Chapter 8: The Digestive System
... Located above, right of stomach Produces sodium bicarbonate (neutralizes HCl) ...
... Located above, right of stomach Produces sodium bicarbonate (neutralizes HCl) ...
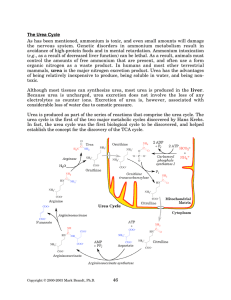
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... (e.g., as a result of decreased liver function) can be lethal. As a result, animals must control the amounts of free ammonium that are present, and often use a form organic nitrogen as a waste product. In humans and most other terrestrial mammals, urea is the major nitrogen excretion product. Urea h ...
... (e.g., as a result of decreased liver function) can be lethal. As a result, animals must control the amounts of free ammonium that are present, and often use a form organic nitrogen as a waste product. In humans and most other terrestrial mammals, urea is the major nitrogen excretion product. Urea h ...
Scholarly Interest Report
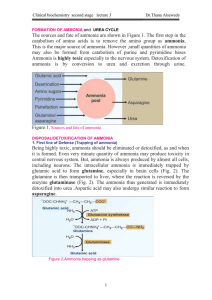
... origin. Liver tissue is the site of gluconeogenesis in higher vertebrates and, during this process, amino acids are deaminated, forming ammonia. Extrahepatic tissues, especially working muscle, form ammonia which must be returned to the liver for detoxication. Working muscle also forms glutamine whi ...
... origin. Liver tissue is the site of gluconeogenesis in higher vertebrates and, during this process, amino acids are deaminated, forming ammonia. Extrahepatic tissues, especially working muscle, form ammonia which must be returned to the liver for detoxication. Working muscle also forms glutamine whi ...
(18 , 19)
... bile is transported actively to portal blood. Albumin works as a carrier. The whole process of conversion and conjugation and transportation to duodenum then return to liver is called enterohepatic circulation. Cholestyramine , a drug which bind to bile acid in the gut and prevents reabsorption and ...
... bile is transported actively to portal blood. Albumin works as a carrier. The whole process of conversion and conjugation and transportation to duodenum then return to liver is called enterohepatic circulation. Cholestyramine , a drug which bind to bile acid in the gut and prevents reabsorption and ...
UNIFORM PARTICLES WITH A LARGE SURFACE AREA FORMED
... by the neutralization of aqueous solutions of ferric salts with ammonium or alkali metal hydroxides [2,6,15–19]. As-formed precipitates usually consist of highly irregular aggregates of very small particles (mostly 4 – 6 nm) [1,2]. Schwertmannite particles are usually spherical aggregates of a chara ...
... by the neutralization of aqueous solutions of ferric salts with ammonium or alkali metal hydroxides [2,6,15–19]. As-formed precipitates usually consist of highly irregular aggregates of very small particles (mostly 4 – 6 nm) [1,2]. Schwertmannite particles are usually spherical aggregates of a chara ...
Renal Physiology 1
... • TM values lower than that of glucose, so can excrete excess in urine. • Amino acid transporters rely upon Na+ gradient at apical membrane, but a couple of exceptions don’t. • Exit across basolateral membrane via diffusion , but again, ...
... • TM values lower than that of glucose, so can excrete excess in urine. • Amino acid transporters rely upon Na+ gradient at apical membrane, but a couple of exceptions don’t. • Exit across basolateral membrane via diffusion , but again, ...
Glycolysis
... • Might be part of a general urea-synthesizing mechanism. • More arginase present in the liver than needed for degradation of arginine. • The principle of evolution. ...
... • Might be part of a general urea-synthesizing mechanism. • More arginase present in the liver than needed for degradation of arginine. • The principle of evolution. ...
15Nitrogen metabolism
... - Urea is the major disposal form of amino group derived from a.a - One nitrogen is supplied by free NH4+ and the other from Aspartate. - Glutamate is the immediate precursor of both ammonia through oxidative deamination and by aspartate aminotransferase - Carbon and Oxygen are derived from CO2 -Ure ...
... - Urea is the major disposal form of amino group derived from a.a - One nitrogen is supplied by free NH4+ and the other from Aspartate. - Glutamate is the immediate precursor of both ammonia through oxidative deamination and by aspartate aminotransferase - Carbon and Oxygen are derived from CO2 -Ure ...
Guideline for the investigation of hyperammonaemia
... collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sample and should be taken directly to the biochemistry laboratory. It is important to inform the laboratory that an ammonia sample is being taken before drawing the blood. Hyperammonaemia can be caus ...
... collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sample and should be taken directly to the biochemistry laboratory. It is important to inform the laboratory that an ammonia sample is being taken before drawing the blood. Hyperammonaemia can be caus ...
The six urea cycle disorders
... stomach. The treatment may also include supplementation with special amino acid formulas developed specifically for urea cycle disorders, multiple vitamins and calcium supplements. Frequent blood tests are required to monitor the disorders and optimize treatment, and frequently hospitalizations are ...
... stomach. The treatment may also include supplementation with special amino acid formulas developed specifically for urea cycle disorders, multiple vitamins and calcium supplements. Frequent blood tests are required to monitor the disorders and optimize treatment, and frequently hospitalizations are ...
