Recombinant DNA Technology
... recombinant DNA using a marker, such as antibiotic resistance genes -If colonies grow, despite the existence of such antibiotics, then the recombinant DNA vector was successfully transformed • The surviving colonies are isolated and are grown in culture to produce multiple copies of the incorporated ...
... recombinant DNA using a marker, such as antibiotic resistance genes -If colonies grow, despite the existence of such antibiotics, then the recombinant DNA vector was successfully transformed • The surviving colonies are isolated and are grown in culture to produce multiple copies of the incorporated ...
genotypes
... Transcription makes messenger RNA (mRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble mRNA. 3. Why is translation necessary? Translati ...
... Transcription makes messenger RNA (mRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble mRNA. 3. Why is translation necessary? Translati ...
DNA Testing Procedures - American Hereford Association
... environment. SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism — referred to as a ‘snip’): A type of genetic marker where alleles different from each other by the sequence of only a single nucleotide base pair. SNP genetic tests focus on detecting precise single nucleotide base pair differences among the 3 billio ...
... environment. SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism — referred to as a ‘snip’): A type of genetic marker where alleles different from each other by the sequence of only a single nucleotide base pair. SNP genetic tests focus on detecting precise single nucleotide base pair differences among the 3 billio ...
POLYMERASE-CHAIN-REACTION (PCR) ANALYSIS OF
... to 15 allelesper locusand heterozygosities in the rangeof 0.46to 0.89.Mendelianinheritance was confirmedfor all four loci in 10 Pied Flycatcherand 2 Barn Swallow families comprising a total of 240 meioses.The occurrenceof nonparentalalleles in offspringfrom two Barn Swallow families was consistentwi ...
... to 15 allelesper locusand heterozygosities in the rangeof 0.46to 0.89.Mendelianinheritance was confirmedfor all four loci in 10 Pied Flycatcherand 2 Barn Swallow families comprising a total of 240 meioses.The occurrenceof nonparentalalleles in offspringfrom two Barn Swallow families was consistentwi ...
emboj7601986-sup
... DNA from targeted ES cell clones, probed with the flanking genomic probe shown in (A). A 6.3 kb fragment is detected from the untargeted locus, while the 7.7 kb fragment indicates the floxed locus. (C) PCR typing analysis of DNA from Crif1flox/+ (flox/+) and Crif1flox/- (flox/-) MEFs, untreated (-) ...
... DNA from targeted ES cell clones, probed with the flanking genomic probe shown in (A). A 6.3 kb fragment is detected from the untargeted locus, while the 7.7 kb fragment indicates the floxed locus. (C) PCR typing analysis of DNA from Crif1flox/+ (flox/+) and Crif1flox/- (flox/-) MEFs, untreated (-) ...
DNA sequencing - Rarechromo.org
... Chromosomes cannot be seen with the naked eye, but if you stain them and magnify them many hundreds of times under a microscope, you can see that each one has a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. By looking at your chromosomes in this way, often referred to as karyotyping, it is possible i ...
... Chromosomes cannot be seen with the naked eye, but if you stain them and magnify them many hundreds of times under a microscope, you can see that each one has a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. By looking at your chromosomes in this way, often referred to as karyotyping, it is possible i ...
DNA sequencing - Rarechromo.org
... Chromosomes cannot be seen with the naked eye, but if you stain them and magnify them many hundreds of times under a microscope, you can see that each one has a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. By looking at your chromosomes in this way, often referred to as karyotyping, it is possible i ...
... Chromosomes cannot be seen with the naked eye, but if you stain them and magnify them many hundreds of times under a microscope, you can see that each one has a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. By looking at your chromosomes in this way, often referred to as karyotyping, it is possible i ...
The human genome: a prospect for paediatrics
... A human cell contains 23 pairs of homologous reflects a difference in the base sequence at the chromosomes, one of each pair inherited from pair of alleles on homologous chromosomes at a the father and one from the mother. During particular locus. meiosis, homologous chromosomes are dupliIt is now r ...
... A human cell contains 23 pairs of homologous reflects a difference in the base sequence at the chromosomes, one of each pair inherited from pair of alleles on homologous chromosomes at a the father and one from the mother. During particular locus. meiosis, homologous chromosomes are dupliIt is now r ...
