Unit 2 Practice Questions 1. Molecules of DNA are referred to as: A
... 1. Molecules of DNA are referred to as: A) cells. B) adenine. C) genes. D) chromosomes. 2. Every normal human body cell contains how many chromosomes? A) 23 pairs B) 23 C) 46 pairs D) about 1,000 3. A genome is: A) the full set of genes for a particular organism. B) a molecule of DNA. C) the basic u ...
... 1. Molecules of DNA are referred to as: A) cells. B) adenine. C) genes. D) chromosomes. 2. Every normal human body cell contains how many chromosomes? A) 23 pairs B) 23 C) 46 pairs D) about 1,000 3. A genome is: A) the full set of genes for a particular organism. B) a molecule of DNA. C) the basic u ...
Leture 19, work session 12
... chromosome separates during cell division .The centromere is a structure of noncoding DNA( DNA that does not convey genetic information). When the cell divides the strands of the chromatids migrate in opposite directions (pull apart) at the centromere. In a photomicrograph, the centromere appears as ...
... chromosome separates during cell division .The centromere is a structure of noncoding DNA( DNA that does not convey genetic information). When the cell divides the strands of the chromatids migrate in opposite directions (pull apart) at the centromere. In a photomicrograph, the centromere appears as ...
Plasmids
... biologists, who used recombinant DNA technology to incorporate many different functional elements into naturally-occurring plasmids. Plasmids have been engineered to carry up to 10 kb of foreign DNA and they are easily isolated from microorganisms for manipulation in the lab. For the next few labs, ...
... biologists, who used recombinant DNA technology to incorporate many different functional elements into naturally-occurring plasmids. Plasmids have been engineered to carry up to 10 kb of foreign DNA and they are easily isolated from microorganisms for manipulation in the lab. For the next few labs, ...
Chapter12_Section05_edit-1
... Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Gene Regulation - Lincoln Park High School
... Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
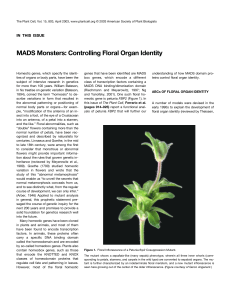
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
2006
... or 48.1%; χ2 = 8.226, d.f. = 2, p < 0.05), a bias that would not be selected for during sequence preparation. There are some differences in frequency of nucleotide polymorphisms among the four regions of the sequenced portion of this gene. In the intron, there are 40 polymorphic sites over 725 base ...
... or 48.1%; χ2 = 8.226, d.f. = 2, p < 0.05), a bias that would not be selected for during sequence preparation. There are some differences in frequency of nucleotide polymorphisms among the four regions of the sequenced portion of this gene. In the intron, there are 40 polymorphic sites over 725 base ...
1.5 - Biology Junction
... sequences. Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes. Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... sequences. Many proteins can bind to different enhancer sequences. Some DNA-binding proteins enhance transcription by: • opening up tightly packed chromatin • helping to attract RNA polymerase • blocking access to genes. Slide 17 of 26 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Phylogenetics Topic 2: Phylogenetic and genealogical homology
... Phylogenetics Topic 2: Phylogenetic and genealogical homology Phylogenies distinguish homology from similarity Previously, we examined how rooted phylogenies provide a framework for distinguishing similarity due to common ancestry (HOMOLOGY) from non-phylogenetic similarity (ANALOGY). Here we extend ...
... Phylogenetics Topic 2: Phylogenetic and genealogical homology Phylogenies distinguish homology from similarity Previously, we examined how rooted phylogenies provide a framework for distinguishing similarity due to common ancestry (HOMOLOGY) from non-phylogenetic similarity (ANALOGY). Here we extend ...
Genetic disorders
... Involves particular genes located on the X chromosome Disorders more commonly affect males Heterozygote female will pass the gene to 50% of her sons who will express the trait, and to 50% of her daughters who will be carriers for the trait Affected males pass the gene to all of their daughters and n ...
... Involves particular genes located on the X chromosome Disorders more commonly affect males Heterozygote female will pass the gene to 50% of her sons who will express the trait, and to 50% of her daughters who will be carriers for the trait Affected males pass the gene to all of their daughters and n ...
Unraveling Your DNA`s Secrets Do-it-yourself genetic tests promise
... in making personal health decisions. "Many of the claims that are being made are quite fanciful," says Francis Collins, director of the National Human Genome Research Institute, who oversaw the project to sequence the human genome. "But the fact that many of these tests have not yet reached the poin ...
... in making personal health decisions. "Many of the claims that are being made are quite fanciful," says Francis Collins, director of the National Human Genome Research Institute, who oversaw the project to sequence the human genome. "But the fact that many of these tests have not yet reached the poin ...
Practical English (2)
... geologic timescale that extends from about 199.6 ± 0.6 to 145.4 ± 4.0 million years ago. It is known as the “Age of Dinosaurs” 2 DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms. ...
... geologic timescale that extends from about 199.6 ± 0.6 to 145.4 ± 4.0 million years ago. It is known as the “Age of Dinosaurs” 2 DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms. ...
Use of methylation profiling to identify genes involved in relapse in
... are usually methylation free. In cancerous cells these same regions frequently exhibit hypermethylation, leading to stable gene inactivation. ...
... are usually methylation free. In cancerous cells these same regions frequently exhibit hypermethylation, leading to stable gene inactivation. ...
