Genetics, Exam 2, Sample A Name ___________________________
... provided strong evidence that the genetic material was DNA rather than RNA or protein. Their experiment was an extension of Griffith’s attempt to develop a vaccine for this bacterium that would protect people against the disease __________________________ When trying to create his vaccine, Griffith ...
... provided strong evidence that the genetic material was DNA rather than RNA or protein. Their experiment was an extension of Griffith’s attempt to develop a vaccine for this bacterium that would protect people against the disease __________________________ When trying to create his vaccine, Griffith ...
Document
... • Identifying (annotating) human genes, i.e. finding what they are and what they do, is a difficult problem. It is considerably harder than the early success story for ßglobin might suggest (see Lesk’s “Introduction to bioinf”). • The human factor VIII gene (whose mutations cause hemophilia A) is sp ...
... • Identifying (annotating) human genes, i.e. finding what they are and what they do, is a difficult problem. It is considerably harder than the early success story for ßglobin might suggest (see Lesk’s “Introduction to bioinf”). • The human factor VIII gene (whose mutations cause hemophilia A) is sp ...
25L-Mutations - Doral Academy Preparatory
... enzyme in a cell is to allow the cell to carry out chemical reactions very quickly. These reactions allow the cell to ________ things or take things apart as needed. Types of Mutations Hereditary mutations are passed from parent to child. They are present in the _____________ and ____________ cells ...
... enzyme in a cell is to allow the cell to carry out chemical reactions very quickly. These reactions allow the cell to ________ things or take things apart as needed. Types of Mutations Hereditary mutations are passed from parent to child. They are present in the _____________ and ____________ cells ...
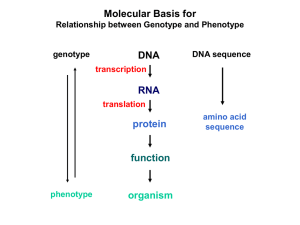
1. What is the Central Dogma of Biology? Draw and label a diagram
... Explain how transcription occurs. Use the terms: hairpin loop, promoter, template. Explain how translation occurs. Use the terms: A-site, P-site, tRNA, mRNA, rRNA, codon, anticodon, nonsense codon. ...
... Explain how transcription occurs. Use the terms: hairpin loop, promoter, template. Explain how translation occurs. Use the terms: A-site, P-site, tRNA, mRNA, rRNA, codon, anticodon, nonsense codon. ...
CHAPTER 10
... have been sequenced. • In 2004 the “finished” version of the human genome was reported. – It contains about 20,000 genes. – Alternate splicing of messenger RNA may account for several proteins from one gene. – Post-translational modifications also account for different protein functions. ...
... have been sequenced. • In 2004 the “finished” version of the human genome was reported. – It contains about 20,000 genes. – Alternate splicing of messenger RNA may account for several proteins from one gene. – Post-translational modifications also account for different protein functions. ...
04/03
... regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
... regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
File
... site (aminoacyl-tRNA site). This site carries the next amino acid to be added to the polypeptide ...
... site (aminoacyl-tRNA site). This site carries the next amino acid to be added to the polypeptide ...
The Central Dogma of Biology states that DNA codes for RNA, and
... termination signal, the mRNA is cut from the Polymerase. ...
... termination signal, the mRNA is cut from the Polymerase. ...
Extend Your Understanding of the Bacterial
... Genetic transformation of bacterial cells involves the uptake of exogenous DNA into the host bacterium. Transformation occurs in nature in certain types of bacteria and scientists have exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmi ...
... Genetic transformation of bacterial cells involves the uptake of exogenous DNA into the host bacterium. Transformation occurs in nature in certain types of bacteria and scientists have exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmi ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
... answers) “We know from our study of the cell that there are many organelles in cells. We also know that we extracted DNA from kiwi cells. That leaves us with the questions…just what is in those cells and what does it do?” 2. Show students the spool of thread and ask them to describe what substances ...
... answers) “We know from our study of the cell that there are many organelles in cells. We also know that we extracted DNA from kiwi cells. That leaves us with the questions…just what is in those cells and what does it do?” 2. Show students the spool of thread and ask them to describe what substances ...
BIO113 Ex 3 sample Q → The questions are NOT comprehensive
... 9. People who take insulin injections today obtain it from: a. human blood c. human cadaver pancreas b. cow and pig pancreas d. genetically engineered, transgenic bacteria 10. The people who advocate (support) clone humans, would like to: a. Have a baby that is a genetic copy of a person b. Raise do ...
... 9. People who take insulin injections today obtain it from: a. human blood c. human cadaver pancreas b. cow and pig pancreas d. genetically engineered, transgenic bacteria 10. The people who advocate (support) clone humans, would like to: a. Have a baby that is a genetic copy of a person b. Raise do ...
