RNA polymerase
... if bacterium has enough tryptophan then it STOP doesn’t need to make enzymes used to build ...
... if bacterium has enough tryptophan then it STOP doesn’t need to make enzymes used to build ...
Themes throughout the course
... You are encouraged to read original source articles. Although articles are not required, they will enhance your understanding of the material. You can obtain articles through PubMed and through the WelDoc service at Welch. Some articles will be available on reserve. ...
... You are encouraged to read original source articles. Although articles are not required, they will enhance your understanding of the material. You can obtain articles through PubMed and through the WelDoc service at Welch. Some articles will be available on reserve. ...
feature - Schlick Group at NYU
... healthcare systems worldwide. The influence of genetic and molecular medicine on the health of patients is already sufficiently ubiquitous that it will have an impact on most common diseases. Its influence will grow over the next few decades (Table 1). It will not, however, answer all of the questio ...
... healthcare systems worldwide. The influence of genetic and molecular medicine on the health of patients is already sufficiently ubiquitous that it will have an impact on most common diseases. Its influence will grow over the next few decades (Table 1). It will not, however, answer all of the questio ...
The_RAY_Manual
... selected on plates containing kanamycin. To apply this principle, you can use the plasmid pRAY-2 which is identical to pRAY-1, with the exception that the dual-selection box has been replaced by the modified neo gene. prerequisites In order to construct targeting vectors with RAY you need i) a phage ...
... selected on plates containing kanamycin. To apply this principle, you can use the plasmid pRAY-2 which is identical to pRAY-1, with the exception that the dual-selection box has been replaced by the modified neo gene. prerequisites In order to construct targeting vectors with RAY you need i) a phage ...
Chapter 18~Regulaton of Gene Expression
... • Even if the lac operon is turned on by the presence of allolactose, the degree of transcription depends on the concentrations of other substrates. • The cellular metabolism is biased toward the utilization of glucose. ...
... • Even if the lac operon is turned on by the presence of allolactose, the degree of transcription depends on the concentrations of other substrates. • The cellular metabolism is biased toward the utilization of glucose. ...
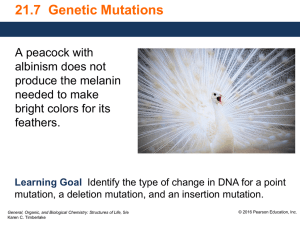
Genetic Mutation
... A mutation • is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • may result in changes to the sequence amino acids that affect the structure and function of cells. • results from mutagens, such as radiation and chemicals (possibly some viruses). When a mutation severely alters proteins or enzymes, the ...
... A mutation • is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • may result in changes to the sequence amino acids that affect the structure and function of cells. • results from mutagens, such as radiation and chemicals (possibly some viruses). When a mutation severely alters proteins or enzymes, the ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... DNA contains a triplet code Every three bases on DNA stands for ONE amino acid Each three-base unit on mRNA is called a codon Most amino acids have more than one codon! There are 20 amino acids with a possible 64 different triplets The code is nearly universal among living organisms ...
... DNA contains a triplet code Every three bases on DNA stands for ONE amino acid Each three-base unit on mRNA is called a codon Most amino acids have more than one codon! There are 20 amino acids with a possible 64 different triplets The code is nearly universal among living organisms ...
Document
... MeCP2 protein • 486 amino acids and 52kD. • An abundant mammalian chromosomal protein that binds to methylated CpG. • Ubiquitously expressed, more abundant in brain. • Can bind to single methyl-CpG pair (unlike MeCP1 which requires >10 methyl-CpGs to bind DNA) ...
... MeCP2 protein • 486 amino acids and 52kD. • An abundant mammalian chromosomal protein that binds to methylated CpG. • Ubiquitously expressed, more abundant in brain. • Can bind to single methyl-CpG pair (unlike MeCP1 which requires >10 methyl-CpGs to bind DNA) ...
minireview - International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary
... suggests that amplification is a structurally based process rather than an accident. In particular, mutants of Klebsiellu pneumoniue which gain the ability to metabolize xylitol selectively amplify the rbtD gene, which specifies ribitol dehydrogenase, and not the adjacent gene, rbtK, which specifies ...
... suggests that amplification is a structurally based process rather than an accident. In particular, mutants of Klebsiellu pneumoniue which gain the ability to metabolize xylitol selectively amplify the rbtD gene, which specifies ribitol dehydrogenase, and not the adjacent gene, rbtK, which specifies ...
ch. 12 Biotechnology-notes-ppt
... • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
... • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
minireview - International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary
... suggests that amplification is a structurally based process rather than an accident. In particular, mutants of Klebsiellu pneumoniue which gain the ability to metabolize xylitol selectively amplify the rbtD gene, which specifies ribitol dehydrogenase, and not the adjacent gene, rbtK, which specifies ...
... suggests that amplification is a structurally based process rather than an accident. In particular, mutants of Klebsiellu pneumoniue which gain the ability to metabolize xylitol selectively amplify the rbtD gene, which specifies ribitol dehydrogenase, and not the adjacent gene, rbtK, which specifies ...
