Ancient Egyptian Economy
... Ancient Egypt – The Economy (handout) 1) Agriculture - Most important economic activity in Ancient Egypt b/c majority of population took part in farming. - Farmers were paid by receiving a small portion of the crop (usually wheat or barley) - Nile dictated everyone’s life: At beginning of year, Nile ...
... Ancient Egypt – The Economy (handout) 1) Agriculture - Most important economic activity in Ancient Egypt b/c majority of population took part in farming. - Farmers were paid by receiving a small portion of the crop (usually wheat or barley) - Nile dictated everyone’s life: At beginning of year, Nile ...
2:1 “The Nile Valley” p. 38-46 1. 1. The Nile River *The Nile flows
... *the world’s longest river *2 rivers meet to form Nile River 1. Blue Nile River 2. White Nile River *Water rapids called cataracts form where 2 rivers meet. -large ships can’t navigate & must stay in last 650 miles of northern part of the Nile. ...
... *the world’s longest river *2 rivers meet to form Nile River 1. Blue Nile River 2. White Nile River *Water rapids called cataracts form where 2 rivers meet. -large ships can’t navigate & must stay in last 650 miles of northern part of the Nile. ...
The Nile River “The Gift of the Nile”
... Funeral barges carried coffins from the east to the west banks ...
... Funeral barges carried coffins from the east to the west banks ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Answer Key The farming conditions along
... authority and also were symbols that he was a pharaoh. King Tutankhamen was 18 or 19 years old when he died, and he died from a disease called malaria. The Nile River was important to ancient Egyptians because they depended on the annual flooding to help them with their agriculture, and it also help ...
... authority and also were symbols that he was a pharaoh. King Tutankhamen was 18 or 19 years old when he died, and he died from a disease called malaria. The Nile River was important to ancient Egyptians because they depended on the annual flooding to help them with their agriculture, and it also help ...
Ch4 Sec1 Egypt - History With Mr. Green
... Increased Food ___________________________ 5. How did farmers use the Nile to grow their crops? ...
... Increased Food ___________________________ 5. How did farmers use the Nile to grow their crops? ...
cataract
... 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. 17. The Nubian section of the Nile contained six cataracts. 18. The Nile affected ancient Egyptian life by creating rich farmland. 19. Pharaohs governed their people with absolute power. 20. Th ...
... 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. 17. The Nubian section of the Nile contained six cataracts. 18. The Nile affected ancient Egyptian life by creating rich farmland. 19. Pharaohs governed their people with absolute power. 20. Th ...
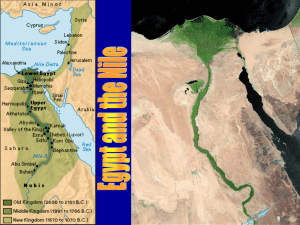
Egypt: Geography The Ancient Egyptian Civilization lasted more that
... Egypt: Geography The Ancient Egyptian Civilization lasted more that 2,000 years. Longer than its Mesopotamian counterparts. The Nile River flows North, from mountains in Central Africa to the Mediterranean Sea. It flows approximately 4,150 miles. Despite an association with Egypt only the last 600 m ...
... Egypt: Geography The Ancient Egyptian Civilization lasted more that 2,000 years. Longer than its Mesopotamian counterparts. The Nile River flows North, from mountains in Central Africa to the Mediterranean Sea. It flows approximately 4,150 miles. Despite an association with Egypt only the last 600 m ...
Geofarming
... Seed planting was done by hand and animals followed behind to stamp the seeds into the ground. ...
... Seed planting was done by hand and animals followed behind to stamp the seeds into the ground. ...
Early River Civilizations
... Nile River Valley Civilization • The Nile River is the longest river in the world. It stretches 4, 187 miles to the Mediterranean Sea. • The source of the Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria, but the lake itself has feeder rivers of considerable size. ...
... Nile River Valley Civilization • The Nile River is the longest river in the world. It stretches 4, 187 miles to the Mediterranean Sea. • The source of the Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria, but the lake itself has feeder rivers of considerable size. ...
