Plate Tectonics and the changing earth ppt
... oceans. As glaciers melt, the changes occur when the actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise ...
... oceans. As glaciers melt, the changes occur when the actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise ...
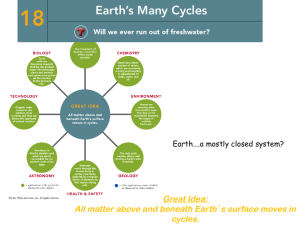
Great Idea: All matter above and beneath Earth`s surface moves in
... sense of the word, in biophysiology, biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and the atmosphere. It is thought that the biosphere has evolved through a process know ...
... sense of the word, in biophysiology, biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and the atmosphere. It is thought that the biosphere has evolved through a process know ...
7.3 Landforms are the result of the interaction of constructive and
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Morphology (-Plate Tectonics)
... c. wave pounding (waves) 3. Air erosion – abrasion (wind blasting) 4. Ice erosion – abrasion (scouring bottom of glacier) ...
... c. wave pounding (waves) 3. Air erosion – abrasion (wind blasting) 4. Ice erosion – abrasion (scouring bottom of glacier) ...
TEORIES OF MASS EXTINCTION
... 70km3 of rock to be vapourised and to spread into the atmosphere. • Location:100 km South of Johannesburg between Vredefort and Parys. ...
... 70km3 of rock to be vapourised and to spread into the atmosphere. • Location:100 km South of Johannesburg between Vredefort and Parys. ...
chapter 17 - Geoclassroom Home
... bring about climatic changes that produce glacial-interglacial intervals. Figure 17.18 According to the Milankovitch Theory, Minor Irregularities in Earth’s Rotation and Orbit May Affect Climatic Changes 11. The causes of short-term climatic changes such as occurred during the Little Ice Age are unk ...
... bring about climatic changes that produce glacial-interglacial intervals. Figure 17.18 According to the Milankovitch Theory, Minor Irregularities in Earth’s Rotation and Orbit May Affect Climatic Changes 11. The causes of short-term climatic changes such as occurred during the Little Ice Age are unk ...
Name: Date: Science 6 Study Guide Vocabulary to know: Climate
... Why does the Earth have seasons? -As Earth revolves around the sun different parts of the planet are tilted toward the sun. Areas tilted toward the sun get more solar radiation than other areas tilted away from the sun. What is an ice age? A time when large sheets of ice covered Earth’s surface. Thi ...
... Why does the Earth have seasons? -As Earth revolves around the sun different parts of the planet are tilted toward the sun. Areas tilted toward the sun get more solar radiation than other areas tilted away from the sun. What is an ice age? A time when large sheets of ice covered Earth’s surface. Thi ...
landforms!!!!!!!
... Plateaus are formed over millions of years. One way is when magma pushes up towards the surface of the Earth’s crust. If the magma does not break through but rises a section of the crust and creates a plateau. Another way plateaus are formed is when lava breaks through the Earth’s crust and builds ...
... Plateaus are formed over millions of years. One way is when magma pushes up towards the surface of the Earth’s crust. If the magma does not break through but rises a section of the crust and creates a plateau. Another way plateaus are formed is when lava breaks through the Earth’s crust and builds ...
Cenozoic Tectonics & Life
... in different directions, the San Andreas Fault formed. • Because of this there is little volcanic activity beneath central and southern California ...
... in different directions, the San Andreas Fault formed. • Because of this there is little volcanic activity beneath central and southern California ...
From the Beginning The earth and the whole universe were formed
... The temperature of the surface was relatively the same or stable, but from time to time, it cooled so that ice sheets and _________________________ spread out like giant _________________________ to form deep valleys and mountains faces from rock debris. The Precambrian mountains had been worn down ...
... The temperature of the surface was relatively the same or stable, but from time to time, it cooled so that ice sheets and _________________________ spread out like giant _________________________ to form deep valleys and mountains faces from rock debris. The Precambrian mountains had been worn down ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces on Earth vocb
... 1. Uniformitarianism- the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes (Erosion and Deposition) 2. Earth Processes dynamic actions that occur on and below the Earth's surface 3. Geology the study of the Earth and ...
... 1. Uniformitarianism- the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes (Erosion and Deposition) 2. Earth Processes dynamic actions that occur on and below the Earth's surface 3. Geology the study of the Earth and ...
- Catalyst - University of Washington
... About 240 M.Y. ago the super-continent Pangaea began to break-up. Note the latitudinal distribution of the continental land masses and configuration of the ocean basins. An equatorial current existed along the Tethyan Seaway. Increased sea floor spreading added CO2 to the atmosphere directly from vo ...
... About 240 M.Y. ago the super-continent Pangaea began to break-up. Note the latitudinal distribution of the continental land masses and configuration of the ocean basins. An equatorial current existed along the Tethyan Seaway. Increased sea floor spreading added CO2 to the atmosphere directly from vo ...
CLIMATE CHANGE IN LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
... vegetation and of biological productivity all around the world. Some of the rivers are disappearing as people notice the increase in planets temperature. If it continues like that we will run out of water and there will be droughts on lowlands. ...
... vegetation and of biological productivity all around the world. Some of the rivers are disappearing as people notice the increase in planets temperature. If it continues like that we will run out of water and there will be droughts on lowlands. ...
download soal
... from one another at one or two inches per year as lava wells up along the line of separation to form new seafloor. Other oceans, such as the Pacific, are shrinking as seafloor descends under their fringing coastlines or offshore arcs of islands. The earth’s crust, in this view, is divided into sever ...