PowerPoint Learning Quest
... two DNA strands bonded together by strand bases. These bonds are hydrogen bonds and are therefore individually weak. However these bonds zip the two strands together with a strength to give the double helix stability. ...
... two DNA strands bonded together by strand bases. These bonds are hydrogen bonds and are therefore individually weak. However these bonds zip the two strands together with a strength to give the double helix stability. ...
Task One: Determining Possible Genetic Diseases
... 2. What is the difference between a frame shift mutation and a point mutation? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between a gametic and a somatic mutation? _____________ ...
... 2. What is the difference between a frame shift mutation and a point mutation? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between a gametic and a somatic mutation? _____________ ...
The yeast two-hybrid assay to discover if known proteins in the
... the ethylene signalling pathway, in order to see if they can interact with each other or not. Having such information on physical interactions between proteins helps scientists to put together pieces of a puzzle in order to understand the signalling pathway. What is the yeast two-hybrid assay? Inter ...
... the ethylene signalling pathway, in order to see if they can interact with each other or not. Having such information on physical interactions between proteins helps scientists to put together pieces of a puzzle in order to understand the signalling pathway. What is the yeast two-hybrid assay? Inter ...
Breeding and Genetics - Faculty Website Listing
... is due to the variation in additive gene effects • In other words, the proportion of differences due to genetic effects and is important in the prediction of response rates from selection. • The square root of the variance is the standard deviation, which is the average deviation of each individual ...
... is due to the variation in additive gene effects • In other words, the proportion of differences due to genetic effects and is important in the prediction of response rates from selection. • The square root of the variance is the standard deviation, which is the average deviation of each individual ...
ecole doctorale « medicament - L`Institut de Formation Doctorale
... including most transcription factors, dissociate from chromatin and freely diffuse in the cytoplasm. At the same time, chromatin compaction leads to the typical packed and transcriptionally inactive mitotic chromosomes. Remarkably, some transcription factors have the ability to remain associated wit ...
... including most transcription factors, dissociate from chromatin and freely diffuse in the cytoplasm. At the same time, chromatin compaction leads to the typical packed and transcriptionally inactive mitotic chromosomes. Remarkably, some transcription factors have the ability to remain associated wit ...
Mcbio 316 – Exam 1 Page 1 (5) 1. Strains with a mutD mutation
... The pdx gene products are required for the biosynthesis of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) in E. coli. Nonsense mutations in the pdxJ gene result in very slow growth due to polarity on the dpj gene, which is located downstream of pdxJ within the same operon. Suppressor mutations were obtained that decreased ...
... The pdx gene products are required for the biosynthesis of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) in E. coli. Nonsense mutations in the pdxJ gene result in very slow growth due to polarity on the dpj gene, which is located downstream of pdxJ within the same operon. Suppressor mutations were obtained that decreased ...
PPT - Blumberg Lab
... • Specific aims – 2 points (this should be about 3/4 to one page) – Write a paragraph introducing the topic, state why it is important and what are the gaps in knowledge that you will address. – State a hypothesis to be tested – Enumerate 2-3 specific aims in the form of questions that test your hyp ...
... • Specific aims – 2 points (this should be about 3/4 to one page) – Write a paragraph introducing the topic, state why it is important and what are the gaps in knowledge that you will address. – State a hypothesis to be tested – Enumerate 2-3 specific aims in the form of questions that test your hyp ...
State a significant event that occurs during each of the following
... paternal and maternal genes Independent assortment of homologous pairs – creates unique combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes Question 14: (6pts) Where does the process of transcription occur? In the nucleus What does this process produce? Three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA, & tRNA How is it ...
... paternal and maternal genes Independent assortment of homologous pairs – creates unique combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes Question 14: (6pts) Where does the process of transcription occur? In the nucleus What does this process produce? Three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA, & tRNA How is it ...
Slide 1
... Antigenic Variation 1- antigenic shift It is the process in which the genetic segment encoding for envelope glycoproteins (HA&NA) is replaced by another one from a different strain through genetic reassortment causing replacement of the original HA or NA by a new one Genetic reassortment: the e ...
... Antigenic Variation 1- antigenic shift It is the process in which the genetic segment encoding for envelope glycoproteins (HA&NA) is replaced by another one from a different strain through genetic reassortment causing replacement of the original HA or NA by a new one Genetic reassortment: the e ...
1 Problem set 3 Due dates: Official date is 12 Dec. However I will
... You are trying to clone up the gene for a protein. You already purified a little of the protein. It took you three weeks working in the cold room and your yield was 0.2 mg from 10 kg of liver tissue. However that was enough to allow N-terminal sequencing and C-terminal sequencing (recall chapter 5). ...
... You are trying to clone up the gene for a protein. You already purified a little of the protein. It took you three weeks working in the cold room and your yield was 0.2 mg from 10 kg of liver tissue. However that was enough to allow N-terminal sequencing and C-terminal sequencing (recall chapter 5). ...
2015-2016 SMART Team Abstract Booklet.
... backbone of the siRNA. P19 binds specifically to 21-nt siRNAs due to a higher affinity caused by two tryptophan residues located on an α helix at the N terminus of each monomer, which provide end-capping interactions to stabilize this length in the binding pocket of the dimer. In humans, small RNAs ...
... backbone of the siRNA. P19 binds specifically to 21-nt siRNAs due to a higher affinity caused by two tryptophan residues located on an α helix at the N terminus of each monomer, which provide end-capping interactions to stabilize this length in the binding pocket of the dimer. In humans, small RNAs ...