Chapter 7: Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Plank’s idea of quantized energy to the situation. Electrons are only ejected from surfaces by radiation with a frequency equal to or greater than some threshold value (the threshold frequency is different for each metal). According to wave theory, this should not be the case; it should be possible ...
... Plank’s idea of quantized energy to the situation. Electrons are only ejected from surfaces by radiation with a frequency equal to or greater than some threshold value (the threshold frequency is different for each metal). According to wave theory, this should not be the case; it should be possible ...
Bose-Einstein Condensation
... • BEC is a quantum mechanical phase-transition, thought to be responsible for superfluidity in liquid helium. • Not until 1995 was it observed in isolated atoms, in 87Rb (NIST), 23Na (MIT) and 7Li (Rice U.). Since then, BEC has been observed around the world, and 1H (MIT) and 4He ...
... • BEC is a quantum mechanical phase-transition, thought to be responsible for superfluidity in liquid helium. • Not until 1995 was it observed in isolated atoms, in 87Rb (NIST), 23Na (MIT) and 7Li (Rice U.). Since then, BEC has been observed around the world, and 1H (MIT) and 4He ...
Document
... the angular momentum ⇒ zero point energy can be zero! 3 Two wavefunctions with different quantum numbers can have the same energy. For example wavefunctions with ml = 1 and −1 have the same energy, ћ2/2I. This is known as degeneracy. Example: Let us treat the π-electrons in benzene as particles of m ...
... the angular momentum ⇒ zero point energy can be zero! 3 Two wavefunctions with different quantum numbers can have the same energy. For example wavefunctions with ml = 1 and −1 have the same energy, ћ2/2I. This is known as degeneracy. Example: Let us treat the π-electrons in benzene as particles of m ...
Standard Model
... The W and Z bosons (together known as the weak bosons) are the elementary particles that mediate the weak interaction; their symbols are W+, W−, and Z. These bosons are among the heavyweights of the elementary particles. With masses of 80.4 GeV/c2 and 91.2 GeV/c2, respectively, the W and Z bosons ar ...
... The W and Z bosons (together known as the weak bosons) are the elementary particles that mediate the weak interaction; their symbols are W+, W−, and Z. These bosons are among the heavyweights of the elementary particles. With masses of 80.4 GeV/c2 and 91.2 GeV/c2, respectively, the W and Z bosons ar ...
Quantum correlations - Uniwersytet otwarty UG
... occurs when particles (subsystems) are generated in ways that the quantum state of each particle can not be described independently ; BUT ...
... occurs when particles (subsystems) are generated in ways that the quantum state of each particle can not be described independently ; BUT ...
Three-dimensional solids in the limit of high magnetic fields
... these very high fields is also reviewed. It is explained how diamagnetic and Pauli pair breaking are avoided, and why materials which are not superconducting at low temperature may be superconducting at high fields. The possibility of triplet superconductive pairing is considered. The suggested prop ...
... these very high fields is also reviewed. It is explained how diamagnetic and Pauli pair breaking are avoided, and why materials which are not superconducting at low temperature may be superconducting at high fields. The possibility of triplet superconductive pairing is considered. The suggested prop ...
$doc.title
... From the figure, we see that the minimum intensity is zero, and occurs when cos φ = −1/ 2 . The condition for primary maxima is cos φ = +1 , which gives I / I 0 = 1 . In addition, there are also secondary maxima that are located at cos φ = −1 . The condition implies φ = (2m + 1)π , which implies tha ...
... From the figure, we see that the minimum intensity is zero, and occurs when cos φ = −1/ 2 . The condition for primary maxima is cos φ = +1 , which gives I / I 0 = 1 . In addition, there are also secondary maxima that are located at cos φ = −1 . The condition implies φ = (2m + 1)π , which implies tha ...
Quantum Computers and Cryptography
... [2] Internet Article: http://arstechnica.com/science/guides/2010/01/atale-of-two-qubits-how-quantum-computers-work.ars . by Joseph B. ...
... [2] Internet Article: http://arstechnica.com/science/guides/2010/01/atale-of-two-qubits-how-quantum-computers-work.ars . by Joseph B. ...
Quantum computing
... (photons, electrons, or nucleus) governed by the laws of quantum mechanics Parameters of the system may include positions of particles, momentum, energy, spin, polarization The quantum system can be characterized by its state that is responsible for the parameters The state can change under external ...
... (photons, electrons, or nucleus) governed by the laws of quantum mechanics Parameters of the system may include positions of particles, momentum, energy, spin, polarization The quantum system can be characterized by its state that is responsible for the parameters The state can change under external ...
Lives of the Stars Lecture 2: Atoms and quantum
... Richard Feynman once said that the one question we cannot ask when we study quantum mechanics is ...
... Richard Feynman once said that the one question we cannot ask when we study quantum mechanics is ...
Chemistry XL-14A Nature of Light and the Atom
... (b) What is the wavelengh of the radiation that caused the photoejection of the electron? (c) What is the longest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that could eject electrons from potassium? The work function of potassium is 2.29 eV. (1 eV = 1.602 x 10-19 J) ...
... (b) What is the wavelengh of the radiation that caused the photoejection of the electron? (c) What is the longest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that could eject electrons from potassium? The work function of potassium is 2.29 eV. (1 eV = 1.602 x 10-19 J) ...
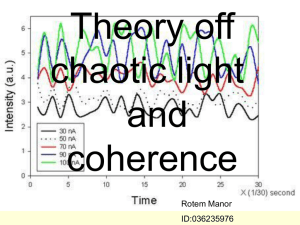
Theory off chaotic light
... The degree of first- and second- order coherence is define by the same pattern. This is just two members of a hierarchy of coherence functions. It is possible to envisage a general interface experiment in which the measured result depends on the correlation of electric fields at an arbitrary number ...
... The degree of first- and second- order coherence is define by the same pattern. This is just two members of a hierarchy of coherence functions. It is possible to envisage a general interface experiment in which the measured result depends on the correlation of electric fields at an arbitrary number ...
UCSF050509
... exactly in the way that William James described it during the nineteenth century. I have spoken as if our attention were wholly determined by neural conditions. I believe that the array of things we can attend to is so determined. No object can catch our attention except by the neural machinery. But ...
... exactly in the way that William James described it during the nineteenth century. I have spoken as if our attention were wholly determined by neural conditions. I believe that the array of things we can attend to is so determined. No object can catch our attention except by the neural machinery. But ...
pdf - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... complete with specification of the positions and momenta of all particles, each of which can be precisely ...
... complete with specification of the positions and momenta of all particles, each of which can be precisely ...
Josephson Effect - Quantum Device Lab
... DiVincenzo Criteria for Implementations of a Quantum Computer: #1. A scalable physical system with well-characterized qubits. #2. The ability to initialize the state of the qubits to a simple fiducial state. #3. Long (relative) decoherence times, much longer than the gate-operation time. #4. A unive ...
... DiVincenzo Criteria for Implementations of a Quantum Computer: #1. A scalable physical system with well-characterized qubits. #2. The ability to initialize the state of the qubits to a simple fiducial state. #3. Long (relative) decoherence times, much longer than the gate-operation time. #4. A unive ...