Cell and Cell Metabolism Quiz
... 9. mRNA is made from the DNA during _______, and protein is produced from the mRNA template during _______. A) B) C) D) ...
... 9. mRNA is made from the DNA during _______, and protein is produced from the mRNA template during _______. A) B) C) D) ...
Final Exam Study Guide Ms. Thomas Spring 2011
... 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are present in a human sex cell? 18. How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next? 19. List the differences between mitosis and meiosis. 20. List the t ...
... 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are present in a human sex cell? 18. How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next? 19. List the differences between mitosis and meiosis. 20. List the t ...
Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the
... eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamHI, Xbal, Hindm, Sail, PstI or PvuII (Figure 1). Thus it is proba ...
... eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamHI, Xbal, Hindm, Sail, PstI or PvuII (Figure 1). Thus it is proba ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... another; as a result of this ultraviolet light induced damage, there can be no hydrogen bonding to the opposite, complementary strand. release factor (17.6) a protein that binds to the termination codons in the empty A-site and causes the peptidyl transferase to hydrolyze the bond between the peptid ...
... another; as a result of this ultraviolet light induced damage, there can be no hydrogen bonding to the opposite, complementary strand. release factor (17.6) a protein that binds to the termination codons in the empty A-site and causes the peptidyl transferase to hydrolyze the bond between the peptid ...
1 - gcisd
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
`RNA world`.
... It has ceded primacy as the repository of genetic information to DNA but it has gained versatility. It is a master architect, forming complex, threedimensional structures, and it can carry out catalysis, a trick it learned long before proteins knew how to be enzymes. In short, life probably evolved ...
... It has ceded primacy as the repository of genetic information to DNA but it has gained versatility. It is a master architect, forming complex, threedimensional structures, and it can carry out catalysis, a trick it learned long before proteins knew how to be enzymes. In short, life probably evolved ...
Indezine Template
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
Chapter 10 - Mantachie High School
... **Although the instructions for making a protein are copied from DNA into mRNA, all three types of RNA are involved in the synthesis of proteins. After transcription, mRNA moves through the pores of the nuclear membrane into the cytosol of the cell, where it will direct the synthesis of proteins. Pr ...
... **Although the instructions for making a protein are copied from DNA into mRNA, all three types of RNA are involved in the synthesis of proteins. After transcription, mRNA moves through the pores of the nuclear membrane into the cytosol of the cell, where it will direct the synthesis of proteins. Pr ...
Protein
... RNA polymerase reaches the “termination signal” sequence of nucleotides that marks the end of transcription. RNA polymerase releases both the DNA strand and the newly formed RNA strand. ...
... RNA polymerase reaches the “termination signal” sequence of nucleotides that marks the end of transcription. RNA polymerase releases both the DNA strand and the newly formed RNA strand. ...
II - Humble ISD
... The function of tRNA is to transfer the _____________________ specified by the __________________ to the ____________________ for protein synthesis. The _______________ of the cell is stocked with all 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis. The tRNA molecule carries an ________________ at one ...
... The function of tRNA is to transfer the _____________________ specified by the __________________ to the ____________________ for protein synthesis. The _______________ of the cell is stocked with all 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis. The tRNA molecule carries an ________________ at one ...
New roles for RNA
... • Whole system properties: – Variations in gene expression (time/space). • Control architecture is the primary source of complex traits variation ...
... • Whole system properties: – Variations in gene expression (time/space). • Control architecture is the primary source of complex traits variation ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... • Sugar-phosphate groups are on the outside as a “backbone” • Bases are arranged like rungs on a ladder, perpendicular to the “backbone” • 10 base pairs per turn of the helix ...
... • Sugar-phosphate groups are on the outside as a “backbone” • Bases are arranged like rungs on a ladder, perpendicular to the “backbone” • 10 base pairs per turn of the helix ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) = complexes of proteins and small nuclear RNAs that are found only in the nucleus; some participate in RNA splicing - Referred to as “snurps” (also referred to as snRNAs) ...
... Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) = complexes of proteins and small nuclear RNAs that are found only in the nucleus; some participate in RNA splicing - Referred to as “snurps” (also referred to as snRNAs) ...
