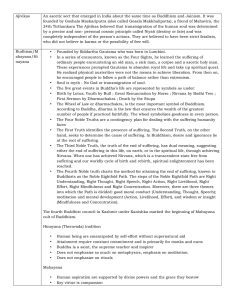
Comparison of Religions
... without any karma attached to it The primary goal is to become a perfected (liberated) soul, known as Siddha or God At liberation the soul remains finite, lives in Moksha forever, and never loses its identity Every living being is eternal, individual, and capable of becoming perfect The path of libe ...
... without any karma attached to it The primary goal is to become a perfected (liberated) soul, known as Siddha or God At liberation the soul remains finite, lives in Moksha forever, and never loses its identity Every living being is eternal, individual, and capable of becoming perfect The path of libe ...
Buddhism
... 2. System of varnas – caste system: a. Born into a class and cannot be changed b. Intermarriage between castes was not encouraged. c. Each separate and possessing a social duty (dharma) 3. Belief that if each member followed dharma, no leadership was necessary 4. Belief that all souls were part of o ...
... 2. System of varnas – caste system: a. Born into a class and cannot be changed b. Intermarriage between castes was not encouraged. c. Each separate and possessing a social duty (dharma) 3. Belief that if each member followed dharma, no leadership was necessary 4. Belief that all souls were part of o ...
Hinduism - LincolnPhillips
... One.” It is based on The Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path while the ultimate goal is to achieve supreme peace, or Nirvana. ...
... One.” It is based on The Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path while the ultimate goal is to achieve supreme peace, or Nirvana. ...
2017 Hinduism PowerPoint Lecture
... • Spiritual leaders are called gurus or sages. • Yoga-integrated physical and mental exercises. They teach people to focus their minds and bodies which will aid their meditation in order to attain moksha • Pilgrimage to Ganges (thought it flows through 2 devas so its water is holy. Bathing in it wil ...
... • Spiritual leaders are called gurus or sages. • Yoga-integrated physical and mental exercises. They teach people to focus their minds and bodies which will aid their meditation in order to attain moksha • Pilgrimage to Ganges (thought it flows through 2 devas so its water is holy. Bathing in it wil ...
Buddhism, Jainism, & Hinduism
... Continuities: what was something that did not change? How does this relate to the region or theme in the thesis? How does this relate to other continuities around the world in the time period? ...
... Continuities: what was something that did not change? How does this relate to the region or theme in the thesis? How does this relate to other continuities around the world in the time period? ...
(Section III): Hinduism and Buddhism
... No “sacred text”. No identifiable beginning. No authority or organization. Came from the many cultures who settled in India. It’s a religion, a history, and a way of life. ...
... No “sacred text”. No identifiable beginning. No authority or organization. Came from the many cultures who settled in India. It’s a religion, a history, and a way of life. ...
Document
... ātman: “That is the Real: That is the Self: That you are!” Avoid actions (karma) that promote selfishness Maximize selflessness Through knowledge of one’s true self and positive karma, attain mokşa (liberation from samsara and full union with Brahman) ...
... ātman: “That is the Real: That is the Self: That you are!” Avoid actions (karma) that promote selfishness Maximize selflessness Through knowledge of one’s true self and positive karma, attain mokşa (liberation from samsara and full union with Brahman) ...
Eurasian Cultural Traditions 500 B.C.E.
... • Brahmin = Priests (learn scriptures) • Kshatriyas = Warrior/Aristocrats (govern and fight) • Vaishyas = Merchants (to sell goods/work) • Shudras = Peasants (to serve) --------------------------------------------------------UNTOUCHABLES • Jati = Sub-castes that further divide the varnas • Samsara = ...
... • Brahmin = Priests (learn scriptures) • Kshatriyas = Warrior/Aristocrats (govern and fight) • Vaishyas = Merchants (to sell goods/work) • Shudras = Peasants (to serve) --------------------------------------------------------UNTOUCHABLES • Jati = Sub-castes that further divide the varnas • Samsara = ...
Ch. 17 - The Roman Republic
... success, dharma, and moksha. Buddhism also began in India. Hindus and Buddhists both believe in reincarnation and karma. However the goal of Buddhism is to achieve enlightenment and reach nirvana. As Buddhism spread, monasteries were built and missionaries traveled throughout Asia. ...