Ancient Egyptians and the Environment
... monuments (ex pyramids) for the pharaoh. (June to October) Crop yields increase so the pharaoh can tax the people more People are happy so they trust the Pharaoh- results in unity build his irrigation systems- increases productivity ...
... monuments (ex pyramids) for the pharaoh. (June to October) Crop yields increase so the pharaoh can tax the people more People are happy so they trust the Pharaoh- results in unity build his irrigation systems- increases productivity ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... white, this is among the most famous South African rock paintings. Although its date of execution is not known, it is estimated to have been painted sometime during the eighteenth or nineteenth centuries A.D. ...
... white, this is among the most famous South African rock paintings. Although its date of execution is not known, it is estimated to have been painted sometime during the eighteenth or nineteenth centuries A.D. ...
I. The Egyptians - Eldred Central School
... 2) Next, they covered the corpse with a natural salt that absorbed the body’s water. Later, they filled the body with spices and wrapped it with layers of linen soaked in resin. At the end of 70 days, a lifelike mask was placed over the head and shoulders of the ...
... 2) Next, they covered the corpse with a natural salt that absorbed the body’s water. Later, they filled the body with spices and wrapped it with layers of linen soaked in resin. At the end of 70 days, a lifelike mask was placed over the head and shoulders of the ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide – EGYPT
... Who was responsible for combining these two lands? What was his capital city? ...
... Who was responsible for combining these two lands? What was his capital city? ...
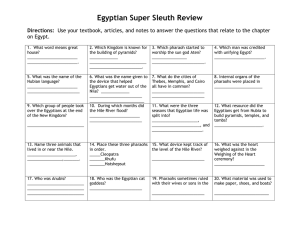
Egyptian Super Sleuth Review Directions
... 6. What was the name given to the device that helped Egyptians get water out of the Nile? _____________ ________________________ _________________________ 10. During which months did the Nile River flood? _______________________ ________________________ ...
... 6. What was the name given to the device that helped Egyptians get water out of the Nile? _____________ ________________________ _________________________ 10. During which months did the Nile River flood? _______________________ ________________________ ...
Nile

The Nile (Arabic: النيل, Eg. en-Nīl, Std. an-Nīl; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲁⲣⲱ, P(h)iaro; Ancient Egyptian: Ḥ'pī and Iteru) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is 6,853 km (4,258 miles) long. The Nile is an ""international"" river as its water resources are shared by eleven countries, namely, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Congo-Kinshasa, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt and Sudan.The Nile has two major tributaries, the White Nile and Blue Nile. The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself. The Blue Nile, however, is the source of most of the water and silt. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. It flows north through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile (Amharic: ዓባይ?, ʿĀbay) begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet near the Sudanese capital of Khartoum.The northern section of the river flows north almost entirely through the Sudanese desert to Egypt, then ends in a large delta and empties into the Mediterranean Sea. Egyptian civilization and Sudanese kingdoms have depended on the river since ancient times. Most of the population and cities of Egypt lie along those parts of the Nile valley north of Aswan, and nearly all the cultural and historical sites of Ancient Egypt are found along riverbanks.In the ancient Egyptian language, the Nile is called Ḥ'pī or Iteru, meaning ""river"", represented by the hieroglyphs shown on the left (literally itrw, and 'waters' determinative). In Coptic, the words piaro (Sahidic) or phiaro (Bohairic) meaning ""the river"" (lit. p(h).iar-o ""the.canal-great"") come from the same ancient name.The English name Nile and the Arabic names en-Nîl and an-Nîl both derive from the Latin Nilus and the Ancient Greek Νεῖλος. Beyond that, however, the etymology is disputed. One possible etymology derives it from a Semitic Nahal, meaning ""river"". The standard English names ""White Nile"" and ""Blue Nile"", to refer to the river's source, derive from Arabic names formerly applied only to the Sudanese stretches which meet at Khartoum.