Unit 08 Notes - Pierce College
... tRNA anticodons that correspond to stop codons; rather, a release factor protein enters the A site. Release factor proteins add an H-OH to the terminal amino acid then releases the polypeptide chain. There are 20 amino acids, each carried by a tRNA with a specific tRNA anticodon that matches a speci ...
... tRNA anticodons that correspond to stop codons; rather, a release factor protein enters the A site. Release factor proteins add an H-OH to the terminal amino acid then releases the polypeptide chain. There are 20 amino acids, each carried by a tRNA with a specific tRNA anticodon that matches a speci ...
File - LFHS AP Biology
... __ DNA as the template molecule for messenger RNA __ The proper base pairing (including the uracil substitution) __ The chemical characteristics of nucleotides __ A comparison of RNA and DNA (other than uracil substitution) __ The triplet arrangement of codons and/or anticodons __ The control of tr ...
... __ DNA as the template molecule for messenger RNA __ The proper base pairing (including the uracil substitution) __ The chemical characteristics of nucleotides __ A comparison of RNA and DNA (other than uracil substitution) __ The triplet arrangement of codons and/or anticodons __ The control of tr ...
Enzyme Mechanisms - Illinois Institute of Technology
... If we set up a DNA library and introduce it into host bacteria as in colony hybridization, we can put nylon membranes on the plates to get replicas of the colonies Replicas are incubated to make protein Cells are treated to release the protein so it binds to the nylon membrane If the antibody sticks ...
... If we set up a DNA library and introduce it into host bacteria as in colony hybridization, we can put nylon membranes on the plates to get replicas of the colonies Replicas are incubated to make protein Cells are treated to release the protein so it binds to the nylon membrane If the antibody sticks ...
nucleic acids 3115
... protein. Protein, as you recall, is the type of molecule of which most living things are made. Here is how it works. The first part of the process is similar to DNA replication – the DNA double helix splits and separates. After the DNA has separated into 2 strands, the RNA comes in and makes a copy ...
... protein. Protein, as you recall, is the type of molecule of which most living things are made. Here is how it works. The first part of the process is similar to DNA replication – the DNA double helix splits and separates. After the DNA has separated into 2 strands, the RNA comes in and makes a copy ...
Plasmid Project due
... is where the human insulin gene was isolated from human DNA, and was then inserted into a bacterium, using a plasmid as a vector (see next paragraph) – the bacterium could then produce the human form of insulin. A plasmid is a circlet of DNA found in a bacterium. Plasmids are unique to bacteria and ...
... is where the human insulin gene was isolated from human DNA, and was then inserted into a bacterium, using a plasmid as a vector (see next paragraph) – the bacterium could then produce the human form of insulin. A plasmid is a circlet of DNA found in a bacterium. Plasmids are unique to bacteria and ...
Chapter 18 Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
... • Certain ones may be beneficial because they enhance the survival rate of the species. ...
... • Certain ones may be beneficial because they enhance the survival rate of the species. ...
Study questions - Pre-lab
... a. Predict whether or not you will exhibit the PTC taster phenotype. b. If you are a taster of PTC, what are your possible genotypes at the TAS2R38 locus? PAV/AVI or PAV/PAV (T/t or T/T) c. In which ways can single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affect the function of a gene? Non-sense mutations (t ...
... a. Predict whether or not you will exhibit the PTC taster phenotype. b. If you are a taster of PTC, what are your possible genotypes at the TAS2R38 locus? PAV/AVI or PAV/PAV (T/t or T/T) c. In which ways can single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affect the function of a gene? Non-sense mutations (t ...
Lecture 8
... 1. Mu elements are known to transpose to any locus, especially genes, therefore it is very useful for creating tagged mutations. 2. Mutator’s frequent transposition activity (even to unlinked locus) is reminiscent of P element system of Drosophila. In Drosophila, P elements have been used as vectors ...
... 1. Mu elements are known to transpose to any locus, especially genes, therefore it is very useful for creating tagged mutations. 2. Mutator’s frequent transposition activity (even to unlinked locus) is reminiscent of P element system of Drosophila. In Drosophila, P elements have been used as vectors ...
Lecture 17 Protein synthesis pp101-110
... 10.8 The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life – Characteristics of the genetic code – Triplet: Three nucleotides specify one amino acid – 61 codons correspond to amino acids – AUG codes for methionine and signals the start of transcription – 3 “stop” codons signal the end of translation ...
