Father of Modern Genetics
... DNA (genes) and “unzips” the hydrogen bonds The RNA polymerase also begins the building of the RNA by adding RNA nucleotides in accordance with the DNA base sequence ...
... DNA (genes) and “unzips” the hydrogen bonds The RNA polymerase also begins the building of the RNA by adding RNA nucleotides in accordance with the DNA base sequence ...
DNA
... DNA Synthesis The synthesis of new DNA strands complementary to both strands of the parental molecule posed an important problem to understanding the biochemistry of DNA replication. Since the two strands of double-helical DNA run in opposite (antiparallel) directions, continuous synthesis of two ...
... DNA Synthesis The synthesis of new DNA strands complementary to both strands of the parental molecule posed an important problem to understanding the biochemistry of DNA replication. Since the two strands of double-helical DNA run in opposite (antiparallel) directions, continuous synthesis of two ...
Sample Exam #2 ( file)
... For a complete translation (including termination) of a protein synthesis containing 330 amino acids would require an mRNA coding region of ____________ bases long. A. 993 B. 663 C. 660 D. 330 E. 990 ...
... For a complete translation (including termination) of a protein synthesis containing 330 amino acids would require an mRNA coding region of ____________ bases long. A. 993 B. 663 C. 660 D. 330 E. 990 ...
DNA WebQuest NAME___________________________
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. 1. How does the mRNA leave the nucleus? ...
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. 1. How does the mRNA leave the nucleus? ...
Ch. 10 DNA Review Questions
... b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA that indicate to RNA polymerase when to begin transcription. 5. Many RNA molecules f ...
... b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA that indicate to RNA polymerase when to begin transcription. 5. Many RNA molecules f ...
This is going to be a long journey, but it is crucial
... 8. What later revisions to the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis were necessary as more information was gained? A ...
... 8. What later revisions to the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis were necessary as more information was gained? A ...
I. Microbial Genetics (Chapter 7) A. Overview 1. all of the information
... 3. DNA helix unravels and actual replication occurs at the replication fork a. bidirectional, replicons (portion of genome containing an origin and replicated as a unit) separate when forks meet opposite the origin b. replication fork and associated enzymes may be attached to plasma membrane 4. euc ...
... 3. DNA helix unravels and actual replication occurs at the replication fork a. bidirectional, replicons (portion of genome containing an origin and replicated as a unit) separate when forks meet opposite the origin b. replication fork and associated enzymes may be attached to plasma membrane 4. euc ...
Origin of life on Earth Two approaches: • bottom-up
... of modern life could have formed from abiotic processes on the early Earth? • top-down - which of the constituents of current cells could have been part of earlier, simpler life ...
... of modern life could have formed from abiotic processes on the early Earth? • top-down - which of the constituents of current cells could have been part of earlier, simpler life ...
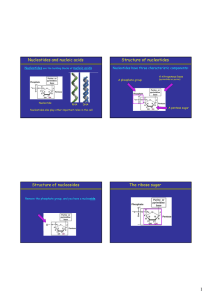
Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information storage and transfer! • Note sequence conventionally i ...
... not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information storage and transfer! • Note sequence conventionally i ...
RNA Polymerase II analysis in Drosophila Melanogaster
... The principle is that DNA-binding proteins in cells are cross-linked to the DNA that they are binding. By using a specific antibody, we can immunoprecipitate the protein–DNA complex. After the crosslinking, the cells are bursted and the DNA is broken into pieces by sonication. The DNA is purified wi ...
... The principle is that DNA-binding proteins in cells are cross-linked to the DNA that they are binding. By using a specific antibody, we can immunoprecipitate the protein–DNA complex. After the crosslinking, the cells are bursted and the DNA is broken into pieces by sonication. The DNA is purified wi ...
Document
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...
Chapter 17 - TeacherWeb
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...
Analytical Questions
... 4. The primary structure of a protein is the linear order of amino acids in the polypeptide chain joined by covalent peptide bonds. The secondary structure refers to the formation of either -helices or pleated sheets by the peptide chain. -helices are stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the s ...
... 4. The primary structure of a protein is the linear order of amino acids in the polypeptide chain joined by covalent peptide bonds. The secondary structure refers to the formation of either -helices or pleated sheets by the peptide chain. -helices are stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the s ...
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 1. In DNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 2. In RNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 3. Transcription takes place in the ________________; translation takes place in the _______________. 4. The building blocks of nucleic ac ...
... 1. In DNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 2. In RNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 3. Transcription takes place in the ________________; translation takes place in the _______________. 4. The building blocks of nucleic ac ...
ppt 2015 edit
... many copies of an RNA made from one copy of DNA. – Regulation of gene expression can be effected by having specific controls at each element of the pathway between DNA and proteins. – The more elements there are in the pathway, the more opportunities there are to control it in different circumstance ...
