Cdc45: the missing RecJ ortholog in eukaryotes?
... Fig. 1. Sequence analysis of the Cdc45 and RecJ protein families. (A) Domain architecture of human Cdc45 and Escherichia coli RecJ proteins. For the E.coli RecJ protein, domains were assigned according to the RecJ core structure (Yamagata et al., 2002) and the Pfam domain database (Finn et al., 2008 ...
... Fig. 1. Sequence analysis of the Cdc45 and RecJ protein families. (A) Domain architecture of human Cdc45 and Escherichia coli RecJ proteins. For the E.coli RecJ protein, domains were assigned according to the RecJ core structure (Yamagata et al., 2002) and the Pfam domain database (Finn et al., 2008 ...
Getting a grip on how DNA polymerases function
... Fig. 1 Structural comparison of family A and B polymerases. Nucleotide incorporation occurs in discrete steps and involves polymerase (E) binding with DNA (TP), followed by binding to dNTP to form the E–TP–dNTP ‘polymerizing complex’. During the dNTP-binding step within family A (PDB code 3KTQ) and ...
... Fig. 1 Structural comparison of family A and B polymerases. Nucleotide incorporation occurs in discrete steps and involves polymerase (E) binding with DNA (TP), followed by binding to dNTP to form the E–TP–dNTP ‘polymerizing complex’. During the dNTP-binding step within family A (PDB code 3KTQ) and ...
Rapid and reproducible DNA isolation from 1 ml of whole blood with
... This application note shows the benefits of KingFisher Flex by using genomic DNA isolation from blood as an example. ...
... This application note shows the benefits of KingFisher Flex by using genomic DNA isolation from blood as an example. ...
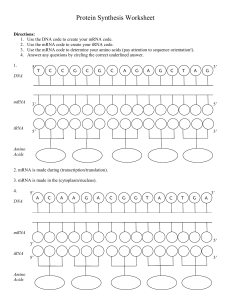
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
LIPIDS
... It has a great flexibility; the conformation is not rigid. There are differences between the native DNA, ”in vivo”, and the one “in vitro”; by removing the water and dependent on the electrolytes in the environment, the double-helix is structurally altered. ...
... It has a great flexibility; the conformation is not rigid. There are differences between the native DNA, ”in vivo”, and the one “in vitro”; by removing the water and dependent on the electrolytes in the environment, the double-helix is structurally altered. ...
A Recipe for Traits.indd
... (T) and Cytosine (C). These bases, G, A, T, C are commonly referred to as the “DNA alphabet.” This DNA alphabet encodes a detailed set of instructions for building an organism’s physical traits. The DNA instructions are divided into segments called genes. Differences in the DNA sequence of each gene ...
... (T) and Cytosine (C). These bases, G, A, T, C are commonly referred to as the “DNA alphabet.” This DNA alphabet encodes a detailed set of instructions for building an organism’s physical traits. The DNA instructions are divided into segments called genes. Differences in the DNA sequence of each gene ...
MS Word - VCU Secrets of the Sequence
... with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form a new strand of DNA. DNA regulates cellular function by directing the creation of certain proteins. It acts as a model for making a molecule similar to itself called messenger RNA (mRNA). This process is known as transcription a ...
... with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form a new strand of DNA. DNA regulates cellular function by directing the creation of certain proteins. It acts as a model for making a molecule similar to itself called messenger RNA (mRNA). This process is known as transcription a ...
procedure - DNA Interactive
... replicating faithfully as cells divided and organisms developed. Observations made by Barbara McClintock at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory told a radically different story. McClintock observed that regions of DNA could jump, or "transpose". This observation challenged the simplistic view of how a gen ...
... replicating faithfully as cells divided and organisms developed. Observations made by Barbara McClintock at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory told a radically different story. McClintock observed that regions of DNA could jump, or "transpose". This observation challenged the simplistic view of how a gen ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... • The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of messenger RNA acts as a genetic message, the complete information for the building of a protein. • As you know, proteins contain chains of amino acids. You could say that the language of proteins uses an alphabet of ...
... • The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of messenger RNA acts as a genetic message, the complete information for the building of a protein. • As you know, proteins contain chains of amino acids. You could say that the language of proteins uses an alphabet of ...
RECOMBINATION IN BACTERIA Transfer of Genetic Material in
... In order to become successfully transformed, bacteria must be competent. This means that the bacteria are expressing the appropriate enzymes (the 'transformation machinery') required to transport the exogenous DNA into the cell. Therefore, the correct genes must be expressed in order to carry out t ...