Genetics - LLI Manassas
... mutations are formed every time a cell divides. By the time we are sixty, we have up to 40,000 mutations per skin cell, with the total in our body numbering in the trillions. An even bigger problem threatening humanity and all organisms is genetic entropy. Offspring inherit a fraction of our mutati ...
... mutations are formed every time a cell divides. By the time we are sixty, we have up to 40,000 mutations per skin cell, with the total in our body numbering in the trillions. An even bigger problem threatening humanity and all organisms is genetic entropy. Offspring inherit a fraction of our mutati ...
Chapter 4A
... even in simple organisms such as yeast. The TRP biosynthesis genes, for example, each have their own promoter and actually are encoded on different chromosomes in yeast (Fig. 4.13b). In addition, gene coding sequences in higher eukaryotes typically are interrupted with non-translated sequences known ...
... even in simple organisms such as yeast. The TRP biosynthesis genes, for example, each have their own promoter and actually are encoded on different chromosomes in yeast (Fig. 4.13b). In addition, gene coding sequences in higher eukaryotes typically are interrupted with non-translated sequences known ...
biochemical composition presentation
... sequence and arrangement of amino acids. • Amino acids are attached to one another by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. • Form determines function of a protein. ...
... sequence and arrangement of amino acids. • Amino acids are attached to one another by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. • Form determines function of a protein. ...
Pre-post test questions
... bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mut ...
... bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mut ...
Revision BIOC 432 LAB
... Ribose Sugar (5 carbon sugar) Phosphate group Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine For RNA, nucleosides are formed similarly to DNA. Hairpin is a common secondary/tertiary structure. ...
... Ribose Sugar (5 carbon sugar) Phosphate group Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine For RNA, nucleosides are formed similarly to DNA. Hairpin is a common secondary/tertiary structure. ...
Fields of Fingerprints Text Passage – 9th Grade
... fingerprinting has been developed using the science of genetics. Genetics is the study of genes, tiny units of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. This chemical is located in the nucleus of every cell. An organism's DNA contains the blueprint of its characteristics --in the case of plants, that would inc ...
... fingerprinting has been developed using the science of genetics. Genetics is the study of genes, tiny units of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. This chemical is located in the nucleus of every cell. An organism's DNA contains the blueprint of its characteristics --in the case of plants, that would inc ...
Chemistry Review
... = working subunits of DNA within chromosomes - Only copy what is needed to make protein - Encodes for specific enzymes or proteins RNA = ribonucleic acid - Single stranded - Made up of: 5- carbon sugar ( Ribose ), phosphate, and nitrogenous base - Contains Uracil ( U) instead of Thymine ( T) - A=U a ...
... = working subunits of DNA within chromosomes - Only copy what is needed to make protein - Encodes for specific enzymes or proteins RNA = ribonucleic acid - Single stranded - Made up of: 5- carbon sugar ( Ribose ), phosphate, and nitrogenous base - Contains Uracil ( U) instead of Thymine ( T) - A=U a ...
1. Which of the following enzymes will untangle DNA? A
... 21. Adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine are what components of DNA? A) Hydrogen bonds B) Sugar moieties C) Phosphodiester groups D) Nitrogen bases 22. The movement of DNA from one bacterium to another through the activity of bacteriophages is called: A) conjugation B) transformation C) transduc ...
... 21. Adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine are what components of DNA? A) Hydrogen bonds B) Sugar moieties C) Phosphodiester groups D) Nitrogen bases 22. The movement of DNA from one bacterium to another through the activity of bacteriophages is called: A) conjugation B) transformation C) transduc ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... Every aspect of cell type differentiation has been linked to energy-dependent changes in hydrogen-atom transfer in DNA base pairs in solution from bacteria [20] to nematodes [21] and all mammals.[22] via RNA mediated events, which are perturbed by viruses, which have been linked from energy theft to ...
... Every aspect of cell type differentiation has been linked to energy-dependent changes in hydrogen-atom transfer in DNA base pairs in solution from bacteria [20] to nematodes [21] and all mammals.[22] via RNA mediated events, which are perturbed by viruses, which have been linked from energy theft to ...
Document
... Sickle cell anaemia is caused due to substitution of: (1) Valine at 6th position of alpha globin chain by glutamic acid. (2) Valine at 6th position of beta globin chain by glutamin. (3) Glutamic acid at the 6th position of beta globin chain by valine. (4) Glycine at the 6th position of alpha globin ...
... Sickle cell anaemia is caused due to substitution of: (1) Valine at 6th position of alpha globin chain by glutamic acid. (2) Valine at 6th position of beta globin chain by glutamin. (3) Glutamic acid at the 6th position of beta globin chain by valine. (4) Glycine at the 6th position of alpha globin ...