Urea
... • In liver, alanine is converted to pyruvate & ammonia • Pyruvate can be converted to glucose (by gluconeogenesis) • Glucose can enter the blood to be used by skeletal muscles ...
... • In liver, alanine is converted to pyruvate & ammonia • Pyruvate can be converted to glucose (by gluconeogenesis) • Glucose can enter the blood to be used by skeletal muscles ...
Detoxikace endogenních a exogenních látek
... Catalyzed by cytochrome P450s: in humans: ~60 isoenzymes; the most abundant: CYP3A4 ...
... Catalyzed by cytochrome P450s: in humans: ~60 isoenzymes; the most abundant: CYP3A4 ...
Amino acid metabolism II. Urea cycle
... • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS-I) in the liver is regulated by changes in demand f ...
... • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS-I) in the liver is regulated by changes in demand f ...
Guidelines for the Investigation of Hyperammonaemia
... Neonates presenting with inherited defects in the urea cycle usually have an initial 2448 hour period of well being after which the clinical features associated with hyperammonaemia become apparent. The initial clinical deterioration is often mistaken for sepsis as the features of feeding difficulti ...
... Neonates presenting with inherited defects in the urea cycle usually have an initial 2448 hour period of well being after which the clinical features associated with hyperammonaemia become apparent. The initial clinical deterioration is often mistaken for sepsis as the features of feeding difficulti ...
The Urea Cycle
... II. The Urea Cycle Excess amino groups are channeled into a single excretory end product. Bony fish excrete ammonia and are thus called ammonoteilic animals. The liver of these bony fish releases ammonia into the blood stream where it is carried to the gills where it is rapidly cleared. Birds and re ...
... II. The Urea Cycle Excess amino groups are channeled into a single excretory end product. Bony fish excrete ammonia and are thus called ammonoteilic animals. The liver of these bony fish releases ammonia into the blood stream where it is carried to the gills where it is rapidly cleared. Birds and re ...
Ch 48 Digestive system
... The kidneys play a major role in maintaining a. the proper breathing rate. b. the proper glucose levels in the blood. c. homeostasis by removing urea, water, and other wastes from the blood. d. the concentration of digestive enzymes in the blood. ...
... The kidneys play a major role in maintaining a. the proper breathing rate. b. the proper glucose levels in the blood. c. homeostasis by removing urea, water, and other wastes from the blood. d. the concentration of digestive enzymes in the blood. ...
Urea cycle
... The activity of urea cycle is regulated at two levels: • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I ( ...
... The activity of urea cycle is regulated at two levels: • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I ( ...
10-Urea cycle
... ammonia and its transport to liver A: Removal of α-amino group of amino acids and formation of ammonia: 1. Transamination to glutamate 2. Oxidative deamination of glutamate ...
... ammonia and its transport to liver A: Removal of α-amino group of amino acids and formation of ammonia: 1. Transamination to glutamate 2. Oxidative deamination of glutamate ...
CATABOLISM OF PROTEINS AND AMINO ACIDS1.36 MB
... • Urea cycle enzymes increase or decrease in response to high or low-protein diet • Starvation and high-protein diets elevate enzyme levels to cope with increased ammonia production that accompanies ...
... • Urea cycle enzymes increase or decrease in response to high or low-protein diet • Starvation and high-protein diets elevate enzyme levels to cope with increased ammonia production that accompanies ...
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... further reactions are taking place in cytoplasm. Citrulline is neither present in tissue proteins nor in blood; but it is present in milk. Step 3. Formation of Argininosuccinate One molecule of aspartic acid adds to citrulline forming a carbon to nitrogen bond which provides the 2nd nitrogen atom of ...
... further reactions are taking place in cytoplasm. Citrulline is neither present in tissue proteins nor in blood; but it is present in milk. Step 3. Formation of Argininosuccinate One molecule of aspartic acid adds to citrulline forming a carbon to nitrogen bond which provides the 2nd nitrogen atom of ...
Summary of Chapter 24
... • Overall reaction uses 4 “high energy” phosphate bond hydrolysis. CO2 + NH3 + Asp + 2H2O + 3ATP → Urea + Fumarate + 2ADP + AMP + 2Pi + PPi (→ 2Pi) • Oxidation of urea cycle produces 2NADH (= 6ATP). • Krebs bicycle: Urea cycle and aspartate-argininosuccinate shunt of citric acid cycle. • Urea cycle ...
... • Overall reaction uses 4 “high energy” phosphate bond hydrolysis. CO2 + NH3 + Asp + 2H2O + 3ATP → Urea + Fumarate + 2ADP + AMP + 2Pi + PPi (→ 2Pi) • Oxidation of urea cycle produces 2NADH (= 6ATP). • Krebs bicycle: Urea cycle and aspartate-argininosuccinate shunt of citric acid cycle. • Urea cycle ...
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH2)2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals, and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and is an important raw material for the chemical industry.Friedrich Wöhler's discovery in 1828 that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials was an important conceptual milestone in chemistry. It showed for the first time that a substance previously known only as a byproduct of life could be synthesized in the laboratory without biological starting materials, contradicting the widely held doctrine of vitalism.