earth science - University of Iceland
... and ductile behaviour of rocks in the crust and mantle. Brittle fracturing. Isostasy, vertical crustal movements and sea level. Plate velocity models, both relative and absolute. Plate boundary deformation. Rifts and rifting structures. Transcurrent faulting and associated structures. Postrifting an ...
... and ductile behaviour of rocks in the crust and mantle. Brittle fracturing. Isostasy, vertical crustal movements and sea level. Plate velocity models, both relative and absolute. Plate boundary deformation. Rifts and rifting structures. Transcurrent faulting and associated structures. Postrifting an ...
earth science - University of Iceland
... and ductile behaviour of rocks in the crust and mantle. Brittle fracturing. Isostasy, vertical crustal movements and sea level. Plate velocity models, both relative and absolute. Plate boundary deformation. Rifts and rifting structures. Transcurrent faulting and associated structures. Postrifting an ...
... and ductile behaviour of rocks in the crust and mantle. Brittle fracturing. Isostasy, vertical crustal movements and sea level. Plate velocity models, both relative and absolute. Plate boundary deformation. Rifts and rifting structures. Transcurrent faulting and associated structures. Postrifting an ...
Inside the Earth
... Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis that all continents were once connected in a single large landmass that broke apart about 200 million years ago and drifted slowly to their current positions ...
... Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis that all continents were once connected in a single large landmass that broke apart about 200 million years ago and drifted slowly to their current positions ...
Tectonic-scale climate change
... impact on human populations, such relatively rapid changes remain embedded in, and superimposed upon, slower changes over longer timescales. Greenhouse gases generated by human activities are expected to affect climate change in the decades and centuries ahead. But the larger-scale tendency towards ...
... impact on human populations, such relatively rapid changes remain embedded in, and superimposed upon, slower changes over longer timescales. Greenhouse gases generated by human activities are expected to affect climate change in the decades and centuries ahead. But the larger-scale tendency towards ...
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic
... Due to land uplift, a new national height system is needed approximately twice / century; How to maintain in the future? ...
... Due to land uplift, a new national height system is needed approximately twice / century; How to maintain in the future? ...
PHS 111 Test 1 Review Answers Chapters 20-22
... If the rock particles in a sedimentary rock are relatively small with well sorted and well rounded grains, we can infer that the sediment grains traveled a: short distance; long distance for a long time; long distance in a short time; short distance for a long time. Layers of limestone in a rock out ...
... If the rock particles in a sedimentary rock are relatively small with well sorted and well rounded grains, we can infer that the sediment grains traveled a: short distance; long distance for a long time; long distance in a short time; short distance for a long time. Layers of limestone in a rock out ...
living on the edge - Suffolk County Community College
... • This, along with effects of Greenland melts, could displace the warm gulf stream and disrupt downwelling of cold, dense salty water. This would disrupt the transport of warm water towards the higher latitudes; and cold waters toward the lower latitudes of the Atlantic. ...
... • This, along with effects of Greenland melts, could displace the warm gulf stream and disrupt downwelling of cold, dense salty water. This would disrupt the transport of warm water towards the higher latitudes; and cold waters toward the lower latitudes of the Atlantic. ...
Sea-level change and shore-line evolution in Aegean Greece since
... ior", to did the shorelines migrate with time, at rates that for some low-lying regions reached about a kilometre per year. Examples of where such rapid ettcro"chtoent of the sea occurred include the Persian GuIf and the Gulf of Carpentaria of northern Australia, between about 12,ô00 and t0,000 year ...
... ior", to did the shorelines migrate with time, at rates that for some low-lying regions reached about a kilometre per year. Examples of where such rapid ettcro"chtoent of the sea occurred include the Persian GuIf and the Gulf of Carpentaria of northern Australia, between about 12,ô00 and t0,000 year ...
Continental Drift Powerpoint
... one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions of years), the continents slowly drifted apart and ended up in the positions we see on Earth toda ...
... one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions of years), the continents slowly drifted apart and ended up in the positions we see on Earth toda ...
Lesson Title: Tectonic Forces World Geography, Module 1, Lesson 6
... Another physical process is called erosion. Erosion in all of its forms reshapes landforms and coastal regions, as well as riverbeds and riverbanks. Erosion occurs when weathered material is moved by the action of wind, water, ice, or even gravity. For erosion to take place, a transporting agent (su ...