34. Measuring Selection in RNA molecules.
... and function. We are using the Rfam dataset consisting of 503 different RNA families. To our knowledge, this is the largest dataset used for investigating RNA selection. The initial focus will be on miRNAs. Currently, the counting approach is being undertaken. For a number of 47 miRNA families, eac ...
... and function. We are using the Rfam dataset consisting of 503 different RNA families. To our knowledge, this is the largest dataset used for investigating RNA selection. The initial focus will be on miRNAs. Currently, the counting approach is being undertaken. For a number of 47 miRNA families, eac ...
Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription
... – In mitochondrial DNA, UGA is not a stop codon as it is in “universal code” – Other codons are different – Chloroplasts and ciliates (protists) have ______________________________ • It is thought that the changes to _____________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
... – In mitochondrial DNA, UGA is not a stop codon as it is in “universal code” – Other codons are different – Chloroplasts and ciliates (protists) have ______________________________ • It is thought that the changes to _____________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
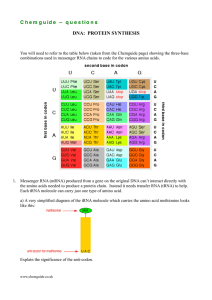
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Gene to Protein
... can also only attach in the 5’->3’ direction produces the chain at the rate of 60 nucleotides/sec the RNA detaches from the RNA polymerase while the DNA goes back into helix g. multiple RNA polymerases can ride along the DNA transcribing multiple copies of the gene in question ...
... can also only attach in the 5’->3’ direction produces the chain at the rate of 60 nucleotides/sec the RNA detaches from the RNA polymerase while the DNA goes back into helix g. multiple RNA polymerases can ride along the DNA transcribing multiple copies of the gene in question ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
... • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
GENE EXPRESSION CH 17
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
Chapter 25
... intron is cleaved, and the two exons are coonected. • The cleaved intron is further spliced into two pieces. Ribozymes Self-splicing function of RNA indicates that some RNAs have an enzyme activity. Small hammerhead RNAs have indeed nuclease activities that cleave a single strand DNA. These RNAs are ...
... intron is cleaved, and the two exons are coonected. • The cleaved intron is further spliced into two pieces. Ribozymes Self-splicing function of RNA indicates that some RNAs have an enzyme activity. Small hammerhead RNAs have indeed nuclease activities that cleave a single strand DNA. These RNAs are ...
DNA Functions
... RNA is made up of numerous nucleotides assembled in exactly the same way as in DNA except that……. ! 1. RNA is mostly single stranded and not a helix. ! 2. the sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose. ! 3. the base thymine is replaced by uracil. ...
... RNA is made up of numerous nucleotides assembled in exactly the same way as in DNA except that……. ! 1. RNA is mostly single stranded and not a helix. ! 2. the sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose. ! 3. the base thymine is replaced by uracil. ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... Intron (non-coding sequences) are cut out by spliceosomes. Leaving only Exons (Coding sequences) making up the mRNA that leaves the nucleus. Alternative splicing patterns means one gene can make more than one protein ...
... Intron (non-coding sequences) are cut out by spliceosomes. Leaving only Exons (Coding sequences) making up the mRNA that leaves the nucleus. Alternative splicing patterns means one gene can make more than one protein ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Innovation
... be once of five different bases. The pyrimidine bases are thymine, cytosine and uracil. The Purine bases are adenine and guanine. There are also two different types of pentose sugar which differ between DNA and RNA, the pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA it is ribose. Shown below is a si ...
... be once of five different bases. The pyrimidine bases are thymine, cytosine and uracil. The Purine bases are adenine and guanine. There are also two different types of pentose sugar which differ between DNA and RNA, the pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA it is ribose. Shown below is a si ...
The RNA World
... RNA interference – The Beginning Fire et al. '98 "Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans " Nature 391: 806-11 Introduction of RNA into cells to interfere with function of an endogeneous gene Investigation of the requirements for structure and deliv ...
... RNA interference – The Beginning Fire et al. '98 "Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans " Nature 391: 806-11 Introduction of RNA into cells to interfere with function of an endogeneous gene Investigation of the requirements for structure and deliv ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.