Genetics Course Outcome Summary Course Information
... b. Describe the roles restriction enzymes and vectors play in recombinant DNA technology. c. Explain how genes can be transferred to eukaryotic cells. d. Describe how polymerase chain reaction makes DNA copies without host cells. e. Describe the genomic library and its role in cloning. f. Describe t ...
... b. Describe the roles restriction enzymes and vectors play in recombinant DNA technology. c. Explain how genes can be transferred to eukaryotic cells. d. Describe how polymerase chain reaction makes DNA copies without host cells. e. Describe the genomic library and its role in cloning. f. Describe t ...
Immunoglobulin and Monoclonal antibodies
... 1. mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigens and induce immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function ...
... 1. mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigens and induce immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function ...
STUDY GUIDE for Dr. Mohnen`s part of Exam #3
... Cis-acting element: DNA sequences that regulate expression of gene located on same DNA molecule Transcription initiation in eukaryotes: TFII: transcription factor for RNA Pol II (TF-D (with TBP),A,B,F (then initiate),E,H TFIIH: opens double helix & phosphorylated CTD of RNA PolII change from initiat ...
... Cis-acting element: DNA sequences that regulate expression of gene located on same DNA molecule Transcription initiation in eukaryotes: TFII: transcription factor for RNA Pol II (TF-D (with TBP),A,B,F (then initiate),E,H TFIIH: opens double helix & phosphorylated CTD of RNA PolII change from initiat ...
1 dent intro
... immunology. As a general definition, the antigen is an entity recognised specifically by the Band T-lymphocytes. The focus of this definition is on “specificity”. This presumes the presence of highly specific receptors that can bind to a given material (or structure), say they specifically recognise ...
... immunology. As a general definition, the antigen is an entity recognised specifically by the Band T-lymphocytes. The focus of this definition is on “specificity”. This presumes the presence of highly specific receptors that can bind to a given material (or structure), say they specifically recognise ...
Document
... Phagocytosis is a specific form of endocytosis by which cells internalise solid matter, including microbial pathogens. While most cells are capable of phagocytosis, it is the professional phagocytes of the immune system, including macrophages, neutrophils and immature dendritic cells, that truly exc ...
... Phagocytosis is a specific form of endocytosis by which cells internalise solid matter, including microbial pathogens. While most cells are capable of phagocytosis, it is the professional phagocytes of the immune system, including macrophages, neutrophils and immature dendritic cells, that truly exc ...
THE ROLE OF TLR-4 IN INTESTINAL HEALING Nectrotizing
... initiate the healing process for the tissue – NOT synonymous with infection Absence of inflammation wounds and infections never heal and progressive destruction of the tissue compromises the survival Unchecked inflammation can also lead to a host of diseases, such as hay fever, atherosclerosis, and ...
... initiate the healing process for the tissue – NOT synonymous with infection Absence of inflammation wounds and infections never heal and progressive destruction of the tissue compromises the survival Unchecked inflammation can also lead to a host of diseases, such as hay fever, atherosclerosis, and ...
Targeted Fluorescent Reporters: Additional slides
... Proto-oncogene: normal gene found in humans and other animals that coded for proteins regulating cell growth and division that can become an ...
... Proto-oncogene: normal gene found in humans and other animals that coded for proteins regulating cell growth and division that can become an ...
Elements of Innate and Acquired Immunity
... - A T-dependent self antigen does not elicit an autoantibody response from a B cell because here are no autoreactive T helper cells available to provide help, since they have been either deleted or energized . - A foreign antigen that contains an epitope that is similar to an epitope on a self antig ...
... - A T-dependent self antigen does not elicit an autoantibody response from a B cell because here are no autoreactive T helper cells available to provide help, since they have been either deleted or energized . - A foreign antigen that contains an epitope that is similar to an epitope on a self antig ...
Discussion of a Recent Paper on Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis:
... might keep the illness from progressing and might also allow the muscles to recover. Another approach is to identify new treatments for T-cell LGL leukemia that might also work for sIBM, assuming that both diseases are in fact caused by clonal expansions of CD8+ cells. One possibility is a monoclona ...
... might keep the illness from progressing and might also allow the muscles to recover. Another approach is to identify new treatments for T-cell LGL leukemia that might also work for sIBM, assuming that both diseases are in fact caused by clonal expansions of CD8+ cells. One possibility is a monoclona ...
LAB EXERCISE: Genetic Transformation
... Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and involves the insertion of a gene into an organism in order to change the orga ...
... Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and involves the insertion of a gene into an organism in order to change the orga ...
DNA, RNA, AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... • Ribosomes will “read” 3 nucleotides in the mRNA code at a time • These 3 nucleotides are called codons (or triplets) • Each codon codes for either an amino acid, a START signal, or a STOP signal ...
