dark energy stars - at www.arxiv.org.
... velocity of sound vanishes in our superfluid column ic completely analogous to the event horizon of a classical black hole. However, in contrast with the behavior of waves or particles as they cross the event horizon of a classical black hole, the sound waves in our thought experiment would not pass ...
... velocity of sound vanishes in our superfluid column ic completely analogous to the event horizon of a classical black hole. However, in contrast with the behavior of waves or particles as they cross the event horizon of a classical black hole, the sound waves in our thought experiment would not pass ...
Experimental Aspects of Jet Reconstruction in Collider
... Electron energy loss through bremsstrahlung after 1 radiation length (X 0 ) in matter: E0 2 Assume this energy is taken by 1 photon, meaning the energy of each shower particle after t X o is: E (t ) E0 2N (t ) , with N (t ) 2t ...
... Electron energy loss through bremsstrahlung after 1 radiation length (X 0 ) in matter: E0 2 Assume this energy is taken by 1 photon, meaning the energy of each shower particle after t X o is: E (t ) E0 2N (t ) , with N (t ) 2t ...
Lecture 17
... symmetric state for bosons; the normalization factor is . In our non-relativistic quantum mechanics we accept the following statement as an axiom: All particles with integer spin are bosons, all particles with half-integer spin are fermions. ...
... symmetric state for bosons; the normalization factor is . In our non-relativistic quantum mechanics we accept the following statement as an axiom: All particles with integer spin are bosons, all particles with half-integer spin are fermions. ...
ppt
... (Quantum-statistical) Noise analysis as a sensitive probe of the source properties, with a wide range of applications : • Quantum optics • Nuclear and particle physics (angular correlations) • Condensed matter physics (electron antibunching, mesoscopics, …) ...
... (Quantum-statistical) Noise analysis as a sensitive probe of the source properties, with a wide range of applications : • Quantum optics • Nuclear and particle physics (angular correlations) • Condensed matter physics (electron antibunching, mesoscopics, …) ...
INFERENCES: Exit Slip
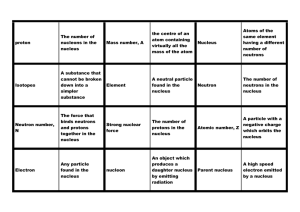
... Atomic Structure: Exit Slip Match each term with its correct definition. Vocabulary ...
... Atomic Structure: Exit Slip Match each term with its correct definition. Vocabulary ...
least action principle and quantum mechanics i. introduction
... The problem is that: According to its definition, function H must be the total energy of the mechanical system gained in the duration of time from t0 to t1. Should we understand this as cause or consequence? Is it action or effect? What if the action doesn’t reach the least action threshold? ...
... The problem is that: According to its definition, function H must be the total energy of the mechanical system gained in the duration of time from t0 to t1. Should we understand this as cause or consequence? Is it action or effect? What if the action doesn’t reach the least action threshold? ...
Exam 3 review
... something like: “Schrödinger, you are not working right now on very important problems…why don’t you tell us some time about that thesis of deBroglie, which seems to have attracted some attention?” So, in one of the next colloquia, Schrödinger gave a beautifully clear account of how deBroglie associ ...
... something like: “Schrödinger, you are not working right now on very important problems…why don’t you tell us some time about that thesis of deBroglie, which seems to have attracted some attention?” So, in one of the next colloquia, Schrödinger gave a beautifully clear account of how deBroglie associ ...
Significant-Loophole-Free Test of Bells Theorem with Entangled Photons
... photon pairs, high-efficiency detectors, and fast random basis choices spacelike separated from both the photon generation and the remote detection. We simultaneously close all three aforementioned loopholes in a single experiment with high statistical significance and thus provide strong support fo ...
... photon pairs, high-efficiency detectors, and fast random basis choices spacelike separated from both the photon generation and the remote detection. We simultaneously close all three aforementioned loopholes in a single experiment with high statistical significance and thus provide strong support fo ...
ATOMIC QUANTUM ENGINES IN OPTICAL TWEEZERS Prof. E. A.
... Prof. E. A. Hinds, Imperial College London Dr G. Barontini, University of Birmingham Background. Thermodynamics is fundamental to our understanding of many topics in science and technology, including the operation of most machines and engines. As research pushes towards ever smaller devices new quan ...
... Prof. E. A. Hinds, Imperial College London Dr G. Barontini, University of Birmingham Background. Thermodynamics is fundamental to our understanding of many topics in science and technology, including the operation of most machines and engines. As research pushes towards ever smaller devices new quan ...
03-02BohrAtom
... Lyman line? The first Lyman line is a transition from -3.4 eV to -13.6 eV, so it releases 10.2 eV of energy. A photon with this energy has this wavelength: E = (10.2)(1.602E-19) = 1.63404E-18 J E = hc/λ, λ = hc/E = (6.626E-34)(3.00E8)/(1.63404E-18) = 1.21649E-07 m = 122 nm ...
... Lyman line? The first Lyman line is a transition from -3.4 eV to -13.6 eV, so it releases 10.2 eV of energy. A photon with this energy has this wavelength: E = (10.2)(1.602E-19) = 1.63404E-18 J E = hc/λ, λ = hc/E = (6.626E-34)(3.00E8)/(1.63404E-18) = 1.21649E-07 m = 122 nm ...
Compton Effect and Spectral Lines
... 1) A photon of initial energy 5.8 103 eV is deflected by 130 in a collision with a free electron, which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron ...
... 1) A photon of initial energy 5.8 103 eV is deflected by 130 in a collision with a free electron, which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron ...
II: Experimental Atomic Spectroscopy
... ±1,..., ± ) for a given n which lead to the same eigenvalue. There is a certain amount of degeneracy. An additional quantum number ms is needed to describe the electron spin. For the alkali “one-electron” atoms the spin-orbit coupling produces an appreciable splitting of all but the = 0 lines wi ...
... ±1,..., ± ) for a given n which lead to the same eigenvalue. There is a certain amount of degeneracy. An additional quantum number ms is needed to describe the electron spin. For the alkali “one-electron” atoms the spin-orbit coupling produces an appreciable splitting of all but the = 0 lines wi ...
Chapter 30
... which has no charge, but makes up the rest of the mass. • The mass number (A), therefore is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. • Rutherford understood that the nucleus was very small. For example, the diameter for a hydrogen atom is now accepted to be about 2.6 x 10-15 m. ...
... which has no charge, but makes up the rest of the mass. • The mass number (A), therefore is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. • Rutherford understood that the nucleus was very small. For example, the diameter for a hydrogen atom is now accepted to be about 2.6 x 10-15 m. ...
Dominoes - Learning on the Loop
... The process of nuclei breaking up and emitting particles or waves to become stable ...
... The process of nuclei breaking up and emitting particles or waves to become stable ...