TOC - Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... Budding yeast cells enter sporulation asynchronously, which makes it challenging to obtain stage specific data using cell population based assays. Methods ensuring that cells enter sporulation synchronously have been lacking. We find that cells undergo pre-meiotic DNA replication and meiosis synchrono ...
... Budding yeast cells enter sporulation asynchronously, which makes it challenging to obtain stage specific data using cell population based assays. Methods ensuring that cells enter sporulation synchronously have been lacking. We find that cells undergo pre-meiotic DNA replication and meiosis synchrono ...
The cell is the functional basic unit of biology
... distinct from the nuclear DNA. Although the mitochondrial DNA is very small compared to nuclear chromosomes, it codes for 13 proteins involved in mitochondrial energy production and specific tRNAs. Foreign genetic material (most commonly DNA) can also be artificially introduced into the cell by a pr ...
... distinct from the nuclear DNA. Although the mitochondrial DNA is very small compared to nuclear chromosomes, it codes for 13 proteins involved in mitochondrial energy production and specific tRNAs. Foreign genetic material (most commonly DNA) can also be artificially introduced into the cell by a pr ...
Section 13-1 Ghanging the Living World
... 2. Why is an electrical current added and in what direction does the DNA move (poSitive to negative or negative to positive)? ...
... 2. Why is an electrical current added and in what direction does the DNA move (poSitive to negative or negative to positive)? ...
for Genetic Testing
... destroys the middle Mstll recognition site. The father and mother each yield two bands on their Southern blots, because they each carry one normal and one mutant gene. • Affected son II-1 has only the larger band, because he has two copies of the mutant gene. Daughter II-2 shows only the smaller ban ...
... destroys the middle Mstll recognition site. The father and mother each yield two bands on their Southern blots, because they each carry one normal and one mutant gene. • Affected son II-1 has only the larger band, because he has two copies of the mutant gene. Daughter II-2 shows only the smaller ban ...
Midterm Studyguide Avery L
... Example: Phospholipids (polar, hydrophilic heads and nonpolar, hydrophobic tails). C. Proteins: Primary Structure- 2-D chain of amino acids Secondary Structure- Assembly of the chain of amino acids using Alpha Helix and Beta-Pleated Sheets (think spiral and accordion), Hydrogen bonds (weak), Heat de ...
... Example: Phospholipids (polar, hydrophilic heads and nonpolar, hydrophobic tails). C. Proteins: Primary Structure- 2-D chain of amino acids Secondary Structure- Assembly of the chain of amino acids using Alpha Helix and Beta-Pleated Sheets (think spiral and accordion), Hydrogen bonds (weak), Heat de ...
Slide 1
... is a secreted protein that is believed to affect development and maintenance of the retina (especially providing blood supply to retina). 70% are point mutations at various places in gene. Use SSCP (Single Stranded Conformation Polymorphism) Analysis 24% are short deletions of part of gene… detected ...
... is a secreted protein that is believed to affect development and maintenance of the retina (especially providing blood supply to retina). 70% are point mutations at various places in gene. Use SSCP (Single Stranded Conformation Polymorphism) Analysis 24% are short deletions of part of gene… detected ...
Pipe Cleaner Genetics
... How many daughter cells did you make? _______ How many chromosomes does each daughter cell have? ______ Are the daughter cells diploid or haploid? _________ Are the genotypes of the daughter cells the same or different? __________ 3. Now use your pipe cleaner chromosomes to model the different phase ...
... How many daughter cells did you make? _______ How many chromosomes does each daughter cell have? ______ Are the daughter cells diploid or haploid? _________ Are the genotypes of the daughter cells the same or different? __________ 3. Now use your pipe cleaner chromosomes to model the different phase ...
Central Dogma Review Sheet
... deoxyribose sugar. Know the four bases of DNA, and be able to characterize each as purine or pyrimidine. 2. Likewise, be able to describe the structure of RNA. Be able to list differences between DNA and RNA, and recognize the two by sight. 3. Understand how base pairing works. Know that A hydrogen- ...
... deoxyribose sugar. Know the four bases of DNA, and be able to characterize each as purine or pyrimidine. 2. Likewise, be able to describe the structure of RNA. Be able to list differences between DNA and RNA, and recognize the two by sight. 3. Understand how base pairing works. Know that A hydrogen- ...
mc2 Genome_Organization
... • Processes pseudogenes come from mRNA that has been reversetranscribed and then randomly inserted into the genome. Processed pseudogenes lack introns because the mRNA was spliced. They also often have poly A tails and they lack promoters and other control regions. – Good example: the ribosomal prot ...
... • Processes pseudogenes come from mRNA that has been reversetranscribed and then randomly inserted into the genome. Processed pseudogenes lack introns because the mRNA was spliced. They also often have poly A tails and they lack promoters and other control regions. – Good example: the ribosomal prot ...
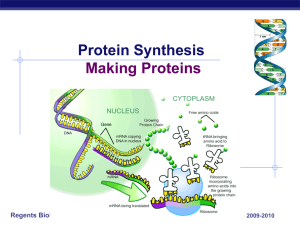
1. What role do chromosomes play when a cell makes proteins? A
... humans eat. The tuber can grow large and provide energy for the plant during the winter, or it can be used to grow new potato plants. A strawberry plant, on the other hand, puts much of its energy into growing flowers to attract insects that aid in pollination. After fertilization, the strawberry pl ...