... 10.8 The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life – Characteristics of the genetic code – Triplet: Three nucleotides specify one amino acid – 61 codons correspond to amino acids – AUG codes for methionine and signals the start of transcription – 3 “stop” codons signal the end of translation ...
How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype?
... Shotgun sequencing was one of the techniques used to sequence the human genome. Below are five DNA fragmentslabeled A, B, C, D, and E, respectivelythat were shotgun sequenced and determined to be part of the same DNA sequence. Notice that the fragments are single stranded. Determine the single-str ...
... Shotgun sequencing was one of the techniques used to sequence the human genome. Below are five DNA fragmentslabeled A, B, C, D, and E, respectivelythat were shotgun sequenced and determined to be part of the same DNA sequence. Notice that the fragments are single stranded. Determine the single-str ...
Genes and causation
... Whatever its proportion would be in my imagined Earth-life capsule, some information may be more important than others. So, which is privileged in inheritance? Would it be the cell or the DNA? ‘How central is the genome?’ as Werner puts the question (Werner 2007). On the basis of our present scienti ...
... Whatever its proportion would be in my imagined Earth-life capsule, some information may be more important than others. So, which is privileged in inheritance? Would it be the cell or the DNA? ‘How central is the genome?’ as Werner puts the question (Werner 2007). On the basis of our present scienti ...
Section 6: Information Flow
... the different isolates look different?) We focus on nucleic acid structure and the central dogma at its most basic level—the mechanism of transcription and translation to produce functional proteins (or RNA) from the genome,.This then serves as a springboard to launch a more in-depth discussion of i ...
... the different isolates look different?) We focus on nucleic acid structure and the central dogma at its most basic level—the mechanism of transcription and translation to produce functional proteins (or RNA) from the genome,.This then serves as a springboard to launch a more in-depth discussion of i ...
Slide 1
... – chrom - The name of the chromosome – chromStart - The starting position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The first base in a chromosome is numbered 0. – chromEnd - The ending position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The chromEnd base is not included in the display of the ...
... – chrom - The name of the chromosome – chromStart - The starting position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The first base in a chromosome is numbered 0. – chromEnd - The ending position of the feature in the chromosome or scaffold. The chromEnd base is not included in the display of the ...
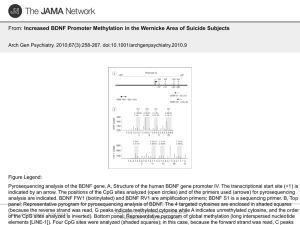
Increased BDNF Promoter Methylation in the
... Figure Legend: Methylation analysis by genomic bisulfite sequencing. Top panel: Diagrammatic representation of BDNF gene (promoter/exon IV). Regulatory upstream region (open box), exon IV (black box), and intron IV (gray box) are indicated. Vertical bars represent the relative positions of each CpG ...
... Figure Legend: Methylation analysis by genomic bisulfite sequencing. Top panel: Diagrammatic representation of BDNF gene (promoter/exon IV). Regulatory upstream region (open box), exon IV (black box), and intron IV (gray box) are indicated. Vertical bars represent the relative positions of each CpG ...
Proceedings - Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle
... testing available for genetic defects and coat color is close to 100% accurate. Most of the economically important traits in beef production, however, are polygenic traits. A polygenic trait is determined by alleles at hundreds of genes. Environmental influences often play a major role in trait expr ...
... testing available for genetic defects and coat color is close to 100% accurate. Most of the economically important traits in beef production, however, are polygenic traits. A polygenic trait is determined by alleles at hundreds of genes. Environmental influences often play a major role in trait expr ...
DNA Testing Applications for Mennonite Genealogists2
... Mitochondrial DNA • Used to determine the relative degree to which two people are related to each other on their maternal lines • Used to determine one’s mitochondrial DNA haplogroup • Values are given as differences to the Cambridge Reference Sequence, which was the first sequence completed for th ...
... Mitochondrial DNA • Used to determine the relative degree to which two people are related to each other on their maternal lines • Used to determine one’s mitochondrial DNA haplogroup • Values are given as differences to the Cambridge Reference Sequence, which was the first sequence completed for th ...