... • Ribosomes will “read” 3 nucleotides in the mRNA code at a time • These 3 nucleotides are called codons (or triplets) • Each codon codes for either an amino acid, a START signal, or a STOP signal ...
Lesson 2 Transformation Laboratory
... Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and involves the insertion of a gene into an organism in order to change the orga ...
... Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and involves the insertion of a gene into an organism in order to change the orga ...
General Biology I Test V
... • Same in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes • Few minor exceptions such as mitochondria. ...
... • Same in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes • Few minor exceptions such as mitochondria. ...
innate adaptive - El Corte Inglés
... SLE is associated with aberrant clearance of nucleic acid containing debris Apoptotic cell debris, NETs, microparticles ...
... SLE is associated with aberrant clearance of nucleic acid containing debris Apoptotic cell debris, NETs, microparticles ...
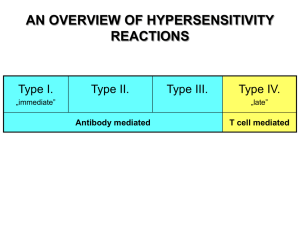
Hypersensitivity
... • Local vasculitis develops as a result of immune complex deposition • Inhaled antigens (fungi, animal feces) may induce similar reaction in the lung • IgG type antibody • ‘Farmers lung’ and ‘piegeon-breeder’s lung’ ...
... • Local vasculitis develops as a result of immune complex deposition • Inhaled antigens (fungi, animal feces) may induce similar reaction in the lung • IgG type antibody • ‘Farmers lung’ and ‘piegeon-breeder’s lung’ ...
Station 1
... Humans have approximately 75,000 to 100,000 genes in a typical cell. A single gene contains about 10,000 nitrogen base pairs. How is it possible for a single mutation to one of these base pairs to cause a life-threatening condition? Journal ...
... Humans have approximately 75,000 to 100,000 genes in a typical cell. A single gene contains about 10,000 nitrogen base pairs. How is it possible for a single mutation to one of these base pairs to cause a life-threatening condition? Journal ...
Ch .15 - Crestwood Local Schools
... types of tRNA instead of 61. Reason - in the third position, U can pair with A or G. Inosine (I), a modified base in the third position can pair ...
... types of tRNA instead of 61. Reason - in the third position, U can pair with A or G. Inosine (I), a modified base in the third position can pair ...
128. immune_team_
... - High levels of autoantibodies (against neutrophils , platelets , red cells ) ] So, low levels of RBCs, neutrophils, and platelets [ Recurrent infections especially ...
... - High levels of autoantibodies (against neutrophils , platelets , red cells ) ] So, low levels of RBCs, neutrophils, and platelets [ Recurrent infections especially ...
DNA: THE INDISPENSIBLE FORENSIC SCIENCE TOOL
... • STRs are locations on the chromosome that contain short sequences that repeat themselves within the DNA molecule. • They serve as useful markers for identification because they are found in great abundance throughout the human genome. ...
... • STRs are locations on the chromosome that contain short sequences that repeat themselves within the DNA molecule. • They serve as useful markers for identification because they are found in great abundance throughout the human genome. ...
Sample poster - Carolina Women`s Health Research Forum
... Macrophage surface marker and intracellular IL-27 were concurrently labeled with fluorophore-conjugated specific antibodies for flow cytometry analysis. Results: The relative gene expression of IL-27 in adult (day 56) mice was significantly lower than the expression in neonatal (day 8) mice. Similar ...
... Macrophage surface marker and intracellular IL-27 were concurrently labeled with fluorophore-conjugated specific antibodies for flow cytometry analysis. Results: The relative gene expression of IL-27 in adult (day 56) mice was significantly lower than the expression in neonatal (day 8) mice. Similar ...
File
... For example, the codon CAA in DNA codes for the amino acid “valine”. If this codon was the third codon in a gene, valine would be the third amino acid in the protein. ...
... For example, the codon CAA in DNA codes for the amino acid “valine”. If this codon was the third codon in a gene, valine would be the third amino acid in the protein. ...
Ongoing and future work Low cost production of tetravalent dengue
... production of tetravalent dengue vaccine (fig. 2A). Several variants of this construct, as well as monovalent versions, will be transformed into tobacco chloroplasts using the biolistic transformation method, and subsequent selection will give raise to homoplasmic plants. The recombinant antigen (fi ...
... production of tetravalent dengue vaccine (fig. 2A). Several variants of this construct, as well as monovalent versions, will be transformed into tobacco chloroplasts using the biolistic transformation method, and subsequent selection will give raise to homoplasmic plants. The recombinant antigen (fi ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.