The Genetic Code
... mRNAs and are not translated into proteins. – These other RNAs perform important functions in the cell. • Sometimes information flows in the opposite direction—from RNA back to DNA. – For example, some viral genes are composed of RNA and use reverse transcriptase, a viral polymerase, to synthesize a ...
... mRNAs and are not translated into proteins. – These other RNAs perform important functions in the cell. • Sometimes information flows in the opposite direction—from RNA back to DNA. – For example, some viral genes are composed of RNA and use reverse transcriptase, a viral polymerase, to synthesize a ...
The Genetic Code
... mRNAs and are not translated into proteins. – These other RNAs perform important functions in the cell. • Sometimes information flows in the opposite direction—from RNA back to DNA. – For example, some viral genes are composed of RNA and use reverse transcriptase, a viral polymerase, to synthesize a ...
... mRNAs and are not translated into proteins. – These other RNAs perform important functions in the cell. • Sometimes information flows in the opposite direction—from RNA back to DNA. – For example, some viral genes are composed of RNA and use reverse transcriptase, a viral polymerase, to synthesize a ...
molecular core facility - College of William and Mary
... supported by the HHMI grant (as will M13L-21 primers). After that, Corelab - on as needed basis - will request to order supplies/reagents in the amount equal to that of the value of the number of sequencing reactions (above those supported by HHMI) performed for that person. If you anticipate having ...
... supported by the HHMI grant (as will M13L-21 primers). After that, Corelab - on as needed basis - will request to order supplies/reagents in the amount equal to that of the value of the number of sequencing reactions (above those supported by HHMI) performed for that person. If you anticipate having ...
Lecture 10 Types of mutations Substitutions that occur in protein
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
GENE REGULATION
... modulated in a variety of ways. These include the binding of small effector molecules, protein–protein interactions, and covalent modifications. ...
... modulated in a variety of ways. These include the binding of small effector molecules, protein–protein interactions, and covalent modifications. ...
3 notes cp u8
... 1. The 3 parts of a nucleotide = … 2. Cytosine pairs with _____ in DNA. 3. Monomer of a protein = ...
... 1. The 3 parts of a nucleotide = … 2. Cytosine pairs with _____ in DNA. 3. Monomer of a protein = ...
asdfs - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... extra sets of chromosomes POLYPLOIDY = _______________ triploid 3N plants are called ____________ ...
... extra sets of chromosomes POLYPLOIDY = _______________ triploid 3N plants are called ____________ ...
CHAPTER 14: DNA: THE GENETIC MATERIAL
... experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand served as a template for the production of a new one and each old and new strand then intertwined to become a new helix. Double-stranded DNA replication is complicated since new nucleotide ...
... experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand served as a template for the production of a new one and each old and new strand then intertwined to become a new helix. Double-stranded DNA replication is complicated since new nucleotide ...
Genetic Technology
... • Because DNA segments that are near each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together, markers are often used as indirect ways of tracking the inheritance pattern of a gene that has not yet been identified, but whose approximate location is known. ...
... • Because DNA segments that are near each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together, markers are often used as indirect ways of tracking the inheritance pattern of a gene that has not yet been identified, but whose approximate location is known. ...
DNA Quiz
... ____ 10. (1 point) When new DNA molecules are formed, almost all errors are detected and fixed by a. the correct nucleotide. b. the sugar-phosphate backbone. c. DNA polymerase. d. one DNA strand. ____ 11. (1 point) The central dogma of molecular biology states that information flows in one direction ...
... ____ 10. (1 point) When new DNA molecules are formed, almost all errors are detected and fixed by a. the correct nucleotide. b. the sugar-phosphate backbone. c. DNA polymerase. d. one DNA strand. ____ 11. (1 point) The central dogma of molecular biology states that information flows in one direction ...
Lecture 7
... • Diploid size = double that • Misincorporation (10-5) x not proofread (10-2) x escape mismatch repair (10-3) = 10-10 • Thus, less than one replication error is fixed per cell division ...
... • Diploid size = double that • Misincorporation (10-5) x not proofread (10-2) x escape mismatch repair (10-3) = 10-10 • Thus, less than one replication error is fixed per cell division ...
Document
... pleiotropism: single gene difference can affect multiple phenotypes Example: Drosophila white mutation • lack of pigment in eye, testis sheath, Malphighian tubules ...
... pleiotropism: single gene difference can affect multiple phenotypes Example: Drosophila white mutation • lack of pigment in eye, testis sheath, Malphighian tubules ...
Phylogeny
... !Understand the most basic concepts of phylogeny !Be able to compute simple phylogenetic trees !Understand/remember the difference between orthologs and paralogs !Understand what bootstrapping means in phylogeny ...
... !Understand the most basic concepts of phylogeny !Be able to compute simple phylogenetic trees !Understand/remember the difference between orthologs and paralogs !Understand what bootstrapping means in phylogeny ...