... many copies of an RNA made from one copy of DNA. – Regulation of gene expression can be effected by having specific controls at each element of the pathway between DNA and proteins. – The more elements there are in the pathway, the more opportunities there are to control it in different circumstance ...
nuclear structure (2): the nucleolus
... In the above review diagram of the role of the nucleolus in the synthesis of the ribosomal subunits you can see the term “loop of nucleolar organizer DNA”. This is really just another term for “all the 45S rRNA genes and the non-transcibed spacer DNA”. This is usually called the nucleolar organizing ...
... In the above review diagram of the role of the nucleolus in the synthesis of the ribosomal subunits you can see the term “loop of nucleolar organizer DNA”. This is really just another term for “all the 45S rRNA genes and the non-transcibed spacer DNA”. This is usually called the nucleolar organizing ...
DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis
... – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
... – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
Transcription and Translation
... Why are there three nucleotides in the code? There are four bases in DNA (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine). Clearly, it is not possible to have one base coding for each of 20 different amino acids. Similarly, using two bases would be insufficient (4n or 16 permutations of two bases, where n = ...
... Why are there three nucleotides in the code? There are four bases in DNA (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine). Clearly, it is not possible to have one base coding for each of 20 different amino acids. Similarly, using two bases would be insufficient (4n or 16 permutations of two bases, where n = ...
Qβ replicase discriminates between legitimate and illegitimate
... Arguments for the feasibility of the RNA world 1. Nucleotides can spontaneously form under conditions that existed on the early Earth or a similar planet. 2. Activated nucleotides can spontaneously polymerize into long (≥ 40 nucleotides) strand. 3. RNA molecules can spontaneously recombine to produ ...
... Arguments for the feasibility of the RNA world 1. Nucleotides can spontaneously form under conditions that existed on the early Earth or a similar planet. 2. Activated nucleotides can spontaneously polymerize into long (≥ 40 nucleotides) strand. 3. RNA molecules can spontaneously recombine to produ ...
Pa I I, hl. L. Blasticidin-S: on... Cycloheximide has been used widely as ...
... in light microscopic studies. 4. Not only spindle fiben (which attach to chromatin regions), but also a tightly compressed longitudinal bundle of filaments (which stretcher the late telophase daughter nuclei ) is seen. This filament bundle may be similar to the “Zentralrtrong” described by Girbordt. ...
... in light microscopic studies. 4. Not only spindle fiben (which attach to chromatin regions), but also a tightly compressed longitudinal bundle of filaments (which stretcher the late telophase daughter nuclei ) is seen. This filament bundle may be similar to the “Zentralrtrong” described by Girbordt. ...
Extracting Nucleic Acids from UK NEQAS LI Samples
... lot of extraction methods (even if our samples are red in colour, lyophilisation will have lysed any red cells present) ...
... lot of extraction methods (even if our samples are red in colour, lyophilisation will have lysed any red cells present) ...
Biol-1406_Ch10Notes.ppt
... 1. The mRNA binds to the _____________ subunit 2. The mRNA slides through the subunit until the first ____ (start codon) is exposed in the first _____ ...
... 1. The mRNA binds to the _____________ subunit 2. The mRNA slides through the subunit until the first ____ (start codon) is exposed in the first _____ ...
Nucleic Acids
... - the pentose sugar in RNA is ribose, in DNA it’s deoxyribose. - in RNA, uracil replaces the base thymine (U pairs with A) - RNA is single stranded while DNA is double stranded - RNA molecules are much smaller than DNA molecules • There are three main types of RNA: - ribosomal (rRNA), messenger (mRN ...
... - the pentose sugar in RNA is ribose, in DNA it’s deoxyribose. - in RNA, uracil replaces the base thymine (U pairs with A) - RNA is single stranded while DNA is double stranded - RNA molecules are much smaller than DNA molecules • There are three main types of RNA: - ribosomal (rRNA), messenger (mRN ...
chapter review answers
... A codon is a set of three nucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid. An example of as codon is any three letter nucleotide combonation… CAA, GAU, UAG (stop!) 6. What is an anticodon? What role does it play? An anticodon is a set of complementary bases on transfer RNA that bind to a mRNA to br ...
... A codon is a set of three nucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid. An example of as codon is any three letter nucleotide combonation… CAA, GAU, UAG (stop!) 6. What is an anticodon? What role does it play? An anticodon is a set of complementary bases on transfer RNA that bind to a mRNA to br ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.