... from one another at one or two inches per year as lava wells up along the line of separation to form new seafloor. Other oceans, such as the Pacific, are shrinking as seafloor descends under their fringing coastlines or offshore arcs of islands. The earth’s crust, in this view, is divided into sever ...
Lecture #6 Causes of Ice Ages & Glacial
... change. The reflectivity of various surfaces is shown on the chart (right side) above. The seasonal and annual changes in the earth’s northern hemisphere albedo are shown on the image above (100% reflectivity is denoted as 1.0 on the scale). The two images on the lower right are infrared satellite i ...
... change. The reflectivity of various surfaces is shown on the chart (right side) above. The seasonal and annual changes in the earth’s northern hemisphere albedo are shown on the image above (100% reflectivity is denoted as 1.0 on the scale). The two images on the lower right are infrared satellite i ...
Geology Unit Review - Bennatti
... The test will cover the entire geology unit including plate tectonics, earthquakes, the structure of the Earth, rocks and minerals, the influence of the last ice age on the Maine landscape and other topics covered in this unit. Go over each of your handouts (paying careful attention to questions tha ...
... The test will cover the entire geology unit including plate tectonics, earthquakes, the structure of the Earth, rocks and minerals, the influence of the last ice age on the Maine landscape and other topics covered in this unit. Go over each of your handouts (paying careful attention to questions tha ...
Powerpoint
... – Changes in the eccentricity of the earth’s orbit (100,000 yrs); the difference in distance is only 3% while the increase in the solar energy is ~7% received at the top of the atmosphere from July to January; when the difference in distance is 9%, the difference in solar energy will be ~20% – Prece ...
... – Changes in the eccentricity of the earth’s orbit (100,000 yrs); the difference in distance is only 3% while the increase in the solar energy is ~7% received at the top of the atmosphere from July to January; when the difference in distance is 9%, the difference in solar energy will be ~20% – Prece ...
METEOROLOGY
... Changes in the eccentricity of the earth’s orbit (100,000 yrs); the difference in distance is only 3% while the increase in the solar energy is ~7% received at the top of the atmosphere from July to January; when the difference in distance is 9%, the difference in solar energy will be ~20% Precessio ...
... Changes in the eccentricity of the earth’s orbit (100,000 yrs); the difference in distance is only 3% while the increase in the solar energy is ~7% received at the top of the atmosphere from July to January; when the difference in distance is 9%, the difference in solar energy will be ~20% Precessio ...
Earth History Study Guide Answers are in RED 1) How has scientific
... to warm more, which causes more ice to melt and more vegetation to grow, which further drives the reinforcing loop. 18) What causes climate to change? Changes in the strength of the Sun, composition of the atmosphere, changes in ocean currents and plate tectonics, reflectivity of Earth’s surface 19) ...
... to warm more, which causes more ice to melt and more vegetation to grow, which further drives the reinforcing loop. 18) What causes climate to change? Changes in the strength of the Sun, composition of the atmosphere, changes in ocean currents and plate tectonics, reflectivity of Earth’s surface 19) ...
Climate Verses Weather
... -The physical climate system involves the earth's atmosphere, land surfaces, and oceans, along with the snow and ice that is so prominent in much of Canada. These components interact with one another and with aspects of the earth's biosphere to determine not only the day-to-day weather, but also the ...
... -The physical climate system involves the earth's atmosphere, land surfaces, and oceans, along with the snow and ice that is so prominent in much of Canada. These components interact with one another and with aspects of the earth's biosphere to determine not only the day-to-day weather, but also the ...
Continuous chemistry in ice cores
... the Greenland NEEM ice core. In the NEGIS firn core concentrations were about 2.7 nM PO43and there was no evidence of any recent anthropogenic impact during the past 300 years. Sources of DRP to the NEGIS site were found to be dust as well as a secondary source-likely of biological origin. The DRP d ...
... the Greenland NEEM ice core. In the NEGIS firn core concentrations were about 2.7 nM PO43and there was no evidence of any recent anthropogenic impact during the past 300 years. Sources of DRP to the NEGIS site were found to be dust as well as a secondary source-likely of biological origin. The DRP d ...
Glacier Outline
... X. Climate records A. Our present atmosphere contains all the same gases, soluble ions, and dusts as in earlier times but possibly in different concentrations B. Ice cores contain information about atmospheric conditions throughout the past 450.000 years C. Sea level change: reallocation of water f ...
... X. Climate records A. Our present atmosphere contains all the same gases, soluble ions, and dusts as in earlier times but possibly in different concentrations B. Ice cores contain information about atmospheric conditions throughout the past 450.000 years C. Sea level change: reallocation of water f ...
Quaternary Climate Change and Geomorphology
... a) Pleistocene Epoch- geologic time period between 10,000 years and 1.6 million years ago. b) Character of Pleistocene: refrigeration of high latitude and high altitude portions of earth, and subsequent development of extensive ice sheets and alpine glaciers. c) Glacial/interglacial relations: Class ...
... a) Pleistocene Epoch- geologic time period between 10,000 years and 1.6 million years ago. b) Character of Pleistocene: refrigeration of high latitude and high altitude portions of earth, and subsequent development of extensive ice sheets and alpine glaciers. c) Glacial/interglacial relations: Class ...
Global Systems - Vocabulary Worksheet File
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
Ice age

An ice age is a period of long-term reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Within a long-term ice age, individual pulses of cold climate are termed ""glacial periods"" (or alternatively ""glacials"" or ""glaciations"" or colloquially as ""ice age""), and intermittent warm periods are called ""interglacials"". Glaciologically, ice age implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in the northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, we are in an interglacial period—the Holocene—of the ice age that began 2.6 million years ago at the start of the Pleistocene epoch, because the Greenland, Arctic, and Antarctic ice sheets still exist.