... humans eat. The tuber can grow large and provide energy for the plant during the winter, or it can be used to grow new potato plants. A strawberry plant, on the other hand, puts much of its energy into growing flowers to attract insects that aid in pollination. After fertilization, the strawberry pl ...
Section 1: Mendelʼs Work * Gregor Mendel was a young priest from
... genetic information from its mother and half from its father. This is why you may have some traits of your mother AND some traits of your father. * Obviously, since Suttonʼs time, research has continued on the chromosomes of different organisms, especially humans. * Each normal, human cells contains ...
... genetic information from its mother and half from its father. This is why you may have some traits of your mother AND some traits of your father. * Obviously, since Suttonʼs time, research has continued on the chromosomes of different organisms, especially humans. * Each normal, human cells contains ...
Document
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
Genetics, health and medicine
... Panel 1: Genes and gene expression — the basics Genetic information is stored inside each cell of the body as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA has two main features: it is a code for directing the formation of proteins (key components of cell structure and function) and it is reproducible. The spec ...
... Panel 1: Genes and gene expression — the basics Genetic information is stored inside each cell of the body as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA has two main features: it is a code for directing the formation of proteins (key components of cell structure and function) and it is reproducible. The spec ...
Short Questions
... 86. What is meant by DNA profiling? 87. In DNA profiling, what are used to cut DNA strands into fragments? 88. Give two applications (uses) of DNA profiling. 89. Name the plant from which you isolated DNA in your practical studies. 90. For what precise purpose did you use freezer-cold ethanol (alcoh ...
... 86. What is meant by DNA profiling? 87. In DNA profiling, what are used to cut DNA strands into fragments? 88. Give two applications (uses) of DNA profiling. 89. Name the plant from which you isolated DNA in your practical studies. 90. For what precise purpose did you use freezer-cold ethanol (alcoh ...
Lecture 15 - Psychology
... toward more association designs, which only work if you already have a good candidate gene (but be wary of false positives) ...
... toward more association designs, which only work if you already have a good candidate gene (but be wary of false positives) ...
CHAPTER 17
... 3. It could be in the dimerization domain, so that the receptor would not dimerize. 4. It could be in the nuclear localization domain, so that the receptor would not travel into the nucleus. 5. It could be in the domain that activates RNA polymerase, so that the receptor would not activate transcrip ...
... 3. It could be in the dimerization domain, so that the receptor would not dimerize. 4. It could be in the nuclear localization domain, so that the receptor would not travel into the nucleus. 5. It could be in the domain that activates RNA polymerase, so that the receptor would not activate transcrip ...
ap® biology 2009 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... DNA packaging...................... loosening/tightening chromatin promotes/inhibits transcription RNA processing ..................... GTP cap or Poly-A tail RNA editing............................ removing of introns Alternative splicing ............... editing in different ways to get new/differe ...
... DNA packaging...................... loosening/tightening chromatin promotes/inhibits transcription RNA processing ..................... GTP cap or Poly-A tail RNA editing............................ removing of introns Alternative splicing ............... editing in different ways to get new/differe ...
AgrawalGizer_ARTSS_part2
... Two major types • Microsatellite/short tandem repeat (STR): a stretch of DNA that is sequentially repeated a variable number of times. • Can cause disease (e.g. CAG repeat expansion causes Huntington’s disease; • Can also be benign variation; • Assume it is close to a disease contributing gene; ...
... Two major types • Microsatellite/short tandem repeat (STR): a stretch of DNA that is sequentially repeated a variable number of times. • Can cause disease (e.g. CAG repeat expansion causes Huntington’s disease; • Can also be benign variation; • Assume it is close to a disease contributing gene; ...
lab- where`s the CAT palffy 2010-1
... DNA restriction enzymes cut the DNA into smaller pieces. These enzymes only cut the DNA at specific places based upon specific sequences of nucleotides. Theses fragments of DNA (known as RFLPs –Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) are placed into wells of an electrophoretic gel and the differen ...
... DNA restriction enzymes cut the DNA into smaller pieces. These enzymes only cut the DNA at specific places based upon specific sequences of nucleotides. Theses fragments of DNA (known as RFLPs –Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) are placed into wells of an electrophoretic gel and the differen ...
Supplementary Methods
... Strains and plasmids All yeast strains were congenic with the MHY501 wild-type (see ref. 4) except where noted. Strains in which various chromosomal genes were tagged in frame with the DNA sequence for enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP) were constructed by single-step PCR amplification of the ...
... Strains and plasmids All yeast strains were congenic with the MHY501 wild-type (see ref. 4) except where noted. Strains in which various chromosomal genes were tagged in frame with the DNA sequence for enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP) were constructed by single-step PCR amplification of the ...
A Healthy Pregnancy
... gene but affects only males. Description Weakness and shrinkage of the muscles Death before adulthood ...
... gene but affects only males. Description Weakness and shrinkage of the muscles Death before adulthood ...