... Another physical process is called erosion. Erosion in all of its forms reshapes landforms and coastal regions, as well as riverbeds and riverbanks. Erosion occurs when weathered material is moved by the action of wind, water, ice, or even gravity. For erosion to take place, a transporting agent (su ...
Continental Drift Notes
... In 1912, a German scientist (he was an explorer, astronomer, and meteorologist proposed that at one time all of the continents had been ______________ to form one huge continent His name was ________________ He called this supercontinent _______________ (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (m ...
... In 1912, a German scientist (he was an explorer, astronomer, and meteorologist proposed that at one time all of the continents had been ______________ to form one huge continent His name was ________________ He called this supercontinent _______________ (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (m ...
What is Global Warming?! Hayanon
... Greenhouse gases such as CO2 and methane emitted from burning fossil fuels contribute a lot to global warming. Various measures are studied to cut those gases. The introduction of “environmental tax” on oil and coal is one of them. When did the Earth start warming? The Earth has gone through warm an ...
... Greenhouse gases such as CO2 and methane emitted from burning fossil fuels contribute a lot to global warming. Various measures are studied to cut those gases. The introduction of “environmental tax” on oil and coal is one of them. When did the Earth start warming? The Earth has gone through warm an ...
Study Questions for Exam #2
... c. Sea level rises because ice sheets calve Ice bergs from surging glaciers which then melt d. Sea level drops because water is tied up in ice sheets instead of in the ocean When was the Pleistocene Epoch? a. Before 540 million years ago b. From 65 million years ago to the present c. From about 1.8 ...
... c. Sea level rises because ice sheets calve Ice bergs from surging glaciers which then melt d. Sea level drops because water is tied up in ice sheets instead of in the ocean When was the Pleistocene Epoch? a. Before 540 million years ago b. From 65 million years ago to the present c. From about 1.8 ...
Document
... (c) Arc accretion of crustal blocks (they mean small terranes; plus later subduction and more volcanic arc building) .. 18) Which of the following statements concerning Tertiary climates is NOT true? (a) Early Tertiary warmth may have resulted from volcanic activity in the Caribbean region. [Yes, ad ...
... (c) Arc accretion of crustal blocks (they mean small terranes; plus later subduction and more volcanic arc building) .. 18) Which of the following statements concerning Tertiary climates is NOT true? (a) Early Tertiary warmth may have resulted from volcanic activity in the Caribbean region. [Yes, ad ...
Practice25_26t
... (c) Arc accretion of crustal blocks (they mean small terranes; plus later subduction and more volcanic arc building) .. 18) Which of the following statements concerning Tertiary climates is NOT true? (a) Early Tertiary warmth may have resulted from volcanic activity in the Caribbean region. [Yes, ad ...
... (c) Arc accretion of crustal blocks (they mean small terranes; plus later subduction and more volcanic arc building) .. 18) Which of the following statements concerning Tertiary climates is NOT true? (a) Early Tertiary warmth may have resulted from volcanic activity in the Caribbean region. [Yes, ad ...
stonehenge: glacial transport of bluestones now confirmed?
... Rob Ixer, says that there are three key conclusions from the recent work: 1. The huge sandstone Altar Stone does not come from Milford Haven but from somewhere between West Wales and Herefordshire and has nothing to do with the Preseli Hills. This calls into question the proposed transport route f ...
... Rob Ixer, says that there are three key conclusions from the recent work: 1. The huge sandstone Altar Stone does not come from Milford Haven but from somewhere between West Wales and Herefordshire and has nothing to do with the Preseli Hills. This calls into question the proposed transport route f ...
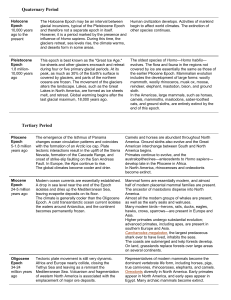
Quaternary Period
... and therefore not a separate epoch in itself. However, it is a period marked by the presence and influence of Homo sapiens. During this time, the glaciers retreat, sea levels rise, the climate warms, and deserts form in some areas. ...
