1 Genetics and Biotechnology Chapter 13 Selective breeding is
... a. Defined-proteins which recognize and bind to specific DNA sequences and cleave (cut) the DNA within that sequence b. -because they constantly fight against viruses entering their DNA ...
... a. Defined-proteins which recognize and bind to specific DNA sequences and cleave (cut) the DNA within that sequence b. -because they constantly fight against viruses entering their DNA ...
Genetic Tools
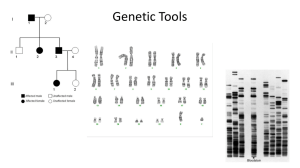
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... o Temperature – warm increases rate; hot denatures protein o pH – narrow range for best pH, excess H+ or OH- break 3-D bonds o concentration of enzyme or of substrate – act like a limiting reagent o inhibitors – slow enzyme action: competitive – on active site; noncompetitive – somewhere else on e ...
... o Temperature – warm increases rate; hot denatures protein o pH – narrow range for best pH, excess H+ or OH- break 3-D bonds o concentration of enzyme or of substrate – act like a limiting reagent o inhibitors – slow enzyme action: competitive – on active site; noncompetitive – somewhere else on e ...
File
... • short region of UNPAIRED nucleotides • Unpaired region is called an overhang – sticky because it wants to and will pair with another sticky end that has complementary overhang sequence – Sticky ends are like long-lost twins seeking to hug each other tightly once they meet ...
... • short region of UNPAIRED nucleotides • Unpaired region is called an overhang – sticky because it wants to and will pair with another sticky end that has complementary overhang sequence – Sticky ends are like long-lost twins seeking to hug each other tightly once they meet ...
Chapter 2 - rci.rutgers.edu
... (iii) Polymerase: an enzyme whose job is to copy genetic material. Starting from the primer, the polymerase reads a template strand and matches it with free complementary bases. This produces two descendant DNA strands. - Cycling through these three steps generates many copies of the target DNA. - T ...
... (iii) Polymerase: an enzyme whose job is to copy genetic material. Starting from the primer, the polymerase reads a template strand and matches it with free complementary bases. This produces two descendant DNA strands. - Cycling through these three steps generates many copies of the target DNA. - T ...
Biology Study Guide
... Describe the structure of DNA. Describe the base-pairing rules for DNA. Where does transcription take place? What is created in this step? Where does translation take place? What is created in this step? Use the genetic code table to translate amino acids. ...
... Describe the structure of DNA. Describe the base-pairing rules for DNA. Where does transcription take place? What is created in this step? Where does translation take place? What is created in this step? Use the genetic code table to translate amino acids. ...
teacherstryscience.org
... another location, the cells regain the ability to make the pigment, this creates a speckled pattern on the kernel ...
... another location, the cells regain the ability to make the pigment, this creates a speckled pattern on the kernel ...
Genetics Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes
... The molecular basis for genes is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids; alongside proteins, they compose the three major macromolecules ...
... The molecular basis for genes is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids; alongside proteins, they compose the three major macromolecules ...
... Bacterial enzyme that stops viral reproduction by cleaving viral DNA; used to cut DNA at specific points during production of recombinant DNA. Free-living organisms in the environment that have had a foreign gene inserted into them. Production of identical copies; in genetic engineering, the product ...
Sample question
... is to store the cell’s genetic information. How does DNA control the cell? A. DNA activates nerve signals B. DNA protects the cell from invaders C. DNA speeds up chemical reactions D. DNA determines what proteins are made Question #2: ...
... is to store the cell’s genetic information. How does DNA control the cell? A. DNA activates nerve signals B. DNA protects the cell from invaders C. DNA speeds up chemical reactions D. DNA determines what proteins are made Question #2: ...
LESSON 4 Genetics: STUDY GUIDE
... • Describe the events of DNA replication. (pg. 350) • Differentiate DNA replication in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes. (pg. 352) ...
... • Describe the events of DNA replication. (pg. 350) • Differentiate DNA replication in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes. (pg. 352) ...
Adapted
... 1. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 2. Phenolics plant wound sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 3. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirG signal passed to VirA T-DNA excise 4. Plant wound Signal passed to VirG phenolics sense ...
... 1. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 2. Phenolics plant wound sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 3. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirG signal passed to VirA T-DNA excise 4. Plant wound Signal passed to VirG phenolics sense ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
three possibile models for replication
... 29) Transformation = Is the alteration of a bacterial cell’s genetic material by the uptake of naked, foreign DNA from the surrounding environment 30) Transduction = bacteriophage viruses (viruses that infect bacteria) can pick up and transfer bacterial DNA to a new host along with viral DNA 31) Con ...
... 29) Transformation = Is the alteration of a bacterial cell’s genetic material by the uptake of naked, foreign DNA from the surrounding environment 30) Transduction = bacteriophage viruses (viruses that infect bacteria) can pick up and transfer bacterial DNA to a new host along with viral DNA 31) Con ...
Unit 2 DNA Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Pretranscriptional Control Eukaryotes use chromatin packing as a way to keep genes turned off. Transcriptional Control The transcriptional level is the most important level of gene control. Transcriptional control is dependent on the interaction of proteins with particular DNA sequences. Posttranscr ...
... Pretranscriptional Control Eukaryotes use chromatin packing as a way to keep genes turned off. Transcriptional Control The transcriptional level is the most important level of gene control. Transcriptional control is dependent on the interaction of proteins with particular DNA sequences. Posttranscr ...
Document
... a) All of these enzymes leave ends that are compatible with ends generated by the others; b) None of the enzymes produce compatible ends; c) Only BamHI and BglII fragments are compatible; d) Only BamHI and XbaI fragments are compatible; e) only BglII and XbaI fragments are compatible. ...
... a) All of these enzymes leave ends that are compatible with ends generated by the others; b) None of the enzymes produce compatible ends; c) Only BamHI and BglII fragments are compatible; d) Only BamHI and XbaI fragments are compatible; e) only BglII and XbaI fragments are compatible. ...
DNA structure in the Cell
... Further tested this preparation by subjecting it to various chemicals……… ...
... Further tested this preparation by subjecting it to various chemicals……… ...
During the last years we have observed a rapid development of
... by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation into routine DNA diagnostics. In this thesis I have focused on evaluation and application of High Resolutio ...
... by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation into routine DNA diagnostics. In this thesis I have focused on evaluation and application of High Resolutio ...
Amount of rearranged DNA in children affected by SLI.
... But it is not only the amount of reorganisation that is important. The location of the moved DNA also plays a role. If rearrangements do not disrupt any critical genes then it does not matter even if that person has lots of changes. If the rearrangement disrupts an important gene then the family mem ...
... But it is not only the amount of reorganisation that is important. The location of the moved DNA also plays a role. If rearrangements do not disrupt any critical genes then it does not matter even if that person has lots of changes. If the rearrangement disrupts an important gene then the family mem ...