... In order to become successfully transformed, bacteria must be competent. This means that the bacteria are expressing the appropriate enzymes (the 'transformation machinery') required to transport the exogenous DNA into the cell. Therefore, the correct genes must be expressed in order to carry out t ...
genotypes
... disease like muscular dystrophy, it is important to consider two steps. The first is to determine if the disorder is autosomal or X-linked. • If the disorder is X-linked most of the males will have the disorder because the Y-chromosome cannot mask the affects of an affected X-chromosome. A female ca ...
... disease like muscular dystrophy, it is important to consider two steps. The first is to determine if the disorder is autosomal or X-linked. • If the disorder is X-linked most of the males will have the disorder because the Y-chromosome cannot mask the affects of an affected X-chromosome. A female ca ...
Chromosomes, Genes and DNA
... A DNA mutation changes the amino acid sequence and so a different protein may be produced. ...
... A DNA mutation changes the amino acid sequence and so a different protein may be produced. ...
An investigation into the relationship between
... September, following the birth / hatching of young reptiles, as these might be more vulnerable to predation. Overall, this study has provided a good foundation for further research into the relationship between pheasants and reptiles as prey items. However, had reptile DNA been found in the faecal s ...
... September, following the birth / hatching of young reptiles, as these might be more vulnerable to predation. Overall, this study has provided a good foundation for further research into the relationship between pheasants and reptiles as prey items. However, had reptile DNA been found in the faecal s ...
Suracell: My Test Results
... letters A (for adenine), T (for thymine), G (for guanine) and C ( for cytosine) - 3 billion strings linked together. If the DNA of any two individuals were compared, a variation would be found approximately once in every two thousand letter positions and this variation is the SNP. These variations a ...
... letters A (for adenine), T (for thymine), G (for guanine) and C ( for cytosine) - 3 billion strings linked together. If the DNA of any two individuals were compared, a variation would be found approximately once in every two thousand letter positions and this variation is the SNP. These variations a ...
HA Nucleic Acids Practice Exam
... NAT: LS_1c STA: 3.2 TOP: 12-8 13. ANS: B Introns, or intervening sequences, get processed out of the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus, so removal of an intron would probably have little effect on bacterial functions such as enzyme synthesis. Feedback A B C D ...
... NAT: LS_1c STA: 3.2 TOP: 12-8 13. ANS: B Introns, or intervening sequences, get processed out of the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus, so removal of an intron would probably have little effect on bacterial functions such as enzyme synthesis. Feedback A B C D ...
DNAandproteinsynthesis
... Your textbook lacks information on certain sections – use these PP slides as your notes. ...
... Your textbook lacks information on certain sections – use these PP slides as your notes. ...
Lecture 17 Protein synthesis pp101-110
... • Amino acid monomers are linked together to form polymeric proteins – This is accomplished by an enzyme-mediated dehydration reaction – This links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid – The covalent linkage resulting is called a peptide bond ...
... • Amino acid monomers are linked together to form polymeric proteins – This is accomplished by an enzyme-mediated dehydration reaction – This links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid – The covalent linkage resulting is called a peptide bond ...
AP Biology
... § The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) u Frederick Griffith (1928) u Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) u Erwin Chargaff (1947) u Hershey & Chase (1952) u Watson & Crick (1953) u ...
... § The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) u Frederick Griffith (1928) u Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) u Erwin Chargaff (1947) u Hershey & Chase (1952) u Watson & Crick (1953) u ...
Chromosomal insertion of foreign DNA
... monomers has been generated by circularization and random cleavage. Extrachromosomal recombination is known to occur by a nonconservative process in transfected mammalian cells in culture. Concatemeric molecules integrate into the chromosomes, more or less at random, by illegitimate recombination. T ...
... monomers has been generated by circularization and random cleavage. Extrachromosomal recombination is known to occur by a nonconservative process in transfected mammalian cells in culture. Concatemeric molecules integrate into the chromosomes, more or less at random, by illegitimate recombination. T ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... DNA Begins the Process • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
... DNA Begins the Process • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... – Restricts viral replication – However, certain bacteriophages have evolved to use methylation as a way to avoid digestion by restriction enzymes ...
... – Restricts viral replication – However, certain bacteriophages have evolved to use methylation as a way to avoid digestion by restriction enzymes ...
... ii) Pick one of the above (indicate your choice), and write the correct ionic form of the amino acid that you would expect to find at pH 7.0.(2 pts) iii) For the following statements, write the letter of the amino acid to which the statement best applies. Note, you may want to use the same amino aci ...
Anatomy of the Gene - University of Missouri
... Hartl and Jones. Genetics Analysis of Genes and Genomes ...
... Hartl and Jones. Genetics Analysis of Genes and Genomes ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.