... success, dharma, and moksha. Buddhism also began in India. Hindus and Buddhists both believe in reincarnation and karma. However the goal of Buddhism is to achieve enlightenment and reach nirvana. As Buddhism spread, monasteries were built and missionaries traveled throughout Asia. ...
Siddhartha
... Until one becomes part of the universal essence, he or she will experience a cycle of rebirth, or reincarnation, based on the life he or she has lived. This cycle is called samsara. ...
... Until one becomes part of the universal essence, he or she will experience a cycle of rebirth, or reincarnation, based on the life he or she has lived. This cycle is called samsara. ...
hinduism
... and distraction Realizing that Brahman or Atman is present in all things sets us free If this is not realized, we are reborn and do not achieve moksha ...
... and distraction Realizing that Brahman or Atman is present in all things sets us free If this is not realized, we are reborn and do not achieve moksha ...
Document
... • Salvation through liberation is the ultimate goal • Might not occur in one lifetime • Hindu belief in reincarnation ...
... • Salvation through liberation is the ultimate goal • Might not occur in one lifetime • Hindu belief in reincarnation ...
Chapter 9 Lesson 2 Religions of Ancient India Outline
... a.) Hindus believe in one great spirit called Brahman. b.) Hindus believe that all living things and even the gods are part of Brahman. c.) Hindus believe that a person’s soul will eventually join Brahman. 4. However, before a person’s soul can join Brahman, Hindus believe a soul must live many live ...
... a.) Hindus believe in one great spirit called Brahman. b.) Hindus believe that all living things and even the gods are part of Brahman. c.) Hindus believe that a person’s soul will eventually join Brahman. 4. However, before a person’s soul can join Brahman, Hindus believe a soul must live many live ...
Comparing World Religions - Townsend Harris High School
... Q: Define the terms religion and philosophy. How are they similar? How are they Different? ...
... Q: Define the terms religion and philosophy. How are they similar? How are they Different? ...
Slide 1
... been associated closely with nature including the _________ River, which is considered especially sacred to Hindus. a) ...
... been associated closely with nature including the _________ River, which is considered especially sacred to Hindus. a) ...
Chapter 9 Lesson 2 Religions of Ancient India BLANKS
... a.) Hindus believe in one great _________________ called Brahman. b.) Hindus believe that all living things and even the gods are ____________ of Brahman. c.) Hindus believe that a person’s soul will eventually join Brahman. 4. However, before a person’s soul can join Brahman, Hindus believe a soul ...
... a.) Hindus believe in one great _________________ called Brahman. b.) Hindus believe that all living things and even the gods are ____________ of Brahman. c.) Hindus believe that a person’s soul will eventually join Brahman. 4. However, before a person’s soul can join Brahman, Hindus believe a soul ...
Hinduism and Buddhism Develop
... Vedic hymns. • These commentaries were written down in the Upanishads. ...
... Vedic hymns. • These commentaries were written down in the Upanishads. ...
Ajivikas An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time
... An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time as Buddhism and Jainism. It was founded by Goshala Maskariputra (also called Gosala Makkhaliputta), a friend of Mahavira, the 24th Tirthankara The Ajivikas believed that transmigration of the human soul was determined by a precise and non- pe ...
... An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time as Buddhism and Jainism. It was founded by Goshala Maskariputra (also called Gosala Makkhaliputta), a friend of Mahavira, the 24th Tirthankara The Ajivikas believed that transmigration of the human soul was determined by a precise and non- pe ...
Saṃsāra

Saṃsāra (Sanskrit), is the repeating cycle of birth, life and death (reincarnation) as well as one's actions and consequences in the past, present, and future in Hinduism, Buddhism, Bon, Jainism, Taoism, and Sikhism.According to these religions, a person's current life is only one of many lives that will be lived—stretching back before birth into past existences and reaching forward beyond death into future incarnations. During the course of each life, the quality of the actions (karma) performed determine the future destiny of each person. The Buddha taught that there is no beginning to this cycle but that it can be ended through perceiving reality. The goal of these religions is to realize this truth, the achievement of which (like ripening of a fruit) is moksha or nirvana (liberation).