the kinetic energy of the mo ...
... • H is set of mathematical instructions called an operator that produce the total energy of the atom when they are applied to the wave function. • E is the total energy of the atom (the sum of the potential energy due to the attraction between the proton and electron and the kinetic energy of the mo ...
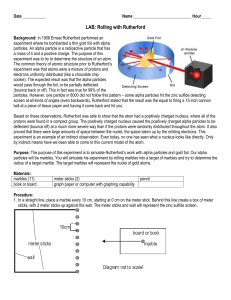
Handout
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
Foundations of Classical and Quantum Electrodynamics Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2516947/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2516947/ ...
ppt - UCSC Bayesian Data Analysis Workshop
... Computation • The basic idea: – run the forward simulation a very large number of times, keeping those runs which triggered the same detectors that were triggered in the event we are analysing – compute the mean, variance etc of the photon direction and energy from the runs that are retained – clea ...
... Computation • The basic idea: – run the forward simulation a very large number of times, keeping those runs which triggered the same detectors that were triggered in the event we are analysing – compute the mean, variance etc of the photon direction and energy from the runs that are retained – clea ...
background
... SUPERPOISION PRINCIPLE When two or more disturbances of the same kind overlap, the resultant amplitude at any point in the region is the algebraic sum of the amplitudes of each contributing wave. The Principle of Superposition leads to the phenomena known as interference. For example, assume that t ...
... SUPERPOISION PRINCIPLE When two or more disturbances of the same kind overlap, the resultant amplitude at any point in the region is the algebraic sum of the amplitudes of each contributing wave. The Principle of Superposition leads to the phenomena known as interference. For example, assume that t ...
ElectromagneticSpectrum - Mr-Durands
... as a particle, others wondered whether matter could behave as a wave. • If a beam of electrons were sprayed at two tiny slits, you might expect that the electrons would strike only the area behind the slits, like the spray paint. ...
... as a particle, others wondered whether matter could behave as a wave. • If a beam of electrons were sprayed at two tiny slits, you might expect that the electrons would strike only the area behind the slits, like the spray paint. ...













![PHY820 Homework Set 12 1. [5 pts] Goldstein, Problem 6-12.](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008846971_1-44b073c28603f7498b9d146ab9bb3803-300x300.png)