... and therefore not a separate epoch in itself. However, it is a period marked by the presence and influence of Homo sapiens. During this time, the glaciers retreat, sea levels rise, the climate warms, and deserts form in some areas. ...
Low Force and Holwick
... On your left, between the path and the river, is an upstanding mass of rock. This is dolerite – part of the Whin Sill – but at its base you’ll see different, layered rocks. These are sandstones and shales which were once above the Whin Sill. When the Whin Sill was molten, this slab of layered rocks ...
... On your left, between the path and the river, is an upstanding mass of rock. This is dolerite – part of the Whin Sill – but at its base you’ll see different, layered rocks. These are sandstones and shales which were once above the Whin Sill. When the Whin Sill was molten, this slab of layered rocks ...
PHS 111 Test 1 Review Chapters 20-22
... proved that heat flows convectively below Earth's surface . Alfred Wegener supported his theory of continental drift by: fitting together the shorelines of the African and South American continents; using paleoclimatic data– evidence of glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere; paleomagnetic data; making ...
... proved that heat flows convectively below Earth's surface . Alfred Wegener supported his theory of continental drift by: fitting together the shorelines of the African and South American continents; using paleoclimatic data– evidence of glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere; paleomagnetic data; making ...
Y9GeU6A Antarctica Intro PPwk26
... world’s last great wilderness. Antarctica is the world’s last great wilderness. It is a continent almost entirely buried by snow and ice. It is so hostile and remote that it has no permanent residents. Surrounded by the Southern Ocean, Antarctica covers nearly 9% of the Earth’s land. ...
... world’s last great wilderness. Antarctica is the world’s last great wilderness. It is a continent almost entirely buried by snow and ice. It is so hostile and remote that it has no permanent residents. Surrounded by the Southern Ocean, Antarctica covers nearly 9% of the Earth’s land. ...
Chap-4-Sec-2-Evidence-Supporting-Continental
... move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift occurs when the continents change position in relation to each other. While plate tectonics is a relativily new idea, scientists have ...
... move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift occurs when the continents change position in relation to each other. While plate tectonics is a relativily new idea, scientists have ...
EXAM 3
... E. 1900 37. The intensity of an earthquake: A. is variable depending on the distance from the earthquake epicenter B. is the same everywhere for an earthquake of a certain magnitude C. is a measure of the amount on energy released D. will be the same for all earthquakes with an identical magnitude E ...
... E. 1900 37. The intensity of an earthquake: A. is variable depending on the distance from the earthquake epicenter B. is the same everywhere for an earthquake of a certain magnitude C. is a measure of the amount on energy released D. will be the same for all earthquakes with an identical magnitude E ...
Word format
... ONLY USE A SOFT PENCIL ON THE SCANTRON FORM!! 1. The bed load of sediment transported by wind moves by: A. surface creep and saltation B. saltation and suspension C. surface creep and suspension D. saltation and hopping E. saltation only 2. Abrasion can cause stones lying on a desert floor to form A ...
... ONLY USE A SOFT PENCIL ON THE SCANTRON FORM!! 1. The bed load of sediment transported by wind moves by: A. surface creep and saltation B. saltation and suspension C. surface creep and suspension D. saltation and hopping E. saltation only 2. Abrasion can cause stones lying on a desert floor to form A ...
- bYTEBoss
... world’s last great wilderness. Antarctica is the world’s last great wilderness. It is a continent almost entirely buried by snow and ice. It is so hostile and remote that it has no permanent residents. Surrounded by the Southern Ocean, Antarctica covers nearly 9% of the Earth’s land. ...
... world’s last great wilderness. Antarctica is the world’s last great wilderness. It is a continent almost entirely buried by snow and ice. It is so hostile and remote that it has no permanent residents. Surrounded by the Southern Ocean, Antarctica covers nearly 9% of the Earth’s land. ...
Ice age

An ice age is a period of long-term reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Within a long-term ice age, individual pulses of cold climate are termed ""glacial periods"" (or alternatively ""glacials"" or ""glaciations"" or colloquially as ""ice age""), and intermittent warm periods are called ""interglacials"". Glaciologically, ice age implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in the northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, we are in an interglacial period—the Holocene—of the ice age that began 2.6 million years ago at the start of the Pleistocene epoch, because the Greenland, Arctic, and Antarctic ice sheets still exist.